Abstract
1147
Objectives: To analyze & determine significance of blood pool phase (BP) uptake patterns on 3-phase bone scans (3PBo) of failed total knee replacements (TKRs).
Methods: 34 TKRs ≥ 1 yr old were included in this retrospective investigation. BP images were clasified as synovial (S) if hyperemia was confined to the synovium, periprosthetic (P) if hyperemia was confined to the prosthesis/bone region, mixed (M) if both S & P were present, & normal (N) if there was no increased S or P activity. 3PBo was interpreted as positive for infection if increased activity was present on all 3 phases. Imaging results were compared to final diagnoses, all histopathologically, microbiologically, & surgically confirmed.
Results: 15 TKR's were infected: staphylococcus (9), multiple organisms (2), streptococcus (1), corynebacterium (1), pseudomonas (1), torulopsis (1). In 2 pts. diagnosis was based on presence of numerous neutrophils only. Final diagnoses in the remaining 19 prostheses were aseptic loosening (13), arthrofibrosis (2), miscellaneous (4). A positive 3PBo, regardless, of BP pattern was highly sensitive (100%) but not specific (5%)or accurate (47%). Test specificity was improved using BP patterns but at the expense of sensitivity. The most accurate criterion (65%) was presence of S pattern on BP images.
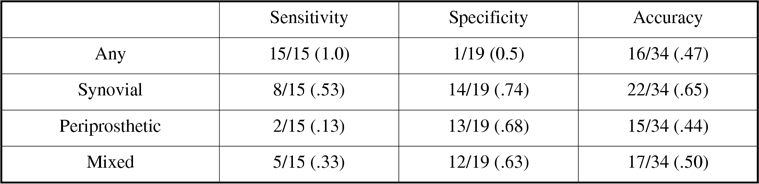
Imaging Results
Conclusions: Although its ability to differentiate infection from other causes of TKR failure is enhanced by analyzing BP uptake patterns, the accuracy of 3PBo (65%) remains too low to be clinically useful.
- Society of Nuclear Medicine, Inc.






