Abstract
1486
Introduction: Immunotherapy targeting PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) has been found to be efficacious in numerous solid & hematologic malignancies. However, its response rate to therapy is only 15-35%. In order to optimize ICI therapies, a reliable assessment of PD-L1 expression is needed for selecting patients for ICI treatment & to assess potential alteration of PD-L1 expression during & post-therapy conferring resistance. Immunohistochemistry quantification of PD-L1 following biopsy is severely limited by random tissue sampling & inherent heterogeneity of PD-L1 expression within & among metastatic lesions. A non-invasive imaging based assessment of PD-L1 expression is critically needed. Although radiolabeled PET probes based on PD-L1 targeted therapeutic antibodies, like Atezolizumab have shown encouraging results, slow blood clearance (half-life = 27 days for therapeutic Atezolizumab) complicates the use of [89Zr]Zr-Atezolizumab as imaging probe. Therefore, alternate PD-L1 imaging probes based on antibodies with faster blood clearance could be advantageous.
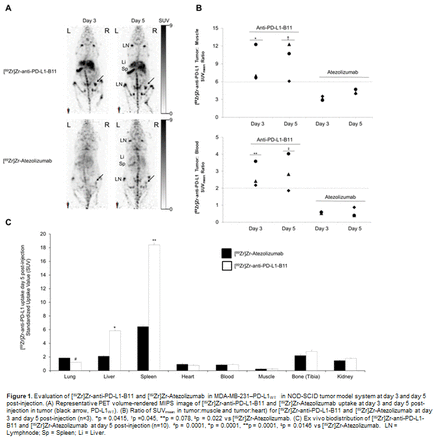
Methods: In this study, we radiolabeled antibody against PD-L1-clone B11 (anti-PD-L1-B11) with zirconium-89 (89Zr) and tested it as a PET probe to detect PD-L1 expressing breast cancer MDA-MB-231 subcutaneous tumor in NOD-SCID mice. Micro-PET imaging was performed at day 3 & at day 5 post-injection using a small animal PET/X-RAY system. The uptake of our novel PET probe [89Zr]Zr-anti-PD-L1-B11 was compared with the known [89Zr]Zr-Atezolizumab. The tumor: background (tumor: blood and tumor: muscle) SUV ratios were also calculated at both time points from PET scans using. Both the PET probes were also evaluated for an ex-vivo biodistribution performed at day 5 post-injection. Results: We successfully radiolabeled anti-PD-L1-B11 with zirconium-89 (89Zr) to produce an immunoPET probe, [89Zr]Zr-anti-PD-L1-B11 with radiolabeling yield of ~89-96% (n=2) with a specific activity of 0.024-0.032MBq/μg. The biodistribution profiles of [89Zr]Zr-anti-PD-L1-B11 and [89Zr]Zr-Atezolizumab were found to be different, [89Zr]Zr-anti-PD-L1-B11 showed higher uptake in tumor, liver and spleen compared to [89Zr]Zr-Atezolizumab. In addition to, [89Zr]Zr-anti-PD-L1-B11 also showed 5 fold higher tumor:blood SUV and 2-fold higher tumor:muscle SUV ratio as compared to [89Zr]Zr-Atezolizumab at both the time points day 3 and day 5, post-injection (Figure 1). Conclusion: In summary, our preliminary data demonstrates that [89Zr]Zr-anti-PD-L1-B11 is a superior PET probe and could potentially be useful as a better imaging probe for a non-invasive assessment of PD-L1 expression in tumors for the therapy management. Acknowledgements: This study was financially supported by Mayo Clinic’s Center for Clinical and Translational Science (CCaTS), Office of Translation to Practice (OTP), the Erivan K. and Helga Haub Family Fund and the Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Jeff R. Anderson and Dr. Bharath Wootla for their support in project management.