Abstract
1146
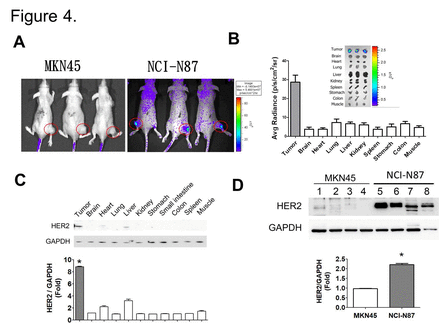
Objectives: Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. The human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) involved proliferation, angiogenesis, and reduced apoptosis in GC, which is a common target for tumor therapy. Because HER2 is usually overexpressed in more than 15% GC patients, developing a reliable diagnostic tool for tumor HER2 detection is important. In this study, we aim to investigate the HER2 expression in serum and tumor from different stages of GC patients and used anti-HER2/Neu peptides linked polyethylene glycol (AHNP-PEG) with indium-111 labeling as a nuclear imaging agent for HER2 detection in GC xenograft animal model. The serum HER2 was correlated with the tumor HER2 levels in different stages of GC patients. In addition, the GC tumor tissue in HER2-postive xenograft mice presented higher HER2 fluorescence imaging as compared with HER2-negative. The HER2 levels at the tumor site were also higher than other organs in NCI-N87-induecd xenograft mice. Finally, we further observed that the radioisotope signal of indium-111 labeled AHNP-PEG (111In-DTPA-AHNP-PEG), which was utilized for HER2 detection in NCI-N87-induced xenograft mice, was significantly enhanced in tumors tissue as compared with non-AHNP-PEG control. Taken together, we believe that the serum HER2 measurement can be as a potential tool for detecting HER2 expressions in GC clinical practice. The radioisotope-labeled AHNP-PEG may be useful to apply in GC patients for HER2 nuclear medicine imaging.