Abstract
242036
Introduction: Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a vital medical imaging tool for studying in vivo metabolism. However, conventional PET systems are limited in their inability to image during motion. To further investigate brain metabolism under naturalistic conditions, this study introduces a novel wearable, full-brain coverage PET device optimized for use during movement.
Methods: To minimize the system’s weight, we using an external Knapsack support structure for free movement(KSS, see Fig.1 ad-b) and we also have Auxiliary support structure (ASS, see Fig.1 c-e) for those who are too weak to bear weight. Besides, this PET scanner consists of 16 detector modules, and the detector module consists of a 6 x 6 LYSO crystal array(single crystal size: 3.1mm x 3.1mm x 5mm), and 3 x 3 SiPM array.
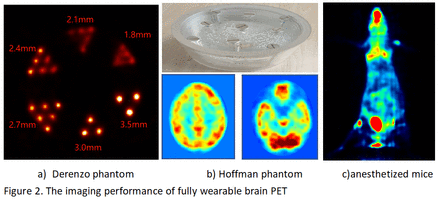
The imaging performance of the device was validated through a series of experiments including point source, Derenzo phantom, Hoffman phantom, and anesthetized mouse imaging. These tests were designed to evaluate the device's resolution, uniformity, and in vivo imaging capability.
Results: The system has an axial field of view(AFOV) of 120mm and diameter of 207.44mm, which can cover the entire brain. The device weighs around 6kg and has an external backpack design, which meets the requirements for real-time imaging while standing or moving (see Fig.1 a-e).
The point source at the center of the FOV image reconstruction with the Ordered Subset Expectation Maximization (OSEM) algorithm with 3 iterations(8 subsets), both radial and axial spatial resolutions were improved to 1.8mm. While Derenzo phantom imaging demonstrated that the device can achieve a resolution of up to 2.4mm(see Fig.2 a). Hoffman phantom imaging results(see Fig.2 b) confirmed uniform tracer distribution and structural consistency with the phantom model. In vivo imaging of anesthetized mice(see Fig.2 c)indicated the device's capability for live subject imaging, producing high-quality images.
Conclusions: Our research aims to achieve real-time whole-brain imaging during exercise to study human brain metabolism in the natural state. The results show that our equipment is not limited to the lying state of traditional PET imaging, but can perform imaging in various states such as standing and moving, and the imaging results are good. Next, human body scanning will be used to further conduct qualitative and quantitative comparisons with traditional PET to prove the feasibility of mobile wearable whole-brain coverage PET.