Abstract
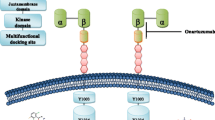
Studies on signal transduction pathways have generated various promising molecular targets for therapeutic inhibition in cancer therapy. Receptor tyrosine kinases represent an important class of such therapeutic targets. c-Met is a receptor tyrosine kinase that has been shown to be overexpressed and/or mutated in a variety of malignancies. A number of c-Met activating mutations, many of which are located in the tyrosine kinase domain, have been detected in various solid tumors and have been implicated in invasion and metastasis of tumor cells. It is known that stimulation of c-Met via its natural ligand, hepatocyte growth factor (also known as scatter factor, HGF/SF) results in a plethora of biological and biochemical effects in the cell. Activation of c-Met signaling can lead to scattering, angiogenesis, proliferation, enhanced cell motility, invasion, and eventual metastasis. In this review, the role of c-Met dysregulation in tumor progression and metastasis is discussed in detail with particular emphasis on c-Met mutations. Moreover, we summarize current knowledge on various pathways of c-Met signal transduction, highlighting the central role in the cytoskeletal functions. In this summary is included recent data in our laboratory indicating that phosphorylation of focal adhesion proteins, such as paxillin, p125FAK, and PYK2, occurs in response to c-Met stimulation in lung cancer cells. Most importantly, current data on c-Met suggest that when mutated or overexpressed in malignant cells, c-Met would serve as an important therapeutic target.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blume-Jensen P, Hunter, T: Oncogenic kinase signaling. Nature 411: 355–365, 2001
Longati P, Comoglio PM, Bardelli A: Receptor tyrosine kinases as therapeutic targets: The model of the MET oncogene. Curr Drug Targets 2: 41–55, 2001
Maulik G, Shrikhande A, Kijima T, Ma PC, Morrison PT, Salgia R: Role of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor, c-Met, in oncogenesis and potential for ther-apeutic inhibition. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13: 41–59, 2002
Arteaga CL, Khuri F, Krystal G, Sebti S: Overview of rationale and clinical trials with signal transduction inhibitors in lungcancer. Semin Oncol 29: 15–26, 2002
Cooper CS, Park M, Blair DG, Tainsky MA, Huebner K, Croce CM, Vande Woude GF: Molecular cloning of a new transformingg ene from a chemically transformed human cell line. Nature 311: 29–33, 1984
Park M, Dean M, Cooper CS, Schmidt M, O'Brien SJ, Blair DG, Vande Woude GF: Mechanism of met oncogene activation. Cell 45: 895–904, 1986
Jeffers M, Rong S, Vande Woude GF: Enhanced tumorigenicity and invasion-metastasis by hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-met signaling in human cells concomitant with induction of the urokinase proteolysis network. Mol Cell Biol 16: 1115–1125, 1996
Schmidt L, Duh FM, Chen F, Kishida T, Glenn G, Choyke P, Scherer SW, ZhuangZ, Lubensky I, Dean M, Allikmets R, Chidambaram A, Bergerheim UR, Feltis JT, Casadevall C, Zamarron A, Bernues M, Richard S, Lips CJ, Walther MM, Tsui LC, Geil L, Orcutt ML, Stackhouse T, Zbar B, Lipan J, Slife L, Brauch H, Decker J, Niehans G, Hughson MD, Moch H, Storkel S, Lerman MI, Linehan WM: Germline and somatic mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of the MET proto-oncogene in papillary renal carcinomas. Nat Genet 16: 68–73, 1997
Di Renzo MF, Narsimhan RP, Olivero M, Bretti S, Giordano S, Medico E, Gaglia P, Zara P, Comoglio PM: Expression of the Met/HGF receptor in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Oncogene 6: 1997–2003, 1991
