Abstract
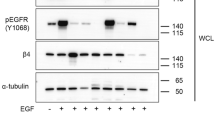
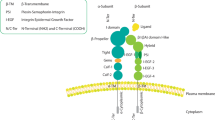
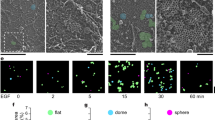
Integrins regulate adhesion-dependent growth, survival and invasion of tumor cells. In particular, expression of integrin αvβ3 is associated with progression of a variety of human tumors. Here we reveal a previously undescribed adhesion-independent role for integrin αvβ3 in pancreatic cancer and other carcinomas. Specifically, αvβ3 expressed in carcinoma cells enhanced anchorage-independent tumor growth in vitro and increased lymph node metastases in vivo. These effects required recruitment of c-Src to the β3 integrin cytoplasmic tail, leading to c-Src activation, Crk-associated substrate (CAS) phosphorylation and tumor cell survival that, unexpectedly, was independent of cell adhesion or focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation. Pharmacological blockade of c-Src kinase activity or decreased expression of endogenous αvβ3 integrin or c-Src not only inhibited anchorage-independent growth but also suppressed metastasis in vivo, yet these manipulations did not affect tumor cell migration or invasion. These data define an unexpected role for an integrin as a mediator of anchorage independence, suggesting that an αvβ3–c-Src signaling module may account for the aggressive behavior of integrin αvβ3–expressing tumors in humans.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guo, W. & Giancotti, F.G. Integrin signalling during tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 816–826 (2004).
Schlaepfer, D.D., Mitra, S.K. & Ilic, D. Control of motile and invasive cell phenotypes by focal adhesion kinase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1692, 77–102 (2004).
Roberts, W.G. et al. Antitumor activity and pharmacology of a selective focal adhesion kinase inhibitor, PF-562,271. Cancer Res. 68, 1935–1944 (2008).
Pylayeva, Y. et al. Ras- and PI3K-dependent breast tumorigenesis in mice and humans requires focal adhesion kinase signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 119, 252–266 (2009).
Lahlou, H. et al. Mammary epithelial-specific disruption of the focal adhesion kinase blocks mammary tumor progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 20302–20307 (2007).
Eide, B.L., Turck, C.W. & Escobedo, J.A. Identification of Tyr-397 as the primary site of tyrosine phosphorylation and pp60Src association in the focal adhesion kinase, pp125FAK. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 2819–2827 (1995).
Ishizawar, R. & Parsons, S.J. c-Src and cooperating partners in human cancer. Cancer Cell 6, 209–214 (2004).
Brábek, J. et al. Crk-associated substrate tyrosine phosphorylation sites are critical for invasion and metastasis of SRC-transformed cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 3, 307–315 (2005).
Klemke, R.L. et al. CAS/Crk coupling serves as a 'molecular switch' for induction of cell migration. J. Cell Biol. 140, 961–972 (1998).
Cho, S.Y. & Klemke, R.L. Extracellular-regulated kinase activation and CAS/Crk coupling regulate cell migration and suppress apoptosis during invasion of the extracellular matrix. J. Cell Biol. 149, 223–236 (2000).
Albelda, S.M. et al. Integrin distribution in malignant melanoma: association of the β3 subunit with tumor progression. Cancer Res. 50, 6757–6764 (1990).
Hsu, M.Y. et al. Adenoviral gene transfer of β3 integrin subunit induces conversion from radial to vertical growth phase in primary human melanoma. Am. J. Pathol. 153, 1435–1442 (1998).
McCabe, N.P., De, S., Vasanji, A., Brainard, J. & Byzova, T.V. Prostate cancer specific integrin αvβ3 modulates bone metastatic growth and tissue remodeling. Oncogene 26, 6238–6243 (2007).
Takayama, S. et al. The relationship between bone metastasis from human breast cancer and integrin αvβ3 expression. Anticancer Res. 25, 79–83 (2005).
Sloan, E.K. et al. Tumor-specific expression of αvβ3 integrin promotes spontaneous metastasis of breast cancer to bone. Breast Cancer Res. 8, R20 (2006).
