Abstract
1184
Objectives: One of the main advantages of myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) is the development of standardized methods for automated quantification using so-called normal databases. In conventional SPECT system, two normal databases addressing only gender differences are typically used. However, due to the new design fast SPECT systems, it is uncertain whether we need new approaches of normal limits. The aim of this study is to access the parameters (genders, stress/rest, BMI) that affect the normal databases in a fast SPECT system.
Methods: Among patients referred for stress/rest MPI using a fast SPECT system (D-SPECT, Spectrum Dynamics, Israel) during 5.1.2014 and 10.11.2016, 151 patients (80 men and 71 women) who had no history of coronary artery disease, or other cardiac diseases, as well as normal perfusion images were accepted for inclusion into normal databases. Using volumetric sampling and automated alignment of the stress and rest cases, polar maps of normalized tracer uptake were generated. Normal databases were constructed based on different parameters (genders; stress/rest; BMI small, medium, large; in male BMI <26.8, 26.8~30.1, >30.1; in female BMI<24.4, 24.4~29.2, >29.2). The mean normalized uptake of the 17-segments in each database was used for statistical analysis (Inter-databases comparisons were performed using Wilcoxon rank sum tests for continuous variables. Statistical significance was defined as p<0.05.)
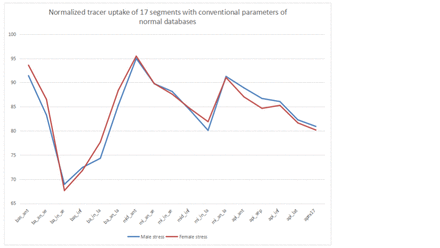
Results: Previously used parameters of normal databases (e.g. Male/Stress, Male/Rest, Female/Stress and Female/Rest) were not significantly different from each other (p-value between 0.22~0.92, Fig. 1) using the fast SPECT system. When adding BMI into statistics analysis, Male/Rest/BMI-large and Male/Rest/BMI-medium were significantly different from other males, especailly in the apex segment. (p=0.0001 and 0.0497 respectively, largest differences are marked in Fig. 2) On the other hand, Female/Stress/BMI-large and Female/Rest/BMI-large were significantly different from other females, especially in apical septal and basal inferolateral segments. (p=0.0267 and 0.0093 respectively).
Conclusion: The conventional parameters of normal databases (genders, stress/rest) did not differ for the investigated fast SPECT system. Furthermore, BMI played a significant role for the creation of normal databases in fast SPECT system. However, the number of segments with significant differences were rather low indicating a smaller subject “geometry” dependence than in conventional cameras. This data suggest that the standard means of MPI data quantification needs to be re-considered.