Abstract
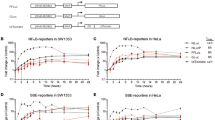
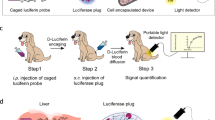
Luciferases are widely used to monitor biological processes. Here we describe the naturally secreted Gaussia princeps luciferase (Gluc) as a highly sensitive reporter for quantitative assessment of cells in vivo by measuring its concentration in blood. The Gluc blood assay complements in vivo bioluminescence imaging, which has the ability to localize the signal and provides a multifaceted assessment of cell viability, proliferation and location in experimental disease and therapy models.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Contag, C.H. & Ross, B.D. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 16, 378–387 (2002).
Bhaumik, S. & Gambhir, S.S. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 377–382 (2002).
Gross, S. & Piwnica-Worms, D. Cancer Cell 7, 5–15 (2005).
Negrin, R.S. & Contag, C.H. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 484–490 (2006).
Adams, J.Y. et al. Nat. Med. 8, 891–897 (2002).
Luker, G.D. et al. J. Virol. 76, 12149–12161 (2002).
Luo, J., Lin, A.H., Masliah, E. & Wyss-Coray, T. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 18326–18331 (2006).
Badr, C.E., Hewett, J.W., Breakefield, X.O. & Tannous, B.A. PLoS ONE 2, e571 (2007).
Tannous, B.A., Kim, D.E., Fernandez, J.L., Weissleder, R. & Breakefield, X.O. Mol. Ther. 11, 435–443 (2005).
Colin, M. et al. Gene Ther. 7, 1333–1336 (2000).
Hiramatsu, N., Kasai, A., Hayakawa, K., Yao, J. & Kitamura, M. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, e93 (2006).
Kramm, C.M. et al. Hum. Gene Ther. 7, 291–300 (1996).
Weissleder, R. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 316–317 (2001).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute P50 CA86355-04 (R.W. and X.O.B.), 1K99CA126839-01 (B.A.T.) and the Brain Tumor Society (X.O.B. and B.A.T.). We thank M. Sena-Esteves for help with vector generation and useful discussions, M. Whalen, F. Swirski and M. Pittet for advice as well as C. Maguire and N. Lewandrowski for technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.A.T., T.W., R.W. and X.O.B. designed the experiments. T.W., B.A.T., C.B. and L.P. performed the experiments. R.d.K. helped with the blood withdrawn and intravenous injections. B.A.T. supervised the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
An invention disclosure submitted by B.A.T., including subject matter of this manuscript was filed with the Massachusetts General Hospital office of technology transfer. This invention disclosure is under evaluation at the office and may be filed as a patent application.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–2, Supplementary Methods (PDF 86 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wurdinger, T., Badr, C., Pike, L. et al. A secreted luciferase for ex vivo monitoring of in vivo processes. Nat Methods 5, 171–173 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1177
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1177
This article is cited by
-
Inter-organ communication involved in metabolic regulation at the whole-body level
Inflammation and Regeneration (2023)
-
A highly sensitive strategy for monitoring real-time proliferation of targeted cell types in vivo
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Novel genetically engineered mouse models for clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Method for quantification of porcine type I interferon activity using luminescence, by direct and indirect means
BMC Biotechnology (2022)
-
Monitoring autochthonous lung tumors induced by somatic CRISPR gene editing in mice using a secreted luciferase
Molecular Cancer (2022)