Abstract
1880
Objectives Evaluate the value of bone scan in therapy response assessment and prognosis of bone metastasis.
Methods 62 lung cancer or prostate cancer patients underwent bone scan respectively in one month before systematic therapy and ≥3 months after treatment. The mean age of them(49 men, 13 women) was 63.77±10.47 years. Survival rates were achieved by Kaplan-Meier method, and prognostic factors were also analyzed by Logrank test and Cox proportional hazards model.
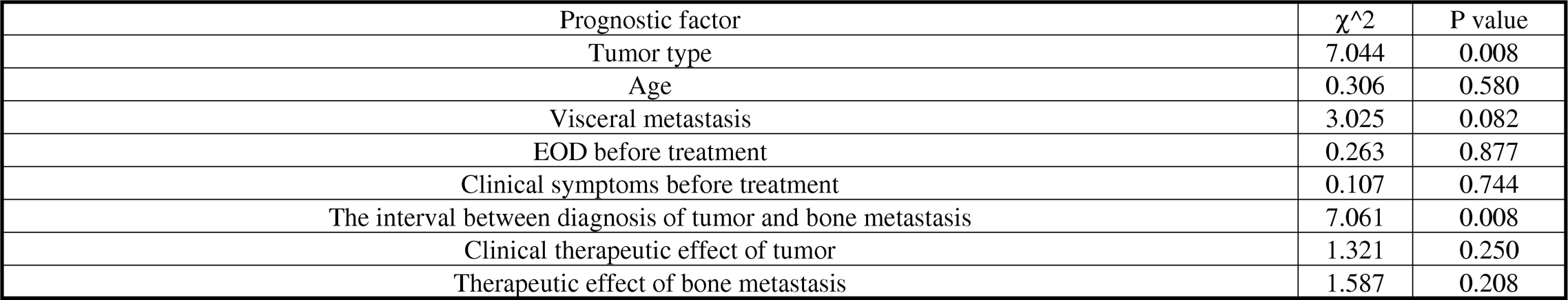
Results Bone therapeutic effect of clinical therapy responders (59.68%, 37/62) in primary tumors was much better than non-responders (40.32%, 25/62), P<0.05. The 1- and 2-year cumulative survival rates after bone metastasis from lung cancer were 54.5% and 22.6%, respectively. Moreover, those after osseous metastasis from prostate cancer were 87.3% and 72%, respectively. Both univariate and multivariate analysis showed tumor type and the interval between diagnosis of tumor and bone metastasis were significant prognostic factors for survival of lung cancer or prostate cancer patients with bone metastasis (P<0.05). In the lung cancer group, tumor subtype, extent of disease (EOD) before treatment and the interval between diagnosis of tumor and bone metastasis were prognostic factors. And in the prostate cancer group, the interval between diagnosis of tumor and bone metastasis impacted survival.
Conclusions Bone scintigraphy provides more abundant information in therapy response monitoring and prognosis of bone metastasis
Univariate analysis of survival rates