Abstract
3215
Introduction: 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT is a promising imaging tool used to detect and monitor disease in patients with advanced gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs). Patients often present with a high disease burden, sometimes with tens to hundreds of lesions, making comprehensive lesion-wise assessment clinically infeasible. Here, we implement automated, convolutional neural network-based (CNN) methods for automatic individual lesion detection and disease burden assessment.
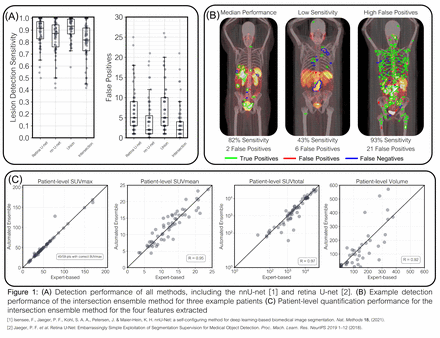
Methods: Baseline and follow-up 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT images from 59 patients with GEP-NETs undergoing theranostic 177Lu-DOTATATE (Lutathera) therapy were retrospectively analyzed (116 total scans, 1-7 per patient). Individual lesions were segmented on all images by a trained radiographer, which served as the gold-standard for this study. Two different CNNs, the nnU-net and the retina U-net, were trained separately on all 116 scans using 5-fold cross validation, matching fold assignments across networks and ensuring all scans from a single patient were included in the same fold (range: 23-25 scans per fold). Lesion detection performance was quantified on baseline images using the lesion detection sensitivity and the number of false positives (FPs) per patient for both U-net outputs and two ensemble methods (union and intersection). Baseline patient-level PET imaging metrics were extracted from each baseline image using the radiographer-based ground truth and predicted lesion masks for all four methods: SUVmax, SUVmean, SUVtotal, and total volume. Quantification performance was assessed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient (R).
Results: A total of 2,634 lesions from the 59 baseline PET/CT images were contoured by the radiographer (range: 1-239 lesions per scan). In these images, the median (interquartile range) performance was 87% (76%-94%) sensitivity with 2 (1-5.5) FPs/patient for nnU-net, and 92% (83-97%) sensitivity with 5 (3-9) FPs/patient for retina U-net. The union ensemble achieved 93% (87-99%) sensitivity with 5 (3-10) FPs/patient, and the intersection achieved 82% (73-92%) sensitivity with 2 (0-4) FPs/patient. For baseline patient-level quantification, the ensemble intersection method achieved the best overall quantification performance, with Pearson correlation coefficients of R=0.95 for SUVmean, R=0.97 for SUVtotal, and R=0.92 for total volume. Patient-level SUVmax was correctly captured in 49 of 59 scans.
Conclusions: An ensemble of two U-net based CNNs trained for lesion detection, acquired by taking the intersection of the two outputs, achieved excellent performance for quantifying patient-level PET imaging metrics. Despite a lower sensitivity, the method with the fewest false positives achieved the best quantification performance, indicating the majority of missed lesions have low uptake and represent a small fraction of the total disease burden.