Abstract
P1048
Introduction: Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is an important molecular imaging biomarker and therapeutic target in prostate cancer. It is highly expressed in over 90% of prostate cancer patients. Recent approvals for radiolabeled PSMA inhibitors, in the context of targeting metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, are rapidly changing prostate cancer patient management. However, the currently FDA-approved [68Ga]-PSMA11 and [18F]-DCFPyL may not be adequate to precisely monitor the delivered radiation dose of longer-lived [177Lu]/[225Ac]-PSMA617 due to pharmacokinetic discrepancies between the diagnostic and therapeutic. Here we evaluate a novel theranostic pair, utilizing a single chelator construct [89Zr]/[227Th]-L804-PSMAUrea for both tumor targeted PET imaging and alpha particle therapy of PSMA-positive cancer. The L804 ligand stably and rapidly coordinates these tetravalent radiometals, facilitating delivery of each radionuclide to PSMA-expressing lesions.
Methods: L804-PSMAUrea was labeled with 89Zr/227Th at 97 oC and characterized with radioHPLC or C18 radioTLC. Saturation binding assays were performed with the luminescent surrogate Eu-L804-PSMAUrea on PIP-PC3 cells by time-resolved luminescence. PIP-PC3 and PC3-flu bearing immunodeficient mice were used to evaluate both diagnostic [89Zr]- and therapeutic [227Th]-L804-PSMAUrea in vivo. Naïve Swiss Webster mice were utilized for pharmacokinetic assessments of the theranostic pair, and the data were compared to 225Ac-PSMA617. The cumulated activities for each organ were computed using the IDAC Dose 2.1 program for radiation dose prediction in man.
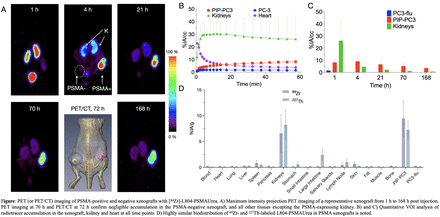
Results: [89Zr]-L804-PSMAUrea was prepared quantitatively in 1-step reaction by directly using [89Zr]Zr-oxalate with a specific activity of (5.73 ± 0.97) MBq/nmole (N = 4). Pure [227Th]-L804-PSMAUrea was obtained with a specific activity up to 72 KBq of 227Th per nmole of L804-PSMAUrea after purification by C18 cartridge. In vitro characterization of Eu-labelled L804-PSMAUrea retained high affinity toward PSMA expressing cells with a Kd value of 7.2 ± 1.6 nM. PET imaging of PIP-PC3 and PC3-flu xenograft-bearing animals with [89Zr]-L804-PSMAUrea showed a high contrast ratio between PSMA-positive tumor and the non-target tissues. [89Zr]-L804-PSMAUrea showed high accumulation in the PSMA-positive cancer tissue similar to the [227Th]-labeled version (9.470 ± 2.983 %IA/g vs 7.264 ± 1.285 %IA/g, P = 0.303). Both [89Zr]/[227Th]-L804-PSMAUrea were excreted predominantly through the urinary system. The estimated effective dose for a 70-kg adult male was 0.06, 90.66, and 21.70 mSv/MBq, for [89Zr]/[227Th]-L804-PSMAUrea, and [225Ac]-PSMA617, respectively.
Conclusions: [89Zr]/[227Th]-L804-PSMAUrea is a next-generation PSMA-binding theranostic pair. It demonstrates comparably high contrast PSMA-mediated accumulation in vitro and in vivo for both 89Zr- and 227Th-labeled agents. These promising preclinical results support further development of [89Zr]/[227Th]-L804-PSMAUrea as an alternative to existing short-lived radiotheranostics.