Abstract
871
Objectives: This study was designed to examine whether quantitative (quant) assessment is superior reproducibility to visual interpretation on SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI).
Methods: We studied 31 pts (age 68±12, 25 male) with abnormal (abnl) MPI by visual analysis who underwent repeat exercise (n=11) or adenosine (n=20) MPI within 9-24 mos (15.2±3.8 mos) and had no change in symptom, medication, interval revascularization or infarction, stress type, rest or stress ECG, or clinical response to stress on the second study. Visual interpretation used 17-segment, 5-point scoring by two independent expert readers with overread of discordance by a third expert, and % myocardium abnl was derived from normalized summed scores. Quant perfusion was assessed by QPS using stress, rest and ischemic total perfusion deficit (TPD).
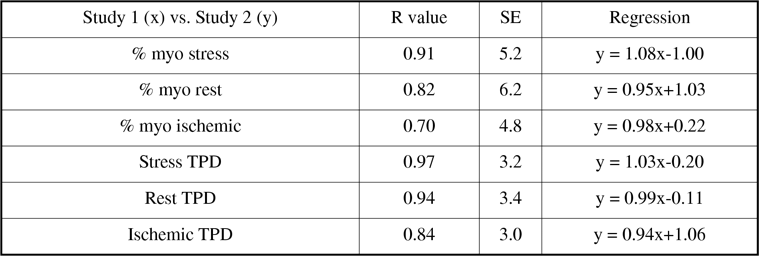
Results: High linear correlations were observed between visual and quant for size of stress, rest and ischemic defects (R=0.94, 0.92, 0.84). Correlations of stress, rest and ischemic defects between tests were higher by quantitative than by visual methods (Table, all p<0.006).
Conclusions: Defect extent by visual and quant analysis is highly correlated. In stable patients having serial SPECT MPI, quant is more reproducible than visual for magnitude of MPI abnl, suggesting its superiority for use in randomized clinical trials.
- Society of Nuclear Medicine, Inc.