Comoglio PM, Boccaccio C: The HGF receptor family: Unconventional signal transducers for invasive cell growth. Genes Cells 1: 347–354, 1996
Comoglio PM: Structure, biosynthesis and biochemical properties of the HGF receptor in normal and malignant cells. Exs 65: 131–165, 1993
Duh FM, Scherer SW, Tsui LC, Lerman MI, Zbar B, Schmidt L: Gene structure of the human MET protooncogene. Oncogene 15: 1583–1586, 1997
Liu Y: The human hepatocyte growth factor receptor gene: Complete structural organization and promoter characterization. Gene 215: 159–169, 1998
Seki T, Hagiya M, Shimonishi M, Nakamura T, Shimizu S: Organization of the human hepatocyte growth factor-encoding gene. Gene 102: 213–219, 1991
Mars WM, Zarnegar R, Michalopoulos GK: Activation of hepatocyte growth factor by the plasminogen activators uPA and tPA. Am J Pathol 143: 949–958, 1993
Lu Q, Lemke G: Homeostatic regulation of the immune system by receptor tyrosine kinases of the Tyro 3 family. Science 293: 306–311, 2001
Maestrini E, Tamagnone L, Longati P, Cremona O, Gulisano M, Bione S, Tamanini F, Neel BG, Toniolo D, Comoglio PM: A family of transmembrane proteins with homology to the MET-hepatocyte growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 674–678, 1996
Artigiani S, Comoglio PM, Tamagnone L: Plexins, semaphorins, and scatter factor receptors: A common root for cell guidance signals? IUBMB Life 48: 477–482, 1999
Tessier-Lavigne M, Goodman CS: The molecular biology of axon guidance. Science 274: 1123–1133, 1996
Tamagnone L, Artigiani S, Chen H, He Z, Ming GI, Song H, Chedotal A, WinbergML, Goodman CS, Poo M, Tessier-Lavigne M, Comoglio PM: Plexins are a large family of receptors for transmembrane, secreted, and GPIanchored semaphorins in vertebrates. Cell 99: 71–80, 1999
Tamagnone L, Comoglio PM: signaling by semaphorin receptors: Cell guidance and beyond. Trends Cell Biol 10: 377–383, 2000
Comoglio PM, Tamagnone L, Boccaccio C: Plasminogenrelated growth factor and semaphorin receptors: A gene superfamily controllinginvasive growth. Exp Cell Res 253: 88–99, 1999
Iwazawa T, Shiozaki H, Doki Y, Inoue M, Tamura S, Matsui S, Monden T, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Monden M: Primary human fibroblasts induce diverse tumor invasiveness: Involvement of HGF as an important paracrine factor. Jpn J Cancer Res 87: 1134–1142, 1996
Takai K, Hara J, Matsumoto K, Hosoi G, Osugi Y, Tawa A, Okada S, Nakamura T: Hepatocyte growth factor is constitutively produced by human bone marrow stromal cells and indirectly promotes hematopoiesis. Blood 89: 1560–1565, 1997
Hayashi S, Morishita R, Higaki J, Aoki M, Moriguchi A, Kida I, Yoshiki S, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Kaneda Y, Ogihara T: Autocrine-paracrine effects of overexpression of hepatocyte growth factor gene on growth of endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 220: 539–545, 1996
Yi S, Chen JR, Viallet J, Schwall RH, Nakamura T, Tsao MS: Paracrine effects of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor on non-small-cell lungcarcinoma cell lines. Br J Cancer 77: 2162–2170, 1998
Weimar IS, Miranda N, Muller EJ, Hekman A, Kerst JM, de Gast GC, Gerritsen WR: Hepatocyte growth factor/ scatter factor (HGF/SF) is produced by human bone marrow stromal cells and promotes proliferation, adhesion and survival of human hematopoietic progenitor cells (CD34+). Exp Hematol 26: 885–894, 1998
