Abstract
208
Objectives The aim is to validate a 3D point kernel (PK) based model for radiation dosimetry used in liver microbrachytherapy. The resulting dose map is based on the activity distribution and can be used to calculate an organ-averaged dose. A comparison was made between the dosimetry for 166Ho (Eβ,mean= 665keV, Eγ=81keV (6.7%), T½= 26.8h) and 90Y (Eβ,mean= 934keV, T½= 64h).
Methods Autoradiographic images were acquired of 6mm slices of a pig liver (body and liver weight 75 and 1.5 kg respectively) after hepatic arterial administration of 500MBq 166Ho microspheres. The resulting stack of data was used as voxelized input (3mm voxel-size) to the proposed model. The radiation transport from 166Ho and 90Y in the pig's liver was calculated with MIRD (OLINDA 15-year-old model), Monte-Carlo (MCNP5) and with the PK model, and the results were compared.
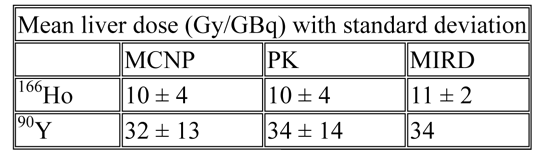
Results Dose volume histograms and isodose distributions were calculated for the MCNP, PK and MIRD models. The table shows the organ-averaged dose with the variance due to regional differences in the voxel dose distribution. The isodose distributions show considerably less structure than in the activity distribution, with hardly any difference between 90Y and 166Ho. The PK dose distribution was in good agreement with the MCNP5 results.
Conclusions The PK method is a fast and accurate method to calculate the 3D dose distributions for liver microbrachytherapy. The dose distributions of 166Ho and 90Y were very similar with the same activity source distribution. Organ-averaged liver dose estimates based on homogeneous activity deposition (MIRD) should be used with caution.
- © 2009 by Society of Nuclear Medicine






