Abstract
259
Objectives Milk scan studies in children not only detect gastroesophageal reflux but also extrapolate gastric emptying rate. Prior research of milk scan report a range of normal gastric residual (GR) remaining at 60 minutes between 50-70%1, however common conditions such as vomiting during the study interfere with the accuracy of assessment of the gastric emptying or the GR rate at 60 minutes. The goal of this study is to determine GR ranges at shorter time points.
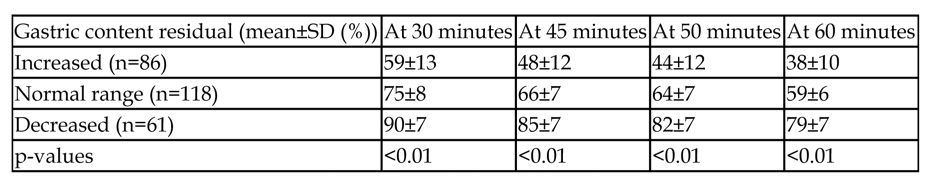
Methods This retrospective study included 265 children (114 girls and 151 boys, age 1-16 years with median age 2 years) who had Tc-99m sulfur colloid milk scan at our hospital. Each scan contained dynamic images of upper gastrointestinal tract for one hour. Children who vomited during the study or had a feeding tube were excluded. For each child, GR percentages at 30, 45, 50 and 60 minutes were calculated, then categorized into 3 groups according to GR percentage at 60 minutes: 1), <50%, increased; 2), 50-70%, normal range and 3), >70%, decreased gastric emptying. Mean, standard deviation (SD), and ANOVA one way test were done to compare the different gastric emptying rate in 3 groups at different time points.
Results Mean and SD at different time points are shown in the Table. Statistically, there are significant differences in gastric emptying rates of each group at 30, 45, 50 and 60 minute time-points which may be potentially useful in the prediction of normal gastric emptying rates when the 60 minute time-point is not available.
Conclusions This data implies that early GR rates might be sufficient to determine the gastric emptying rate accurately.
Research Support 1 Heyman S. Gastric emptying in children. J Nucl Med. 1998 May;39(5):865-9
- © 2009 by Society of Nuclear Medicine






