Abstract
1937
Objectives : Correct preoperative localization of insulinomas is often a challenging clinical problem. We have shown before that glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor imaging using 111In-DOTA-exendin-4 SPECT/CT offers a new diagnostic approach to localize small insulinomas (Wild et al. NEJM. 2008; 359: 766-8). However, the preparation of 111In-DOTA-exendin-4 is difficult. The goal of this study is the clinical evaluation of GLP-1 receptor imaging with a novel more advanced tracer, 111In-DTPA-exendin-4, in patients with endogenous hyperinsulinaemia.
Methods So far, two patients with endogenous hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia were scanned. Whole-body images and SPECT/CT of the abdomen were obtained at 4 h, 23 h and 120 h after injection of ~90 MBq (10 microgram) 111In-DTPA-exendin-4. During surgery tumor samples were collected for GLP-1 receptor quantification using in vitro autoradiography.
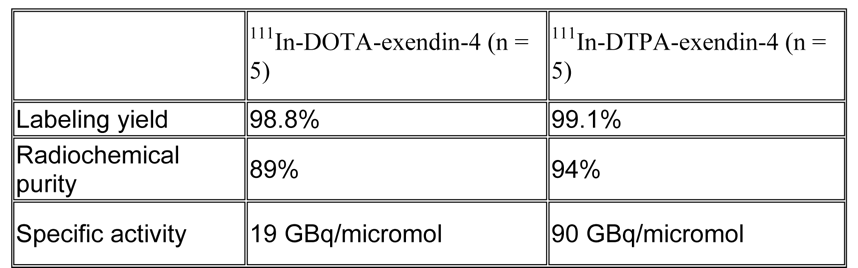
Results The radiochemical characteristics of 111In-DTPA- and 111In-DOTA-exendin-4 are shown in the table below. Only 111In-DTPA-exendin-4 SPECT/CT could localize the tumor in both patients, whereas CT, MRI and endoscopic ultrasound were negative.
Conclusions Compared to 111In-DOTA-exendin-4, 111In-DTPA-exendin-4 has superior radiochemical characteristics. These preliminary data suggest that 111In-DTPA-exendin-4 SPECT/CT offers a new diagnostic approach that permits the successful localization of hardly detectable insulinomas and is likely to affect medical practice.
Research Support Supported by grant (PASMP3-123269/1) from the Swiss National Science Foundation.
- © 2009 by Society of Nuclear Medicine






