Abstract
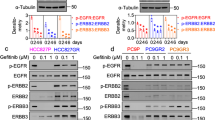
We have recently reported that treatment with gemcitabine, a potent chemotherapeutic agent and radiation sensitizer, stimulates phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Because phosphorylation of EGFR is known to precede receptor degradation, we hypothesized that gemcitabine treatment may also result in EGFR degradation. In two human head and neck cancer cell lines, UMSCC-1 and UMSCC-6, we demonstrated an approximately 80% decrease in total EGFR levels at 72 h after a 2-h treatment with 1 μ M gemcitabine. Neither cisplatin nor 5-fluorouracil, which are used to treat head and neck cancer, caused EGFR degradation. EGFR downregulation did not occur at the level of transcription, as assessed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT–PCR), but instead occurred via phosphorylation and ubiquitination of the receptor along a proteosome/lysosome-mediated pathway. Inhibition of EGFR degradation, by either pretreatment with the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib or by exposure to the proteosome/lysosome inhibitor MG132, significantly reduced gemcitabine-induced cell death. These results suggest that EGFR degradation may be a novel mechanism for gemcitabine-mediated cell death. These findings also indicate that caution should be exercised when combining gemcitabine with agents that may prevent EGFR degradation, such as EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors administered in a suboptimal sequence or proteosome inhibitors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbruzzese JL, Grunewald R, Weeks EA, Gravel D, Adams T, Nowak B et al. (1991). A phase I clinical, plasma, and cellular pharmacology study of gemcitabine. J Clin Oncol 9: 491–498.
Ang KK, Berkey BA, Tu X, Zhang HZ, Katz R, Hammond EH et al. (2002). Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor expression on survival and pattern of relapse in patients with advanced head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res 62: 7350–7356.
Baselga J, Trigo JM, Bourhis J, Tortochaux J, Cortes-Funes H, Hitt R et al. (2005). Phase II multicenter study of the antiepidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with platinum-refractory metastatic and/or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol 23: 5568–5577.
Benhar M, Engelberg D, Levitzki A . (2002). Cisplatin-induced activation of the EGF receptor. Oncogene 21: 8723–8731.
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB et al. (2006). Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 354: 567–578.
Burke P, Schooler K, Wiley HS . (2001). Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling by endocytosis and intracellular trafficking. Mol Biol Cell 12: 1897–1910.
Chinnaiyan P, Vallabhaneni G, Armstrong E, Huang SM, Harari PM . (2005). Modulation of radiation response by histone deacetylase inhibition. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 62: 223–229.
Chun PY, Feng FY, Scheurer AM, Davis MA, Lawrence TS, Nyati MK . (2006). Synergistic effects of gemcitabine and gefitinib in the treatment of head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res 66: 981–988.
Cohen EE, Rosen F, Stadler WM, Recant W, Stenson K, Huo D et al. (2003). Phase II trial of ZD1839 in recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol 21: 1980–1987.
Cross TG, Scheel-Toellner D, Henriquez NV, Deacon E, Salmon M, Lord JM . (2000). Serine/threonine protein kinases and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 256: 34–41.
Dittmann K, Mayer C, Fehrenbacher B, Schaller M, Raju U, Milas L et al. (2005). Radiation-induced epidermal growth factor receptor nuclear import is linked to activation of DNA-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 280: 31182–31189.
Eisbruch A, Lyden T, Bradford CR, Dawson LA, Haxer MJ, Miller AE et al. (2002). Objective assessment of swallowing dysfunction and aspiration after radiation concurrent with chemotherapy for head-and-neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53: 23–28.
Eisbruch A, Shewach DS, Bradford CR, Littles JF, Teknos TN, Chepeha DB et al. (2001). Radiation concurrent with gemcitabine for locally advanced head and neck cancer: a phase I trial and intracellular drug incorporation study. J Clin Oncol 19: 792–799.
Felder S, Miller K, Moehren G, Ullrich A, Schlessinger J, Hopkins CR . (1990). Kinase activity controls the sorting of the epidermal growth factor receptor within the multivesicular body. Cell 61: 623–634.
Grandis JR, Tweardy DJ . (1993). Elevated levels of transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor messenger RNA are early markers of carcinogenesis in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 53: 3579–3584.
He YY, Huang JL, Gentry JB, Chignell CF . (2003). Epidermal growth factor receptor down-regulation induced by UVA in human keratinocytes does not require the receptor kinase activity. J Biol Chem 278: 42457–42465.
Lawrence TS, Davis MA, Hough A, Rehemtulla A . (2001). The role of apoptosis in 2′,2′-difluoro-2′-deoxycytidine (gemcitabine)-mediated radiosensitization. Clin Cancer Res 7: 314–319.
Lawrence TS, Davis MA, Maybaum J, Mukhopadhyay SK, Stetson PL, Normolle DP et al. (1992). The potential superiority of bromodeoxyuridine to iododeoxyuridine as a radiation sensitizer in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 52: 3698–3704.
Levkowitz G, Waterman H, Zamir E, Kam Z, Oved S, Langdon WY et al. (1998). c-Cbl/Sli-1 regulates endocytic sorting and ubiquitination of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Genes Dev 12: 3663–3674.
