Abstract
P530
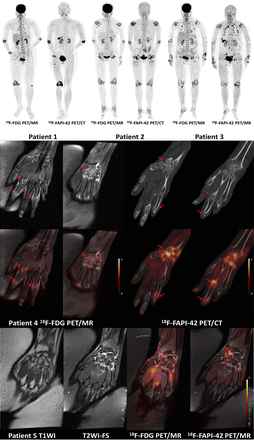
Introduction: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease involving multiple peripheral joints. Activated fibroblast-like synoviocytes with high fibroblast activation protein (FAP) expression are a key component in the development of RA. This study aimed to compare the performance of 18F-FAP inhibitor (FAPI)-42 PET/CT or PET/MR to 18F-FDG PET/MR in RA.
Methods: Ten patients with RA were prospectively recruited in this study. They underwent whole-body 18F-FDG PET/MR and 18F-FAPI-42 PET/CT (n = 7) or PET/MR (n = 3). PET/MR scans included T1-weighted fast spin echo (FSE) and fat-suppressed T2-weighted FSE or Short Tau Inversion Recovery images covering bilateral temporomandibular joints, hands and wrists, shoulders, hips, knees, ankles and feet. MR images were evaluated for the presence or absence of synovitis, bone marrow edema (BME), and bone erosion in 78 joints. PET images were evaluated for 18F-FDG and 18F-FAPI-42 uptake by positive uptake and target-to-background ratio (TBR defined as a ratio between the joint SUVmax normalized by the SUVmax of blood pool at the descending aorta) in 78 joints.
Results: In 10 patients with RA, the median joint counts of positive FAPI uptake and FDG uptake had no significant difference (15 [interquartile range, IQR 5, 24] vs. 12 [IQR 4, 19]). 18F-FDG PET/MR detected 164/633 (25.9%) joints with MR synovitis, 98/633 (15.5%) with MR BME, 136/633 (21.5%) with MR bone erosion, and 142/780 (18.2%) with positive FDG uptake. 18F-FAPI PET detected 172/762 (22.6%) joints with positive FAPI uptake. FAPI and FDG positivity showed high agreement (κ = 0.728, P < 0.001). TBRs of FAPI positively correlated with TBRs of FDG (r = 0.711, P < 0.001). The median TBRs of FAPI were significantly higher than TBRs of FDG in joints with MR synovitis, BME, and bone erosion (2.62 [IQR 0.95, 4.34] vs. 1.83 [IQR 1.08, 3.72] for MR synovitis; 2.83 [IQR 1.06, 5.15] vs. 2.05 [IQR 1.19, 3.69] for MR BME; 2.54 [IQR 0.68, 4.56] vs. 1.92 [IQR 0.95, 3.90] for MR bone erosion, P < 0.01 for all).
Conclusions: In this pilot study, 18F-FAPI-42 PET showed agreement with 18F-FDG PET for detecting joint involvement in rheumatoid arthritis and had higher TBR than 18F-FDG PET. Whole-body 18F-FAPI-42 PET/MR is a promising tool for the evaluation of disease activity in patients with RA.