Abstract
1035
Objectives: To evaluate the feasibility of preablative stimulated thyroglobulin (ps-Tg) predicting therapeutic response in non-distant-metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer patients (DTC).
Methods: In this study, 169 non-distant-metastatic DTC patients who had received radioactive iodine(RAI) therapy between January 2013 to June 2015 for the first time in the First Hospital of China Medical University were adopted. All of those patients had undergone total/near total/subtotal thyroidectomy before RAI and were followed for a median of 27.6 months after RAI. The clinical outcome of each patient was evaluated, based on the response to therapy restaging system proposed by American Thyroid Association in 2015. The DTC patients were divided into 4 groups according to their clinical outcomes: Excellent Response group (ER,n=85), In-Determinate Response group (IDR,n=44), Biochemical Incomplete Response group (BIR,n=32), Structural Incomplete Response group(SIR,n=8). The Kruskal-Wallis test was used to evaluate the clinicopathologic features and ps-Tg levels among 4 groups .The ps-Tg level between ER group and non-ER group was compared using Mann-Whitney rank-sum test. The ROC curve and optimal cut-off point were employed to evaluate the predictive value of ps-Tg level for ER group. These patients were as well divided into three groups in terms of ps-Tg level: group 1, less than 1 ng/ml (n=46); group 2, 1-10 ng/ml (n=66); and group 3, more than 10 ng/ml (n=57). The composition ratio of group 1, group 2 and group 3 was compared with each other by chi-square/Fisher exact test.
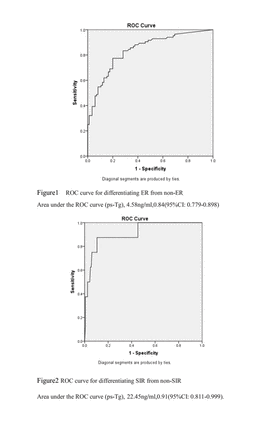
Results: There was no significant difference in sex (H=2.41,P=0. 49), age(H=4.84,P=0.18), T stage(H=0.44,P=0 .93), recurrence risk (H=1.39,P=0.71), pathological type (H=2.82,P=0.49) and Surgery scope(H=6.28,P=0.10),but in ps-Tg level(H=78.89,P<0.01).The median level of ps-Tg in ER group was significantly lower than non-ER groups(with IDR, U=918.00,P<0.01;with BIR, U=151.00,P<0.01;with SIR, U=18.00,P<0.01).The optimal cut-off value of ps-Tg for ER group was 4.58ng/ml (sensitivity 77.40%, specificity 80.00%), with an area under the ROC curve of 0.84(95%CI: 77.91%-89.84%). The median level of ps-Tg in SIR group was significantly higher than non-SIR groups(with ER, U=18.00,P<0.01;with IDR U=28.00;with BIR, U=67.53,P=0.041).The optimal cut-off value of ps-Tg for SIR group was 22.45ng/ml (sensitivity 87.50%, specificity 89.40%), with an area under the ROC curve of 0.91(95%CI: 81.10%-99.99%). There was a significant difference of composition ratio among group 1 [ER 42 cases (91.30%), IDR 4 cases (8.70%), BIR 0 case, SIR 0 case ], group 2 [ER 35 cases (53.03%), IDR 23 cases (34.84%),BIR 7 cases (10.60%), SIR 1 case(1.53%)] and group 3 [ER 10 cases (17.54%), IDR 15 cases (26.32%), BIR 25 cases (43.85%), SIR 7 cases (12.29%)] (group1 with group 2, Х2=19.55,P<0.001; group1 with group 3, Х2=64.29,P<0.001; group2 with group 3, Х2=29.69,P<0.001). Conclusion: The serum ps-Tg level can be used for predicting radioiodine therapeutic response in non-distant-metastatic DTC patients.