Abstract
2630
Objectives Tomography can be corrected by scatter correction (SC) to improve image quality. Siemens SPECT has several function of optional marked SC in the tomographic image reconstruction. The aim of this research is to distinguish the difference between the different function settings.
Methods "SC-Tc99m-NMG" energy peak of Brain model tomographic data were used. "Tomo Reconstruction" activity and double lsotopes loaded primary and secondary energy peak to analyze separately in 2 groups. "Tomo Reconstruction" activity and single lsotopes loaded, divided into SC and NSC to analyze separately in 2 groups. We use "AutoRecon" activity and double lsotopes loaded, divided into SC and NSC to analyze separately in 2 groups. Been limited by "AutoRecon" activity, so we use Flash3D function to reconstruct and analyze the range of image to the largest extent. Repeat this analysis set of data 10 times.
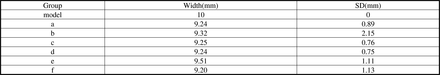
Results To reconstruct all 128 layers in axial section, the average radioactive counts of the 6 groups respectively were 10092.30±24.20, 4199.40±13.41, 10092.60±24.95, 10084.30±16.05, 8151.60±20.64 and 10238.80±20.64 counts. Their maximum counts were 10328, 3621, 10370, 10338, 8546 and 10445 counts. Except secondary energy peak data met the clinical requirements through visual assessment brain SPECT. There was no statistically significant differences between a, c, d groups after pair T test.The measurement posterior horn of the right lateral ventricle width data in Table 1, and compared with the model group, the E data is most close to the model.
Conclusions By comparison of the data, we found that only Group e completed the SC. It also shows that Siemens syngo V60B only use "AutoRecon" activity with Flash3D function can do SC.
posterior horn of the right lateral ventricle width