Longva KE, Blystad FD, Stang E, Larsen AM, Johannessen LE, Madshus IH . (2002). Ubiquitination and proteasomal activity is required for transport of the EGF receptor to inner membranes of multivesicular bodies. J Cell Biol 156: 843–854.
Macabeo-Ong M, Ginzinger DG, Dekker N, McMillan A, Regezi JA, Wong DT et al. (2002). Effect of duration of fixation on quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analyses. Mod Pathol 15: 979–987.
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J . (2003). Status of epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists in the biology and treatment of cancer. J Clin Oncol 21: 2787–2799.
Mizuno H, Cho YY, Zhu F, Ma WY, Bode AM, Yang CS et al. (2005). Theaflavin-3,3′-digallate induces epidermal growth factor receptor downregulation. Mol Carcinog.
Nelson JM, Fry DW . (2001). Akt, MAPK (Erk1/2), and p38 act in concert to promote apoptosis in response to ErbB receptor family inhibition. J Biol Chem 276: 14842–14847.
Nyati MK, Maheshwari D, Hanasoge S, Sreekumar A, Rynkiewicz SD, Chinnaiyan AM et al. (2004). Radiosensitization by pan ErbB inhibitor CI-1033 in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 10: 691–700.
Oksvold MP, Thien CB, Widerberg J, Chantry A, Huitfeldt HS, Langdon WY . (2003). Serine mutations that abrogate ligand-induced ubiquitination and internalization of the EGF receptor do not affect c-Cbl association with the receptor. Oncogene 22: 8509–8518.
Pignon JP, Bourhis J, Domenge C, Designe L . (2000). Chemotherapy added to locoregional treatment for head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma: three meta-analyses of updated individual data. MACH-NC Collaborative Group. Meta-Analysis of Chemotherapy on Head and Neck Cancer. Lancet 355: 949–955.
Pomerantz RG, Grandis JR . (2004). The epidermal growth factor receptor signaling network in head and neck carcinogenesis and implications for targeted therapy. Semin Oncol 31: 734–743.
Rajkumar SV, Richardson PG, Hideshima T, Anderson KC . (2005). Proteasome inhibition as a novel therapeutic target in human cancer. J Clin Oncol 23: 630–639.
Rubin Grandis J, Melhem MF, Gooding WE, Day R, Holst VA, Wagener MM et al. (1998). Levels of TGF-alpha and EGFR protein in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and patient survival. J Natl Cancer Inst 90: 824–832.
Rubin Grandis J, Zeng Q, Tweardy DJ . (1996). Retinoic acid normalizes the increased gene transcription rate of TGF-alpha and EGFR in head and neck cancer cell lines. Nat Med 2: 237–240.
Sato K, Sato A, Aoto M, Fukami Y . (1995). c-Src phosphorylates epidermal growth factor receptor on tyrosine 845. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 215: 1078–1087.
Shewach DS, Lawrence TS . (1996). Gemcitabine and radiosensitization in human tumor cells. Invest New Drugs 14: 257–263.
Soulieres D, Senzer NN, Vokes EE, Hidalgo M, Agarwala SS, Siu LL . (2004). Multicenter phase II study of erlotinib, an oral epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol 22: 77–85.
Supino-Rosin L, Yoshimura A, Yarden Y, Elazar Z, Neumann D . (2000). Intracellular retention and degradation of the epidermal growth factor receptor, two distinct processes mediated by benzoquinone ansamycins. J Biol Chem 275: 21850–21855.
Tempero M, Plunkett W, Ruiz Van Haperen V, Hainsworth J, Hochster H, Lenzi R et al. (2003). Randomized phase II comparison of dose-intense gemcitabine: thirty-minute infusion and fixed dose rate infusion in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 21: 3402–3408.
Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S, Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, Sun XW et al. (2005). Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science 310: 644–648.
Waterman H, Yarden Y . (2001). Molecular mechanisms underlying endocytosis and sorting of ErbB receptor tyrosine kinases. FEBS Lett 490: 142–152.
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX . (2001). Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 127–137.
Zhuang S, Ouedraogo GD, Kochevar IE . (2003). Downregulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling by singlet oxygen through activation of caspase-3 and protein phosphatases. Oncogene 22: 4413–4424.
Acknowledgements
We thank Avraham Eisbruch, Mats Ljungman, Alnawaz Rehemtulla and Aaron Spalding for helpful discussion and Steven Kronenberg for assistance in making figures. Grant support: NIH through the University of Michigan Head and Neck Specialized Program of Research Excellence grant (1 P50 CA97248) and University of Michigan Cancer Center support grant 5 P30 CA46592.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, F., Varambally, S., Tomlins, S. et al. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor degradation in gemcitabine-mediated cytotoxicity. Oncogene 26, 3431–3439 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210129
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210129
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Akt kinase LANCL2 functions as a key driver in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Non-metabolic role of UCK2 links EGFR-AKT pathway activation to metastasis enhancement in hepatocellular carcinoma
Oncogenesis (2020)
-
Glycerol kinase 5 confers gefitinib resistance through SREBP1/SCD1 signaling pathway
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)
-
GLRX inhibition enhances the effects of geftinib in EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLC cells through FoxM1 signaling pathway
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2019)
-
Dual inhibition of EGFR at protein and activity level via combinatorial blocking of PI4KIIα as anti-tumor strategy
Protein & Cell (2014)