Abstract
76
Purpose: Lu-177-DOTATATE (Lutathera®), a type of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) targeting the somatostatin receptor (SSTR), has been shown effective in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) [1, 2]. Pretherapeutic personalized determination of PRRT dosimetry is essential to maximize its therapeutic effects, and identify the critical organs and maximum tolerated accumulated activity for individual patients [3, 4]. Ga-68-DOTATOC is routinely used to evaluate the feasibility of PRRT and select appropriate candidates by targeting SSTRs [5, 6]. The absorbed dose of Lu-177-DOTATE therapy can be estimated by single time-point SPECT/CT after Lu-177-DOTATATE treatment, making it an alternative to Lu-177-DOTATATE scintigraphy performed at least 4-5 times [7, 8]. The present study investigated whether the standardized uptake value (SUV) of pretherapeutic Ga-68-DOTATOC PET/CT could predict absorbed dose of tumors and critical organs after Lu-177-DOTATATE treatment.
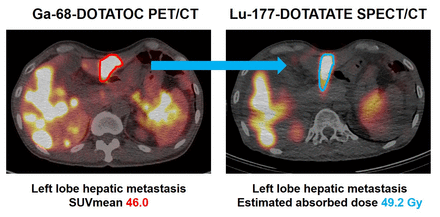
Methods: Patients who underwent pretherapeutic Ga-68-DOTATOC PET/CT within 3 months prior to Lu-177-DOTATATE therapy between December 2019 and November 2020 were retrospectively evaluated. Mean SUVs (SUVmean) of tumors (hepatic metastases and other tumors) larger than 2 cm in diameter were measured on Ga-68-DOTATOC PET/CT by determining volumes-of-interest (VOIs) with 50% of SUVmax cut-off [9]. For critical organs (kidneys, liver, and bone marrow), the SUVmean of spherical VOIs 4 cm3 were drawn for normal kidney parenchyme, liver parenchyme, and L5-S1 bone marrow [3, 10]. Four days after treatment with 200 mCi of Lu-177 DOTATATE, the absorbed dose by tumors and critical organs was estimated on SPECT/CT images by drawing the VOIs in the same manner with Ga-68-DOTATOC PET/CT [7]. SUVs of each lesion were measured twice using Syngo.Via (Siemens Healthcare, Knoxville, TN, USA), and the results were averaged. The SUVmean on Ga-68-DOTATOC PET/CT and estimated absorbed doses after Lu-177-DOTATATE treatment were compared by correlation and linear regression analyses. A P-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: This study enrolled 13 consecutive patients with metastatic NETs, including seven men and six women, of mean age; 51.1 ± 12.5 years. The primary sites of NETs were pancreas in nine patients, duodenum, rectum, kidney, and unknown site in each patient, respectively. The mean Ki-67 index was 17.9 ± 17.0%. Mean treatment dose of Lu-177-DOTATATE was 196.9 ± 5.2 mCi, with Lu-177-DOTATATE SPECT/CT performed 98.7 ± 0.9 hours after the start of treatment. The mean absorbed dose by tumors was 19.2 ± 16.1 Gy (24.3 ± 15.8 Gy by the hepatic metastases and 10.3 ± 12.4Gy by the other tumors). The mean absorbed dose by critical organs was 2.7 ± 2.5 Gy (4.7 ± 1.7 Gy by the kidneys, 1.2 ± 1.2 Gy by the liver, and 0.2 ± 0.2 Gy by bone marrow). The SUVmean on Ga-68-DOTATOC PET/CT and estimated absorbed doses after Lu-177-DOTATATE correlated significantly in tumors (R = 0.77, P < 0.001) and critical organs (R = 0.62, P < 0.001). Linear regression analysis showed that estimated absorbed dose after Lu-177-DOTATATE therapy could be predicted as follows; (1) Tumor absorbed dose (Gy) = 0.98 × (SUVmean of Ga-68-DOTATOC PET/CT) - 0.32, (2) Critical organ absorbed dose (Gy) = 0.53 × (SUVmean of Ga-68-DOTATOC PET/CT) + 0.41.
Conclusions: Quantitative measurement on pretherapeutic Ga-68-DOTATOC PET/CT was predictive of the absorbed dose by tumors after Lu-177-DOTATATE therapy in individual patients. In addition, prediction of absorbed doses by critical organs might help to estimate possible toxicities. Pretherapeutic prediction of absorbed dose of Lu-177-DOTATATE therapy could serve as the platform of personalized therapy guide.
Absorbed dose after Lu-177-DOTATATE therapy and correlation analysis with Ga-68-DOTATOC PET/CT