Nakashiro K, Okamoto M, Hayashi Y, Oyasu R: Hepatocyte growth factor secreted by prostate-derived stromal cells stimulates growth of androgen-independent human prostatic carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol 157: 795–803, 2000
Stella MC, Comoglio PM: HGF: A multifunctional growth factor controlling cell scattering. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 31: 1357–1362, 1999
Horiguchi N, Takayama H, Toyoda M, Otsuka T, Fukusato T, Merlino G, Takagi H, Mori M: Hepatocyte growth factor promotes hepatocarcinogenesis through c-Met autocrine activation and enhanced angiogenesis in transgenic mice treated with diethylnitrosamine. Oncogene 21: 1791–1799, 2002
Furge KA, Zhang YW, Vande Woude GF: Met receptor tyrosine kinase: Enhanced signaling through adapter proteins. Oncogene 19: 5582–5589, 2000
Petrelli A, Gilestro GF, Lanzardo S, Comoglio PM, Migone N, Giordano S: The endophilin-CIN85-Cbl complex mediates ligand-dependent downregulation of c-Met. Nature 416: 187–190, 2002
Natali PG, Prat M, Nicotra MR, Bigotti A, Olivero M, Comoglio PM, Di Renzo MF: Overexpression of the met/ HGF receptor in renal cell carcinomas. Int J Cancer 69: 212–217, 1996
Olivero M, Rizzo M, Madeddu R, Casadio C, Pennacchietti S, Nicotra MR, Prat M, Maggi G, Arena N, Natali PG, Comoglio PM, Di Renzo MF: Overexpression and activation of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor in human non-small-cell lungcarcinomas. Br J Cancer 74: 1862–1868, 1996
Porte H, Triboulet JP, Kotelevets L, Carrat F, Prevot S, Nordlinger B, DiGioia Y, Wurtz A, Comoglio P, Gespach C, Chastre E: Overexpression of stromelysin-3, BM-40/ SPARC, and MET genes in human esophageal carcinoma: Implications for prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 4: 1375–1382, 1998
Maulik G, Kijima T, Ma PC, Ghosh SK, Lin J, Shapiro GI, Schaefer E, Tibaldi E, Johnson BE, Salgia R: Modulation of the c-Met/hepatocyte growth factor pathway in small cell lungcancer. Clin Cancer Res 8: 620–627, 2002
Ramirez R, Hsu D, Patel A, Fenton C, Dinauer C, Tuttle RM, Francis GL: Over-expression of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF) and the HGF/SF receptor (cMET) are associated with a high risk of metastasis and recurrence for children and youngadults with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 53: 635–644, 2000
Hellman A, Zlotorynski E, Scherer SW, Cheung J, Vincent JB, Smith DI, Trakhtenbrot L, Kerem B: A role for common fragile site induction in amplification of human oncogenes. Cancer Cell 1: 89–97, 2002
Ferracini R, Di Renzo MF, Scotlandi K, Baldini N, Olivero M, Lollini P, Cremona O, Campanacci M, Comoglio PM: The Met/HGF receptor is over-expressed in human osteosarcomas and is activated by either a paracrine or an autocrine circuit. Oncogene 10: 739–749, 1995
Di Renzo MF, Olivero M, Giacomini A, Porte H, Chastre E, Mirossay L, Nordlinger B, Bretti S, Bottardi S, Giordano S, Plebani M, Gespach C, Comoglio PM: Overexpression and amplification of the met/HGF receptor gene during the progression of colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 1: 147–154, 1995
Di Renzo MF, Olivero M, Katsaros D, Crepaldi T, Gaglia P, Zola P, Sismondi P, Comoglio PM: Overexpression of the Met/HGF receptor in ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer 58: 658–662, 1994
Jeffers M, Fiscella M, Webb CP, Anver M, Koochekpour S, Vande Woude GF: The mutationally activated Met receptor mediates motility and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 14417–14422, 1998
