Abstract
2607
Objectives Routine radiation survey in every Nuclear Medicine department is an important part of over all radiation safety of working staff, radiation workers, patients and visitors. Radiation monitoring is usually done using either Geiger Muller Counter or Ionization Chamber based survey meters. The choice of instrument is governed by the nature and level of radiation anticipated in the environment. The present study was performed to compare the sensitivity of Geiger Muller Counter and Ionization Chamber based survey meters.
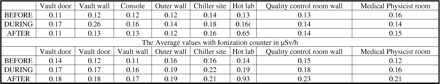
Methods Exposure level were recorded before, during and after operating the cyclotron. The readings were recorded at various locations including where high radiation field was expected and results were recorded, tabulated and analyzed.
Results Comparison between the readings of Geiger Muller Counter (µSv/h) and Ionization Chamber based survey meter (µSv/h) was performed. All the values recorded before, during and after cyclotron operation are shown in the table. Spearmen rank correction (r) = 0.324.
Conclusions The graph suggested positive correlation between the reading of Geiger Muller Counter and Ionization Chamber based survey meters. However, this is not a perfect linear correlation. Correlation ‘r’ value suggests that there is random variation between the readings of two survey meters. Positive Linear Correlation with random variation exists between the readings of two survey meter
The Average values with GM counter in µSv/h