Felding-Habermann, B. et al. Integrin activation controls metastasis in human breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 1853–1858 (2001).
Gruber, G. et al. Correlation between the tumoral expression of β3-integrin and outcome in cervical cancer patients who had undergone radiotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 92, 41–46 (2005).
Hosotani, R. et al. Expression of integrin αvβ3 in pancreatic carcinoma: relation to MMP-2 activation and lymph node metastasis. Pancreas 25, e30–e35 (2002).
Giancotti, F.G. & Ruoslahti, E. Elevated levels of the α5β1 fibronectin receptor suppress the transformed phenotype of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell 60, 849–859 (1990).
Varner, J.A., Emerson, D.A. & Juliano, R.L. Integrin α5β1 expression negatively regulates cell growth: reversal by attachment to fibronectin. Mol. Biol. Cell 6, 725–740 (1995).
Stupack, D.G., Puente, X.S., Boutsaboualoy, S., Storgard, C.M. & Cheresh, D.A. Apoptosis of adherent cells by recruitment of caspase-8 to unligated integrins. J. Cell Biol. 155, 459–470 (2001).
Stupack, D.G. et al. Potentiation of neuroblastoma metastasis by loss of caspase-8. Nature 439, 95–99 (2006).
Ginsberg, M.H., Partridge, A. & Shattil, S.J. Integrin regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 17, 509–516 (2005).
Arias-Salgado, E.G. et al. Src kinase activation by direct interaction with the integrin β cytoplasmic domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 13298–13302 (2003).
Tsatsanis, C. & Spandidos, D.A. Oncogenic kinase signaling in human neoplasms. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1028, 168–175 (2004).
Simpson, C.D., Anyiwe, K. & Schimmer, A.D. Anoikis resistance and tumor metastasis. Cancer Lett. 272, 177–185 (2008).
Leavesley, D.I., Ferguson, G.D., Wayner, E.A. & Cheresh, D.A. Requirement of the integrin β3 subunit for carcinoma cell spreading or migration on vitronectin and fibrinogen. J. Cell Biol. 117, 1101–1107 (1992).
Miyauchi, A. et al. Recognition of osteopontin and related peptides by an α5β3 integrin stimulates immediate cell signals in osteoclasts. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 20369–20374 (1991).
Loftus, J.C. et al. A β3 integrin mutation abolishes ligand binding and alters divalent cation-dependent conformation. Science 249, 915–918 (1990).
Shin, N.Y. et al. Subsets of the major tyrosine phosphorylation sites in Crk-associated substrate (CAS) are sufficient to promote cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 38331–38337 (2004).
Summy, J.M. & Gallick, G.E. Src family kinases in tumor progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 22, 337–358 (2003).
Reddig, P.J. & Juliano, R.L. Clinging to life: cell to matrix adhesion and cell survival. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 24, 425–439 (2005).
Westhoff, M.A., Serrels, B., Fincham, V.J., Frame, M.C. & Carragher, N.O. SRC-mediated phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase couples actin and adhesion dynamics to survival signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24, 8113–8133 (2004).
Uhm, J.H., Dooley, N.P., Kyritsis, A.P., Rao, J.S. & Gladson, C.L. Vitronectin, a glioma-derived extracellular matrix protein, protects tumor cells from apoptotic death. Clin. Cancer Res. 5, 1587–1594 (1999).
De, S. et al. VEGF-integrin interplay controls tumor growth and vascularization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 7589–7594 (2005).
Matter, M.L. & Ruoslahti, E. A signaling pathway from the α5β1 and αvβ3 integrins that elevates bcl-2 transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 27757–27763 (2001).
Bao, W. & Stromblad, S. Integrin αv-mediated inactivation of p53 controls a MEK1-dependent melanoma cell survival pathway in three-dimensional collagen. J. Cell Biol. 167, 745–756 (2004).
Scatena, M. et al. NF-kappaB mediates αvβ3 integrin–induced endothelial cell survival. J. Cell Biol. 141, 1083–1093 (1998).
