Abstract
3260
Introduction: SPECT systems can distinguish various isotope data by setting up multiple energy windows. For CZT detectors, the energy spectrum has a low energy tail due to the incomplete charge collection and inter-detector scattering leading to additional crosstalk between the radionuclides. Thus, scatter projections are overestimated when window-based methods are applied for scatter correction, e.g. triple energy window. Previous works have developed models to correct the scatter and crosstalk for 99mTc/123I dual-radionuclide CZT-based dedicated cardiac systems. These models iteratively estimate the dual-radionuclide primary and scatter components by solving a set of equations using the MLEM approach. Due to the photopeaks proximity, a penalty term is applied to ensure convergence. This term in previous works assume that the radionuclides have similar spatial tracer distributions. The present work extends the established methods for the dedicated GE NM Discovery 530c/570c SPECT system for any distribution combinations of dual-radionuclide tracers. Instead of precomputing penalty terms, a framework was developed to incorporate Monte Carlo simulation-based penalty term estimation into each loop of iterative image reconstruction with scatter and crosstalk compensation to dynamically estimate the penalty terms for any dual-radionuclide acquisition.
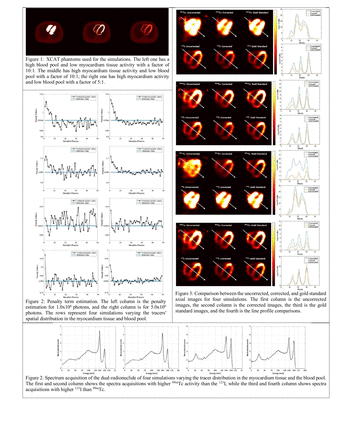
Methods: An iterative approach was developed to estimate the penalty term used in the deconvolutional model previously developed for CZT-based dedicated cardiac systems with pinhole collimators. The approach comprises SIMIND and XCAT phantoms. The phantoms were generated for 99mTc and 123I with a matrix of 128×128×128 and a voxel size of 4.0×4.0×4.0 mm3. Tracers spatial distribution of the myocardium tissue and the blood pool varied to mimic a dynamic acquisition. Monte Carlo simulations using SIMIND package of each radionuclide were performed separately, with a history of 3.0x106 photons per projection and a scatter order of 7 to ensure accuracy, then combined to form a simultaneous acquisition while still maintaining the gold standard single radionuclide result. At each image reconstruction iteration, the images of each isotope provided a rough estimation of the dual-radionuclide distribution combination. The two isotope image reconstructions in each iteration were included in SIMIND to simulate new 99mTc and 123I projections. Two numbers of histories of photons per projection were used: (i) 1.0x106 and (ii) 5.0x106. The area under the primary and self-scatter projection curves was calculated for each radionuclide primary energy window. The ratio among them is denominated as primary-to-scatter ratio (PTS). The penalty term was obtained by the ratio between PTSs, and incorporated into the deconvolution model. The penalty terms estimations were compared to the ground truth penalty terms precomputed using XCAT activity maps. The images after correction were compared with the uncorrected and the gold standard images. The myocardium to blood pool ratio was calculated using the ROI regions of the myocardium tissue and the blood pool for quantitative analysis.
Results: The penalty terms converged to the true penalty terms precomputed. Higher photons per projection had less fluctuations than lower photons per projection. However, the whole iterative process took about 12 hours. While for fewer photons per projection, it took about 2 hours. All corrected images presented a good agreement with the gold standard images. The line profiles demonstrate that the proposed approach corrects scatter and crosstalk for any dual-radionuclide spatial distribution. Myocardium to blood pool ratio demonstrates that the corrected images achieved more consistent quantification accuracy agreement to the gold standard images.
Conclusions: By dynamically estimating the penalty terms for any dual-radionuclide spatial distribution, we developed a CZT crosstalk correction method for quantitative imaging of any 99mTc/123I dual-radionuclide spatial distribution.