Abstract
230
Objectives The accuracy of US, CT ,MRI ,SMM and PET in diagnosing the recurrent and/or breast cancer has never been systematically assessed, and present systematic review was aimed at this issue.
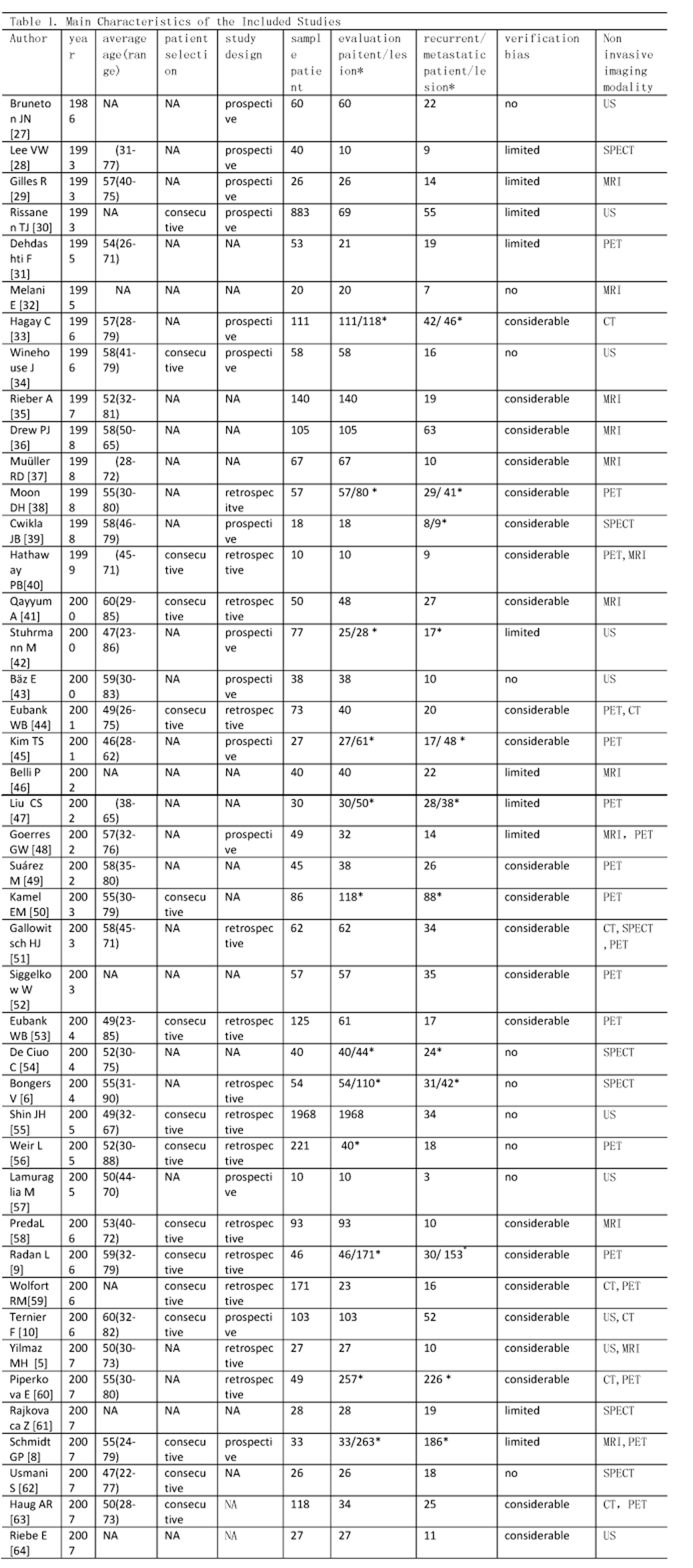
Methods We searched for articles published from January 1995 to August 2008, inclusion criteria including: Articles were reported in English or Chinese; US, CT , MRI ,SMM or PET whether interpreted with or without the use of CT, was used to detect recurrent and/or breast cancer; Histopathologic analysis and/or close clinical and imaging follow-up for at least 6 months. We extracted data to calculate sensitivity, specificity, SROC curves and AUC and to test for heterogeneity.
Results In 42 included studies, US and MRI had highest pooled specificity (0.962 and 0.929 respectively); MRI and PET(with or without CT) had highest pooled sensitivity (0.9500 and 0.9530 respectively). The AUC of US, CT, MRI, SMM and PET were 0.9251, 0.8596, 0.9718, 0.9386 and 0.9604 respectively. Results of pairwise comparison between each modality demonstrated AUC of MRI and PET(with or without CT), were higher than that of US or CT, p<0.05.No statistical significance was found when compared with that of MRI and PET. There was heterogeneity among studies and evidence of publication bias.
Conclusions In conclusion, MRI seemed to be a more useful supplement to current surveillance techniques to assess patients with suspected recurrent and/or metastatic breast cancer. If MRI shows an indeterminate or benign lesion or MRI was not applicable, FDG-PET could be performed in addition.
Research Support Supported by Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project,Project Number:S 30203
- © 2009 by Society of Nuclear Medicine






