Abstract
1227
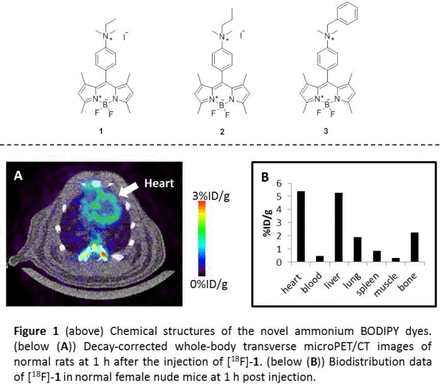
Objectives PET myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) holds several benefits for diagnosing coronary artery disease and related cardiac disorder. Previously, we have demonstrated the potential of the [18F]-trimethyl ammonium BODIPY dye for the cardiac imaging application. In this study, we report novel ammonium BODIPY derivatives and their capability as PET-MPI agents.
Methods Three new cationic BODIPY dyes were prepared with different ammonium substituents, including ethyl, propyl, and benzyl groups (1, 2, and 3). The synthesized BODIPY dyes were radio-labeled via SnCl4-promoted 18F-19F isotopic exchange protocol. The resulting radiotracers were subjected to in vivo metabolic stability evaluation, microPET imaging, and biodistribution studies in murine model.
Results The novel [18F]-ammonium BODIPY dyes were obtained in high radiochemical purity (>95%). Noninvasive microPET experiments revealed that the ethyl BODIPY showed the most promising heart uptake images. The biodistribution data demonstrated that the radioactivity uptake in the heart at 1 hour post-injection of the ethyl BODIPY (5.34 %ID/g) is higher than that of the propyl BODIPY (4.63 %ID/g) and the benzyl BODIPY (1.74 %ID/g), respectively, which are consistent with the microPET studies.
Conclusions Our experiments displayed that subtle ammonium substituent changes have a drastic effect on the stability and the cardiac uptake of the [18F]-BODIPY dyes in murine model.