Schmidt L, Junker K, Weirich G, Glenn G, Choyke P, Lubensky I, ZhuangZ, Jeffers M, Vande Woude G, Neumann H, Walther M, Linehan WM, Zbar B: Two North American families with hereditary papillary renal carcinoma and identical novel mutations in the MET proto-oncogene. Cancer Res 58: 1719–1722, 1998
Schmidt L, Junker K, Nakaigawa N, Kinjerski T, Weirich G, Miller M, Lubensky I, Neumann HP, Brauch H, Decker J, Vocke C, Brown JA, Jenkins R, Richard S, Bergerheim U, Gerrard B, Dean M, Linehan WM, Zbar B: Novel mutations of the MET proto-oncogene in papillary renal carcinomas. Oncogene 18: 2343–2350, 1999
Miller M, Ginalski K, LesyngB, Nakaigawa N, Schmidt L, Zbar B: Structural basis of oncogenic activation caused by point mutations in the kinase domain of the MET proto-oncogene: Modeling studies. Proteins 44: 32–43, 2001
Wybenga-Groot LE, Baskin B, Ong SH, Tong J, Pawson T, Sicheri F: Structural basis for autoinhibition of the Ephb2 receptor tyrosine kinase by the unphosphorylated juxtamembrane region. Cell 106: 745–757, 2001
Baxter RM, Secrist JP, Vaillancourt RR, Kazlauskas A: Full activation of the platelet-derived growth factor betareceptor kinase involves multiple events. J Biol Chem 273: 17050–17055, 1998
Irusta PM, DiMaio D: A single amino acid substitution in a WW-like domain of diverse members of the PDGF receptor subfamily of tyrosine kinases causes constitutive receptor activation. Embo J 17: 6912–6923, 1998
Nakao M, Yokota S, Iwai T, Kaneko H, Horiike S, Kashima K, Sonoda Y, Fujimoto T, Misawa S: Internal tandem duplication of the flt3 gene found in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 10: 1911–1918, 1996
Yokota S, Kiyoi H, Nakao M, Iwai T, Misawa S, Okuda T, Sonoda Y, Abe T, Kahsima K, Matsuo Y, Naoe T: Internal tandem duplication of the FLT3 gene is preferentially seen in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome among various hematological malignancies. A study on a large series of patients and cell lines. Leukemia 11: 1605–1609, 1997
Hayakawa F, Towatari M, Kiyoi H, Tanimoto M, Kitamura T, Saito H, Naoe T: Tandem-duplicated Flt3 constitutively activates STAT5 and MAP kinase and introduces autonomous cell growth in IL-3-dependent cell lines. Oncogene 19: 624–631, 2000
Zhao M, Kiyoi H, Yamamoto Y, Ito M, Towatari M, Omura S, Kitamura T, Ueda R, Saito H, Naoe T: In vivo treatment of mutant FLT3-transformed murine leukemia with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Leukemia 14: 374–378, 2000
Kelly LM, Yu JC, Boulton CL, Apatira M, Li J, Sullivan CM, Williams I, Amaral SM, Curley DP, Duclos N, NeubergD, Scarborough RM, Pandey A, Hollenbach S, Abe K, Lokker NA, Gilliland DG, Giese NA: CT53518, a novel selective FLT3 antagonist for the treatment of acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). Cancer Cell 1: 421–432, 2002
Weisberg E, Boulton C, Kelly LM, Manley P, Fabbro D, Meyer T, Gilliland DG, Griffin JD: Inhibition of mutant FLT3 receptors in leukemia cells by the small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor PKC412. Cancer Cell 1: 433–443, 2002
Lee JH, Han SU, Cho H, Jennings B, Gerrard B, Dean M, Schmidt L, Zbar B, Vande Woude GF: A novel germ line juxtamembrane Met mutation in human gastric cancer. Oncogene 19: 4947–4953, 2000
Soman NR, Wogan GN, Rhim JS: TPR-MET oncogenic rearrangement: Detection by polymerase chain reaction amplification of the transcript and expression in human tumor cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 738–742, 1990
Soman NR, Correa P, Ruiz BA, Wogan GN: The TPRMET oncogenic rearrangement is present and expressed in human gastric carcinoma and precursor lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 4892–4896, 1991
