Abstract
449
Objectives [123I]5-iodo-6-[(2-iminoimidazolidinyl)methyl]uracil ([123I]IIMU) is a novel imaging tracer that targets thymidine phosphorylase (TP). The expression of TP is highly associated with angiogenesis, infiltration, and metastasis of tumor, and thus patients with high TP expression have poor prognosis. Moreover, TP is the key enzyme to activate 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and its prodrugs, such as tegafur and capecitabine. Therefore, [123I]IIMU will contribute not only to the diagnosis of tumor aggressiveness but also have potential to predict the clinical prognosis and therapeutic effect of cancer chemotherapy using fluoropyrimidine-based anticancer drugs. The objective of this study was to evaluate radiation dosage, biodistribution, human safety, tolerability, and early elimination of 123I activity in urine after injection of a single dose of the tracer in healthy subjects.
Methods Healthy male adults (20-60 years old) as determined by medical history, physical examination, vital signs, and clinical laboratory testing participated in the study. Subjects were tested within 7-14 day before enrollment to confirm eligibility at Hokkaido University Hospital. Subjects were injected with [123I]IIMU intravenously and remained at the hospital until completion of safety assessments 48 h after dosing. All subjects returned to the hospital approximately 1 week after dosing for a follow-up safety visit. A 60-minute dynamic scan was obtained covering from the heart to the kidney, followed by sequential whole-body planar scans after 1, 3, 6, 24, and 48 h post injection. Clinical laboratory parameters were evaluated in blood and urine after 1, 3, 6, 9, 24, 48 h and 7 days post injection. To evaluate renal clearance of [123I]IIMU, urine was collected for 48 h post injection. All adverse events were recorded until the follow-up safety visit. Absorbed dose estimates for all target organs were determined using MIRD schema with OLINDA/EXM software.
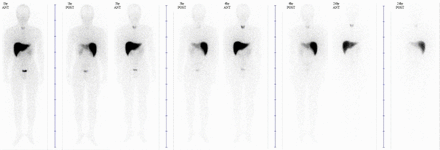
Results Two healthy male subjects satisfied the inclusion criteria, and were injected with 56 and 111 MBq of IIMU, respectively. Single administration of [123I]IIMU caused no adverse events without any abnormal findings by physical examinations or blood tests. [123I]IIMU was rapidly excreted from all the organs except the thyroid and the liver. Despite relatively high uptake in the thyroid, the accumulated dosage was low (0.61 and 0.96 % injected dose at 48h, subject #1 and #2, respectively). The liver strongly expresses TP, and the high uptake in the liver can be ascribed to TP binding but not to nonspecific hepatic metabolism because no tracer excretion was observed in the GI tract at any phases. The organ receiving the largest mean absorbed dose was the thyroid for both subjects (0.104 and 0.113 mSv/MBq), followed by the liver (0.068 and 0.051 mSv/MBq). The whole-body mean effective dose was 0.013 and 0.011 mSv/MBq. These results were consistent with the previous report from the animal experiments. Excretion of radioactivity via the urinary system was very rapid and completed after 10 h with the renal excretion rate reaching 53.1 and 52.2% of the administered dose.
Conclusions These preliminary data suggest that [123I]IIMU is well tolerated and its radiation dose may be comparable to other 123I radiopharmaceuticals. TP imaging using [123I]IIMU will be useful for clinical diagnosis of malignant tumors and also has potential for selecting the best chemotherapeutic agent for individual patient.