Charo, I.F., Nannizzi, L., Smith, J.W. & Cheresh, D.A. The vitronectin receptor αvβ3 binds fibronectin and acts in concert with α5β1 in promoting cellular attachment and spreading on fibronectin. J. Cell Biol. 111, 2795–2800 (1990).
Cabodi, S. et al. p130Cas as a new regulator of mammary epithelial cell proliferation, survival, and HER2-neu oncogene-dependent breast tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 66, 4672–4680 (2006).
Bouton, A.H., Riggins, R.B. & Bruce-Staskal, P.J. Functions of the adapter protein Cas: signal convergence and the determination of cellular responses. Oncogene 20, 6448–6458 (2001).
Sakai, R. et al. A novel signaling molecule, p130, forms stable complexes in vivo with v-Crk and v-Src in a tyrosine phosphorylation–dependent manner. EMBO J. 13, 3748–3756 (1994).
Honda, H. et al. Cardiovascular anomaly, impaired actin bundling and resistance to Src-induced transformation in mice lacking p130Cas. Nat. Genet. 19, 361–365 (1998).
Jove, R. & Hanafusa, H. Cell transformation by the viral Src oncogene. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 3, 31–56 (1987).
Huveneers, S. et al. Integrin α5 β3 controls activity and oncogenic potential of primed c-Src. Cancer Res. 67, 2693–2700 (2007).
Huveneers, S., Arslan, S., van de Water, B., Sonnenberg, A. & Danen, E.H. Integrins uncouple Src-induced morphological and oncogenic transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 13243–13251 (2008).
Nip, J., Shibata, H., Loskutoff, D.J., Cheresh, D.A. & Brodt, P. Human melanoma cells derived from lymphatic metastases use integrin α5 β3 to adhere to lymph node vitronectin. J. Clin. Invest. 90, 1406–1413 (1992).
Allan, A.L. et al. Role of the integrin-binding protein osteopontin in lymphatic metastasis of breast cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 169, 233–246 (2006).
Reinmuth, N. et al. αvβ3 integrin antagonist S247 decreases colon cancer metastasis and angiogenesis and improves survival in mice. Cancer Res. 63, 2079–2087 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank D. Stupack, L. Acevedo and S. Anand for critical reading of the manuscript. We also want to express our gratitude to M. Bouvet and A. Lowy for their help in obtaining human pancreatic tumor sections. J.S.D. was supported by a US National Institutes of Health Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award Post-doctoral Fellowship (grant CA123774). This work was supported by funding from the US National Institutes of Health grant numbers CA78045, CA45726, CA95262, CA129660 and HL57900 (to D.A.C.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.S.D. designed the project, performed most of the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. L.A.B. helped design and conduct the orthotopic tumor experiments. D.J.S. designed and conducted the dasatinib treatment study. M.H. initiated and performed the CAS experiments, whereas S.K.L. planned, conducted and analyzed many of the experiments with breast cancer cell lines. N.P. planned and analyzed the experiments involving the Src-β3 interaction. D.T. analyzed and interpreted the immunohistochemistry and histology experiments. S.J.S. helped conceive of the study and analyzed the data. D.A.C. initiated the study, analyzed the data, supervised the overall project and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–19 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 2663 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desgrosellier, J., Barnes, L., Shields, D. et al. An integrin αvβ3–c-Src oncogenic unit promotes anchorage-independence and tumor progression. Nat Med 15, 1163–1169 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2009
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2009
This article is cited by
-
Role of adhesion molecules in cancer and targeted therapy
Science China Life Sciences (2024)
-
Pancreatic cancer cells upregulate LPAR4 in response to isolation stress to promote an ECM-enriched niche and support tumour initiation
Nature Cell Biology (2023)
-
A novel superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles-based SPECT/MRI dual-modality probe for tumor imaging
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry (2023)
-
Tumor regionalization after surgery: Roles of the tumor microenvironment and neutrophil extracellular traps
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2022)
-
Stem-like breast cancer cells in the activated state resist genetic stress via TGFBI-ZEB1
npj Breast Cancer (2022)