Vigna E, Gramaglia D, Longati P, Bardelli A, Comoglio PM: Loss of the exon encodingthe juxtamembrane domain is essential for the oncogenic activation of TPRMET. Oncogene 18: 4275–4281, 1999
Peschard P, Fournier TM, Lamorte L, Naujokas MA, Band H, Langdon WY, Park M: Mutation of the c-Cbl TKB domain bindingsite on the Met receptor tyrosine kinase converts it into a transformingprotein. Mol Cell 8: 995–1004, 2001
Lee CC, Yamada KM: Identification of a novel type of alternative splicingof a tyrosine kinase receptor. Juxtamembrane deletion of the c-met protein kinase C serine phosphorylation regulatory site. J Biol Chem 269: 19457–19461, 1994
Lee CC, Yamada KM: Alternatively spliced juxtamembrane domain of a tyrosine kinase receptor is a multifunctional regulatory site. Deletion alters cellular tyrosine phosphorylation pattern and facilitates binding of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase to the hepatocyte growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem 270: 507–510, 1995
Modrek B, Lee C: A genomic view of alternative splicing. Nat Genet 30: 13–19, 2002
Brett D, Pospisil H, Valcarcel J, Reich J, Bork P: Alternative splicingand genome complexity. Nat Genet 30: 29–30, 2002
Comoglio PM: Pathway specificity for Met signaling. Nat Cell Biol 3: E161-E162, 2001
Comoglio PM, Trusolino L: Invasive growth: From development to metastasis. J Clin Invest 109: 857–862, 2002
Muller M, Morotti A, Ponzetto C: Activation of NFkappaB is essential for hepatocyte growth factor-mediated proliferation and tubulogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 22: 1060–1072, 2002
Wang X, DeFrances MC, Dai Y, Pediaditakis P, Johnson C, Bell A, Michalopoulos GK, Zarnegar R: A mechanism of cell survival: Sequestration of Fas by the HGF receptor Met. Mol Cell 9: 411–421, 2002
Birchmeier C, Gherardi E: Developmental roles of HGF/ SF and its receptor, the c-Met tyrosine kinase. Trends Cell Biol 8: 404–410, 1998
Maina F, Casagranda F, Audero E, Simeone A, Comoglio PM, Klein R, Ponzetto C: Uncouplingof Grb2 from the Met receptor in vivo reveals complex roles in muscle development. Cell 87: 531–542, 1996
Maina F, Klein R: Hepatocyte growth factor, a versatile signal for developing neurons. Nat Neurosci 2: 213–217, 1999
Weisberg E, Sattler M, Ewaniuk DS, Salgia R: Role of focal adhesion proteins in signal transduction and oncogenesis. Crit Rev Oncog 8: 343–358, 1997
Sattler M, Salgia R: Role of the adapter protein CRKL in signal transduction of normal hematopoietic and BCR/ABL-transformed cells. Leukemia 12: 637–644, 1998
Sattler M, Pisick E, Morrison PT, Salgia R: Role of the cytoskeletal protein paxillin in oncogenesis. Crit Rev Oncog11: 63–76, 2000
Salgia R, Li JL, Lo SH, Brunkhorst B, Kansas GS, Sobhany ES, Sun Y, Pisick E, Hallek M, Ernst T et al. Molecular cloningof human paxillin, a focal adhesion protein phosphorylated by P210BCR/ABL. J Biol Chem 270: 5039–5047, 1995
Parr C, Davies G, Nakamura T, Matsumoto K, Mason MD, Jiang WG: The HGF/SF-induced phosphorylation of paxillin, matrix adhesion, and invasion of prostate cancer cells were suppressed by NK4, an HGF/SF variant. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 285: 1330–1337, 2001
Turner CE: Paxillin interactions. J Cell Sci 113Pt 23: 4139–4140, 2000
Turner CE: Paxillin and focal adhesion signaling. Nat Cell Biol 2: E231–236, 2000
Fernandez-Valle C, Tang Y, Ricard J, Rodenas-Ruano A, Taylor A, Hackler E, Biggerstaff J, Iacovelli J: Paxillin binds schwannomin and regulates its density-dependent localization and effect on cell morphology. Nat Genet 31: 354–362, 2002
