Abstract
115
Objectives: 11C-PS13 is a PET radioligand that targets the neuroinflammatory biomarker cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1). 11C-PS13 can quantify COX-1 in the human brain [1]. We performed human whole-body PET imaging with the aim of 1) evaluating the COX-1 selectivity of 11C-PS13 within other organs and 2) assessing the utility of 11C-PS13 for evaluating the in vivo potency of COX-1 anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), COX-1 preferring aspirin (ASA) and COX-1 selective ketoprofen (KTP) [2]. ASA and KTP pharmacokinetics have been studied in blood but not in humans in vivo [2].
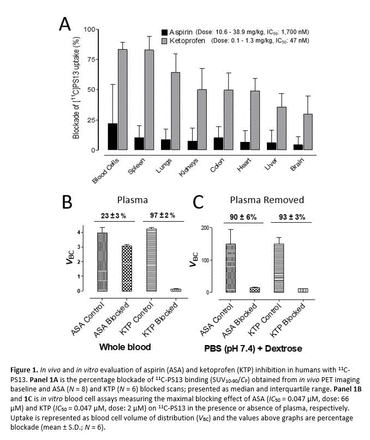
Methods: We performed whole-body PET imaging with 11C-PS13, which is selective and potent for COX-1 (IC50 = 1 nM) [3]. Baseline scans were obtained in 22 healthy volunteers and followed by scans blocked with NSAIDs ASA (N = 8; 975 - 1950 mg p.o.) or KTP (N = 6; 5 - 75 mg p.o.). Preliminary results indicated that COX-1 blockade was strong with KTP but low and variable with ASA. Blood cells collected for input function determination had blockade levels like those of spleen and brain. Therefore, we explored the pharmacology of ASA in blood. An in vitro assay, using blood from healthy volunteers, was used to quantify the role of plasma in the blocking effects of ASA (IC50 = 0.047 µM, dose: 66 µM) and KTP (IC50 = 0.047 µM, dose: 2 µM) [2]. Results: High 11C-PS13 uptake was observed in spleen, lungs, kidneys, colon, heart, liver, blood cells, and brain. The blockades of uptake were low and variable for ASA (median 9%; range: 0-83%) but much higher and still variable for KTP (median 56%; range: 0 - 92%) [Fig. 1A]. The in vitro blood cell assay showed that a maximal dose of ASA blocked only 23 ± 3% of blood COX-1, whereas KTP blocked 97 ± 2% [Fig. 1B]. When plasma was removed, ASA was able to reach a maximal blockade of 90 ± 3%, which compares to KTP at 93 ± 3% [Fig. 1C]. Conclusion: 11C-PS13 binds selectively to COX-1 within human organs and can be used to measure the in vivo potency of NSAIDs. Whole-body PET imaging showed that ASA had low and variable COX-1 blockade within the organs of healthy humans, whereas KTP showed strong blockade. Our in vitro blood cell assays showed that plasma can reduce ASA maximal blockade from 90 ± 6% to 23 ± 3%. Acknowledgment: NIMH Intramural Research Program References: [1] M-J Kim et al. 2020, PMID: 32399622 [2] Warner et al. 1999, PMID: 10377455 [3] Shrestha et al. 2016, PMID: 29792035