Abstract
P791
Introduction: Positron emission tomography (PET) can provide insight into both the biochemical and physiological processes of the human body and is widely used in oncology, cardiology and neurology. During clinical PET scanning, a full-dose radioactive tracer is required to obtain high-quality PET images, which inevitably raises concerns about potential health hazards for patients[1]. When dose reduction degrades the image quality, the image contains considerable noise and artifacts[2]. A range of deep learning methods have been proposed to improve the low-dose PET image quality, which usually construct end-to-end networks for standard-dose PET estimation with a certain radiation dose input. However, these methods suffer when fed with images of unknown dose level. Additionally, the PET image noise level may differ among individuals and medical devices[3]. Considering noise level differences, our work aims to develop an adaptive noise-level-aware method for low-dose PET imaging.
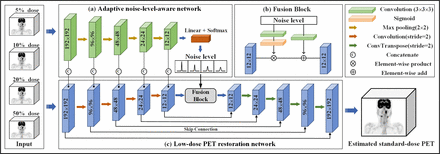
Methods: In this paper, we propose a 3D noise-level-aware network for low-dose PET images. Our method consists of two subnetworks: (1) an adaptive noise-level-aware network and (2) a low-dose PET restoration network. Unlike the other end-to-end networks that directly find mapping functions between low-dose and standard-dose images, we first roughly define the noise in four levels and then pretrain the adaptive noise-level-aware network to estimate the closet noise level to which the input images belong. After that, we use the noise level category information as a priori to guide the reconstruction process. Moreover, to enrich the features of the second network, the feature maps from the adaptive noise-level-aware network at different scales are also integrated into the low-dose PET restoration network.
Results: Experiments were performed on a real human head and neck dataset including 50 subjects, and the average dosage was 234 MBq (from 152 MBq to 365 MBq, 18F-FDG). During PET scanning, the standard-dose image is obtained in a 600s period while the low-dose PET scans were acquired in a shorter period with the standard dose tracer injection. The scan duration corresponding to 5%, 10%, 20%, and 50% dose were 30s, 60s, 120s, and 300s, respectively. PSNR and SSIM were used to evaluate the recovery performance of low-dose PET, and the proposed algorithm was compared with CNN(3D), RED-CNN(3D), U-net(2D), U-net(3D). Compared with the original low-dose PET images, using the proposed method to recover PET at different dose levels has a significant denoising performance. Specifically, for 5% dose PET, PSNR improved by 12% and SSIM by 5%. Compare to the state-of-the-art methods, our method still achieves much better performance. For all the input images, our method increased PSNR from 33.98 dB to 36.10 dB, and SSIM from 0.92 to 0.96 while the best performing in other deep learning methods only increased PSNR to 35.63 dB, SSIM to 0.93.
Conclusions: Compared with other networks, the proposed method can estimate the image noise level and perform adaptive restoration of low-dose PET images, achieving superior performance in both visual and quantitative evaluation. The division and estimation of noise levels with more uniform and smaller intervals will be carried out in future work to improve the robustness and generalization of the model.