Schaller MD, Sasaki T: Differential signaling by the focal adhesion kinase and cell adhesion kinase beta. J Biol Chem 272: 25319–25325, 1997
Nobes CD, Hall A: Rho, rac and cdc42 GTPases: Regulators of actin structures, cell adhesion and motility. Biochem Soc Trans 23: 456–459, 1995
Nobes CD, Hall A: Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell 81: 53–62, 1995
Derman MP, Cunha MJ, Barros EJ, Nigam SK, Cantley LG: HGF-mediated chemotaxis and tubulogenesis require activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Am J Physiol 268: F1211–1217, 1995
Derman MP, Chen JY, Spokes KC, Songyang Z, Cantley LG: An 11-amino acid sequence from c-met initiates epithelial chemotaxis via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and phospholipase C. J Biol Chem 271: 4251–4255, 1996
Besser D, Bardelli A, Didichenko S, Thelen M, Comoglio PM, Ponzetto C, Nagamine Y: Regulation of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene by the oncogene Tpr-Met involves GRB2. Oncogene 14: 705–711, 1997
Dunsmore SE, Rubin JS, Kovacs SO, Chedid M, Parks WC, Welgus HG: Mechanisms of hepatocyte growth c-Met: Structure, functions and potential 323 factor stimulation of keratinocyte metalloproteinase production. J Biol Chem 271: 24576–24582, 1996
Wojta J, Nakamura T, Fabry A, Hufnagl P, Beckmann R, McGrath K, Binder BR: Hepatocyte growth factor stimulates expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 and tissue factor in HepG2 cells. Blood 84: 151–157, 1994
Gilmore AP, Burridge K: Regulation of vinculin binding to talin and actin by phosphatidyl-inositol–4–5-bisphosphate. Nature 381: 531–535, 1996
Bladt F, Riethmacher D, Isenmann S, Aguzzi A, Birchmeier C: Essential role for the c-met receptor in the migration of myogenic precursor cells into the limb bud. Nature 376: 768–771, 1995
Di Renzo MF, Olivero M, Martone T, Maffe A, Maggiora P, Stefani AD, Valente G, Giordano S, Cortesina G, Comoglio PM: Somatic mutations of the MET oncogene are selected during metastatic spread of human HNSC carcinomas. Oncogene 19: 1547–1555, 2000
Dong G, Loukinova E, Chen Z, Gangi L, Chanturita TI, Liu ET, Van Waes C: Molecular profilingof transformed and metastatic murine squamous carcinoma cells by differential display and cDNA microarray reveals altered expression of multiple genes related to growth, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and the NF-kappaB signal pathway. Cancer Res 61: 4797–4808, 2001
Jeffers M, Rong S, Woude GF: Hepatocyte growth factor/ scatter factor-Met signaling in tumorigenicity and invasion/ metastasis. J Mol Med 74: 505–513, 1996
Comoglio PM, Boccaccio C: Scatter factors and invasive growth. Semin Cancer Biol 11: 153–165, 2001
Tuck AB, Park M, Sterns EE, Boag A, Elliott BE: Coexpression of hepatocyte growth factor and receptor (Met) in human breast carcinoma. Am J Pathol 148: 225–232, 1996
Koochekpour S, Jeffers M, Rulong S, Taylor G, Klineberg E, Hudson EA, Resau JH, Vande Woude GF: Met and hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor expression in human gliomas. Cancer Res 57: 5391–5398, 1997
Li G, Schaider H, Satyamoorthy K, Hanakawa Y, Hashimoto K, Herlyn M: Downregulation of E-cadherin and Desmoglein 1 by autocrine hepatocyte growth factor duringmelanoma development. Oncogene 20: 8125–8135, 2001
Giordano S, Bardelli A, Zhen Z, Menard S, Ponzetto C, Comoglio PM: A point mutation in the MET oncogene abrogates metastasis without affecting transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 13868–13872, 1997
