Abstract
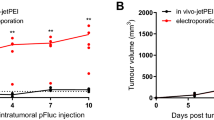
RNA interference (RNAi)-mediated gene silencing approaches appear very promising for therapies based on the targeted inhibition of disease-relevant genes. The major hurdle to the therapeutic development of RNAi strategies remains, however, the efficient delivery of the RNAi-inducing molecules, the short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs), to the target tissue. With respect to cancer treatment the development of efficient delivery methods into solid tumors appears as a critical issue. However, very few studies have addressed this problem. In this study we have investigated the contribution of electrically mediated delivery of siRNA into murine tumors stably expressing an enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) target reporter gene. The silencing of EGFP gene expression was quantified over time by fluorescence imaging in the living animal. Our study indicates that electric field can be used as an efficient method for siRNA delivery and associated gene silencing into cells of solid tumors in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC . Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998; 391: 806–811.
Tomari Y, Zamore PD . Perspective: machines for RNAi. Genes Dev 2005; 19: 517–529.
Caplen NJ, Parrish S, Imani F, Fire A, Morgan RA . Specific inhibition of gene expression by small double-stranded RNAs in invertebrate and vertebrate systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 9742–9747.
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T . Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 2001; 411: 494–498.
Hannon GJ, Rossi JJ . Unlocking the potential of the human genome with RNA interference. Nature 2004; 431: 371–378.
Ito M, Kawano K, Miyagishi M, Taira K . Genome-wide application of RNAi to the discovery of potential drug targets. FEBS Lett 2005; 579: 5988–5995.
Leung RK, Whittaker PA . RNA interference: from gene silencing to gene-specific therapeutics. Pharmacol Therapy 2005; 107: 222–239.
Ryther RC, Flynt AS, Phillips JA, Patton JG . siRNA therapeutics: big potential from small RNAs. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 5–11.
Xu Z, Xia XG . RNAi therapy: dominant disease gene gets silenced. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 1159–1160.
Behlke MA . Progress towards in vivo use of siRNAs. Mol Therapy 2006; 13: 644–670.
Zimmermann TS, Lee AC, Akinc A, Bramlage B, Bumcrot D, Fedoruk MN et al. RNAi-mediated gene silencing in non-human primates. Nature 2006; 441: 111–114.
Xie FY, Woodle MC, Lu PY . Harnessing in vivo siRNA delivery for drug discovery and therapeutic development. Drug Discov Today 2006; 11: 67–73.
Rossi JJ . RNAi therapeutics: SNALPing siRNAs in vivo. Gene Therapy 2006; 13: 583–584.
Schiffelers RM, Xu J, Storm G, Woodle MC, Scaria PV . Cancer siRNA therapy by tumor selective delivery with ligand-targeted sterically stabilized nanoparticle. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: e149.
Song E, Zhu P, Lee SK, Chowdhury D, Kussman S, Dykxhoorn DM et al. Antibody mediated in vivo delivery of small interfering RNAs via cell-surface receptors. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 709–717.
Dykxhoorn DM, Palliser D, Lieberman J . The silent treatment: siRNAs as small molecule drugs. Gene Therapy 2006; 13: 541–552.
Rossi J . Helping RNAi deliver. Mol Therapy 2005; 11: 653.
Mocellin S, Costa R, Nitti D . RNA interference: ready to silence cancer? J Mol Med 2006; 32: 9–27.
Aharinejad S, Paulus P, Sioud M, Hofmann M, Zins K, Schafer R et al. Colony-stimulating factor-1 blockade by antisense oligonucleotides and small interfering RNAs suppresses growth of human mammary tumor xenografts in mice. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 5378–5384.
Takei Y, Kadomatsu K, Yuzawa Y, Matsuo S, Muramatsu T . A small interfering RNA targeting vascular endothelial growth factor as cancer therapeutics. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 3365–3370.
Leng Q, Mixson AJ . Small interfering RNA targeting Raf-1 inhibits tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 682–690.
Filleur S, Courtin A, Ait-Si-Ali S, Guglielmi J, Merle C, Harel-Bellan A et al. SiRNA-mediated inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor severely limits tumor resistance to antiangiogenic thrombospondin-1 and slows tumor vascularization and growth. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 3919–3922.
Takahashi Y, Nishikawa M, Kobayashi N, Takakura Y . Gene silencing in primary and metastatic tumors by small interfering RNA delivery in mice: quantitative analysis using melanoma cells expressing firefly and sea pansy luciferases. J Control Release 2005; 105: 332–343.
Ocker M, Neureiter D, Lueders M, Zopf S, Ganslmayer M, Hahn EG et al. Variants of bcl-2 specific siRNA for silencing antiapoptotic bcl-2 in pancreatic cancer. Gut 2005; 54: 1298–1308.
Golzio M, Teissie J, Rols MP . Direct visualization at the single-cell level of electrically mediated gene delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 1292–1297.
