Abstract
477
Objectives To assess the increment in patient radiation dose in routine nuclear medicine imaging due to addition of single photon emission tomography-computed tomography (SPECT-CT).
Methods Data of 340 consecutive patients (Age: 38.2±19.8 years; Male: Female-168/172) who had underwent nuclear medicine imaging along with SPECT-CT of a selected volume was retrospectively evaluated. The dose of injected radiopharmaceutical (MBq) was noted and the effective dose (mSv) was calculated as per ICRP guidelines. The CTDIvol and dose length product (DLP) of the CT were also assessed using standard phantoms. The effective dose (mSv) due to CT was calculated as the product of DLP and a correction factor depending on the region of investigation, using standard guidelines. The dose for CT was compared among different groups. The increment in effective dose was calculated as CT dose expressed as a percentage of radiopharmaceutical (RP) dose.
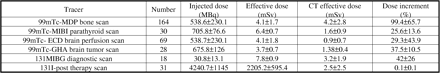
Results The findings are summarized in Table. The increment was higher for bone scintigraphy compared to parathyroid scintigraphy (p<0.0001), ECD scan (p<0.0001), GHA scan (p<0.0001). Similarly, the increment for GHA scan as compared to ECD (p<0.0001) and MIBI scan (p=0.0004).
Conclusions Addition of CT to nuclear medicine imaging in form of SPECT-CT can significantly increase the patient radiation dose, with CT dose exceeding the RP dose in many instances. This is most marked for bone scan. Hence, SPECT-CT should be used only when absolutely necessary