Bardelli A, Basile ML, Audero E, Giordano S, Wennstrom S, Menard S, Comoglio PM, Ponzetto C: Concomitant activation of pathways downstream of Grb2 and PI 3-kinase is required for MET-mediated metastasis. Oncogene 18: 1139–1146, 1999
Saucier C, Papavasiliou V, Palazzo A, Naujokas MA, Kremer R, Park M: Use of signal specific receptor tyrosine kinase oncoproteins reveals that pathways downstream from Grb2 or Shc are sufficient for cell transformation and metastasis. Oncogene 21: 1800–1811, 2002
Medico E, Gentile A, Lo Celso C, Williams TA, Gambarotta G, Trusolino L, Comoglio PM: Osteopontin is an autocrine mediator of hepatocyte growth factorinduced invasive growth. Cancer Res 61: 5861–5868, 2001
Yu Y, Merlino G: Constitutive c-Met signaling through a nonautocrine mechanism promotes metastasis in a transgenic transplantation model. Cancer Res 62: 2951–2956, 2002
Wang R, Ferrell LD, Faouzi S, Maher JJ, Bishop JM: Activation of the Met receptor by cell attachment induces and sustains hepatocellular carcinomas in transgenic mice. J Cell Biol 153: 1023–1034, 2001
Christensen CR, Klingelhofer J, Tarabykina S, Hulgaard EF, Kramerov D, Lukanidin E: Transcription of a novel mouse semaphorin gene, M-semaH, correlates with the metastatic ability of mouse tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 58: 1238–1244, 1998
Kagoshima M, Ito T: Diverse gene expression and function of semaphorins in developinglung: Positive and negative regulatory roles of semaphorins in lung branchingmorphog enesis. Genes Cells 6: 559–571, 2001
Roche J, Boldog F, Robinson M, Robinson L, Varella-Garcia M, Swanton M, Waggoner B, Fishel R, Franklin W, Gemmill R, Drabkin H: Distinct 3p21.3 deletions in lungcancer and identification of a new human semaphorin. Oncogene 12: 1289–1297, 1996
Goshima Y, Ito T, Sasaki Y, Nakamura F: Semaphorins as signals for cell repulsion and invasion. J Clin Invest 109: 993–998, 2002
Giordano S, Corso S, Conrotto P, Artigiani S, Gilestro G, Barberis D, Tamagnone L, Comoglio PM: The semaphorin 4D receptor controls invasive growth by coupling with Met. Nat Cell Biol 4: 720–724, 2002
Otsuka T, Jakubczak J, Vieira W, Bottaro DP, Breckenridge D, Larochelle WJ, Merlino G: Disassociation of met-mediated biological responses in vivo: the natural hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor splice variant NK2 antagonizes growth but facilitates metastasis. Mol Cell Biol 20: 2055–2065, 2000
Date K, Matsumoto K, Shimura H, Tanaka M, Nakamura T: HGF/NK4 is a specific antagonist for pleiotrophic actions of hepatocyte growth factor. FEBS Lett 420: 1–6, 1997
Parr C, Hiscox S, Nakamura T, Matsumoto K, JiangWG: Nk4, a new HGF/SF variant, is an antagonist to the influence of HGF/SF on the motility and invasion of colon cancer cells. Int J Cancer 85: 563–570, 2000
Tomioka D, Maehara N, Kuba K, Mizumoto K, Tanaka M, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T: Inhibition of growth, invasion, and metastasis of human pancreatic carcinoma cells by NK4 in an orthotopic mouse model. Cancer Res 61: 7518–7524, 2001
Mark MR, Lokker NA, Zioncheck TF, Luis EA, Godowski PJ: Expression and characterization of hepatocyte growth factor receptor-IgG fusion proteins. Effects of mutations in the potential proteolytic cleavage site on processing and ligand binding. J Biol Chem 267: 26166–26171, 1992
Michieli P, Basilico C, Pennacchietti S, Maffe A, Tamagnone L, Giordano S, Bardelli A, Comoglio PM: Mutant Met-mediated transformation is ligand-dependent and can be inhibited by HGF antagonists. Oncogene 18: 5221–5231, 1999
