Abstract
1055
Objectives [18F](2S,4R)-4-fluoroglutamine ([18F]FGln) is a potential PET imaging probe for tumor diagnosis, especially for tumors with negative [18F]FDG scan.1 Our goal is to improve the radiosynthesis of [18F]FGln and developed fully automated synthesis to allow efficient and reproducible production of this tracer.
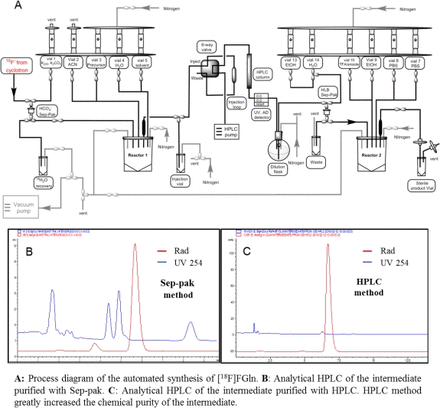
Methods The 2-step automated synthesis of [18F]FGln was performed on a GE FX-N Pro module (Figure A). Briefly, to the dried K[18F]F/18-C-6 mixture in reactor 1 was added a solution of the tosylate precursor (5-6 mg in 0.6 mL of ACN) and heated to 70 °C for 15 min. The reaction mixture was purified by HPLC (Agilent XDB-C18 column, 250 × 10 mm, 5 µM; mobile phase: 73.5% MeOH and 26.5% formic acid; 4 mL/min). The collected intermediate was diluted with water and caught on a HLB light cartridge, which was rinsed with water and eluted in reactor 2. The hydrolysis was carried out with TFA/anisole at 60 °C for 5 min, and volatiles were removed. The final product was formulated in PBS (pH 7.4) and sterile filtered. In vitro stability study was performed by incubating [18F]FGln with mouse serum at 37 °C for 30, 60, and 120 min, samples were analyzed by HPLC.
Results In the [18F]FGln synthesis, the use of a mild base (KHCO3) and phase transfer reagent (18-C-6) is necessary to avoid unwanted epimerization. To ensure good [18F]F- elution from the PS-HCO3 cartridge under mild condition, methanol was used as the elution solvent instead of ACN, which provided superior elution efficiency (>95%).2 In the reported manual syntheses, a sep-pak method was used to purify the intermediate.1 However, this process cannot fully remove the chemical impurities, and it occasionally forms precipitate which may block the cartridge and lower the reproducibility on an automated module. Therefore, an HPLC purification was performed which was able to avoid the formation of precipitate, greatly increase chemical purity and yield of the automated synthesis (Figure B&C). As a result, [18F]FGln was produced in 80 ± 3 min synthesis time, with a RCY of 21 ± 3% (uncorrected, n > 5), radiochemical purity > 98% and stereochemical purity 90 ± 5%. In vitro stability study in mouse serum revealed that [18F]FGln remains >98% intact after 120 min of incubation, no defluorination was detected.
Conclusions In this study, the radiosynthesis of [18F]FGln has been optimized and translated to a fully-automated synthesis. [18F]FGln was obtained in high radiochemical yield and purity which allows for more efficient and reproducible production of this tracer.