Heller LC, Ugen K, Heller R . Electroporation for targeted gene transfer. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2005; 2: 255–268.
Li S . Electroporation gene therapy: new developments in vivo and in vitro. Curr Gene Therapy 2004; 4: 309–316.
Wells DJ . Gene therapy progress and prospects: electroporation and other physical methods. Gene Therapy 2004; 11: 1363–1369.
Zhang L, Nolan E, Kreitschitz S, Rabussay DP . Enhanced delivery of naked DNA to the skin by non-invasive in vivo electroporation. Biochim Biophys Acta 2002; 1572: 1–9.
Matsuda T, Cepko CL . Electroporation and RNA interference in the rodent retina in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 16–22.
Akaneya Y, Jiang B, Tsumoto T . RNAi-induced gene silencing by local electroporation in targeting brain region. J Neurophysiol 2005; 93: 594–602.
Golzio M, Mazzolini L, Moller P, Rols MP, Teissie J . Inhibition of gene expression in mice muscle by in vivo electrically mediated siRNA delivery. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 246–251.
Kishida T, Asada H, Gojo S, Ohashi S, Shin-Ya M, Yasutomi K et al. Sequence-specific gene silencing in murine muscle induced by electroporation-mediated transfer of short interfering RNA. J Gene Med 2004; 6: 105–110.
Schiffelers RM, Ansari A, Xu J, Zhou Q, Tang Q, Storm G et al. Effects of treatment with small interfering RNA on joint inflammation in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52: 1314–1318.
Inoue A, Takahashi KA, Mazda O, Terauchi R, Arai Y, Kishida T et al. Electro-transfer of small interfering RNA ameliorated arthritis in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 336: 903–908.
Takabatake Y, Isaka Y, Mizui M, Kawachi H, Shimizu F, Ito T et al. Exploring RNA interference as a therapeutic strategy for renal disease. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 965–973.
Bettan M, Ivanov MA, Mir LM, Boissiere F, Delaere P, Scherman D . Efficient DNA electrotransfer into tumors. Bioelectrochemistry 2000; 52: 83–90.
Rols MP, Delteil C, Golzio M, Dumond P, Cros S, Teissie J . In vivo electrically mediated protein and gene transfer in murine melanoma. Nat Biotechnol 1998; 16: 168–171.
Cemazar M, Sersa G, Wilson J, Toze GM, Hart SL, Grosel A et al. Effective gene transfer to solid tumors using different nonviral gene delivery techniques: electroporation, liposomes, and integrin-targeted vector. Cancer Gene Therapy 2002; 9: 399–406.
Coralli C, Cemazar M, Kanthou C, Tozer GM, Dachs GU . Limitations of the reporter green fluorescent protein under simulated tumor conditions. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 4784–4790.
Bierhuizen MF, Westerman Y, Visser TP, Dimjati W, Wognum AW, Wagemaker G . Enhanced green fluorescent protein as selectable marker of retroviral-mediated gene transfer in immature hematopoietic bone marrow cells. Blood 1997; 90: 3304–3315.
De Vos J, Bagnis C, Bonnafoux L, Requirand G, Jourdan M, Imbert MC et al. Comparison of murine leukemia virus, human immunodeficiency virus, and adeno-associated virus vectors for gene transfer in multiple myeloma: lentiviral vectors demonstrate a striking capacity to transduce low-proliferating primary tumor cells. Hum Gene Therapy 2003; 14: 1727–1739.
Sersa G, Cemazar M, Semrov D, Miklavcic D . Changing electrode orientation improves the efficacy of electrochemotherapy of solid tumors in mice. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 1996; 39: 61–66.
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A et al. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 2002; 3: research0034.1–research0034.11.
Klein D, Bugl B, Gunzburg WH, Salmons B . Accurate estimation of transduction efficiency necessitates a multiplex real-time PCR. Gene Therapy 2000; 7: 458–463.
Nakai N, Kishida T, Shin-Ya M, Imanishi J, Ueda Y, Kishimoto S et al. Therapeutic RNA interference of malignant melanoma by electrotransfer of small interfering RNA targeting Mitf. Gene Therapy 2007; 14: 357–365.
Acknowledgements
Financial supports were obtained from the ‘Ligue nationale contre le Cancer’, the CNRS CEA ‘Imagerie du petit animal’ program, the ‘Région Midi-Pyrenées’, the Cancéropôle GSO (Grand Sud-Ouest) and the AFM (Association Française contre les Myopathies).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golzio, M., Mazzolini, L., Ledoux, A. et al. In vivo gene silencing in solid tumors by targeted electrically mediated siRNA delivery. Gene Ther 14, 752–759 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302920
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302920
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pre-clinical investigation of the synergy effect of interleukin-12 gene-electro-transfer during partially irreversible electropermeabilization against melanoma
Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer (2019)
-
Mcam Silencing With RNA Interference Using Magnetofection has Antitumor Effect in Murine Melanoma
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids (2014)