Bardelli A, Longati P, Williams TA, Benvenuti S, Comoglio PM: A peptide representing the carboxylterminal tail of the met receptor inhibits kinase activity and invasive growth. J Biol Chem 274: 29274–29281, 1999
Webb CP, Hose CD, Koochekpour S, Jeffers M, Oskarsson M, Sausville E, Monks A, Vande Woude GF: The geldanamycins are potent inhibitors of the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-met-urokinase plasminogen activator-plasmin proteolytic network. Cancer Res 60: 342–349, 2000
Neckers L, Schulte TW, Mimnaugh E: Geldanamycin as a potential anti-cancer agent: Its molecular target and biochemical activity. Invest New Drugs 17: 361–373, 1999
Ottmann OG, Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, Goldman JM, Reiffers J, Silver RT, Tura S, Fischer T, Deininger MW, Schiffer CA, Baccarani M, Gratwohl A, Hochhaus A, Hoelzer D, Fernandes-Reese S, Gathmann I, Capdeville R, O'Brien SG: A phase 2 study of imatinib in patients with relapsed or refractory Philadelphia chromosomepositive acute lymphoid leukemias. Blood 100: 1965–1971, 2002
Mauro MJ, O'Dwyer M, Heinrich MC, Druker BJ: STI571: A paradigm of new agents for cancer therapeutics. J Clin Oncol 20: 325–334, 2002
Apperley JF, Gardembas M, Melo JV, Russell-Jones R, Bain BJ, Baxter EJ, Chase A, Chessells JM, Colombat M, Dearden CE, Dimitrijevic S, Mahon FX, Marin D, Nikolova Z, Olavarria E, Silberman S, Schultheis B, Cross NC, Goldman JM: Response to imatinib mesylate in patients with chronic myeloproliferative diseases with rearrangements of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta. N Engl J Med 347: 481–487, 2002
Heinrich MC, Blanke CD, Druker BJ, Corless CL: Inhibition of KIT tyrosine kinase activity: A novel molecular approach to the treatment of KIT-positive malignancies. J Clin Oncol 20: 1692–1703, 2002
Salgia R, Sattler M: Molecular and cellular biology of small cell lungcancer. Seminars in Oncology 30: 57–71, 2003.
Morotti A, Mila S, Accornero P, Tagliabue E, Ponzetto C: K252a inhibits the oncogenic properties of Met, the HGF receptor. Oncogene 21: 4885–4893, 2002
Liang HAJ, Laterra J, Maher VM, McCormick JJ: Inhibtion of human fibrosarcoma tumorigenecity by U1 small nuclear RNA/ribozyme targeting of c-Met expression. Abstract #73. Proceedings of AACR 2002, 42, 2001
Herynk MH TR, Abounader R, Laterra JJ, Gallick G, Radinsky R: Inhibtion of colorectal carcinoma metastases through ribozyme mediated downregulation of c-Met. Abstract #4235. Proceedings of the AACR 2001, 42, 2001
Herynk M, Abounader R, Laterra J, Radinsky R, Gallick GE: Inhibition of c-met signaling through ribozymemediated downregulation decreases tumorigenic growth and metastasis of colon tumor cell lines through a Srcmediated pathway. Abstract #5268. Proceedings of the AACR 2002, 2002
Kim JL ZH, Gu Y, Rose PE, Nunes JJ, Stover DR, Long AM: A high resolution crystal structure of the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase domain: An aid for the rational design of kinase inhibitors. Abstract #4575. Proceedings of the AACR 2001, 42, 2001
Chan PC, Liang CC, Yu KC, Chang MC, Ho WL, Chen BH, Chen HC: Synergistic effect of focal adhesion kinase overexpression and hepatocyte growth factor stimulation on cell transformation. J Biol Chem 277: 50373–50379, 2002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, P.C., Maulik, G., Christensen, J. et al. c-Met: Structure, functions and potential for therapeutic inhibition. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22, 309–325 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023768811842
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023768811842