Abstract
Purpose. N-terminal site-specific mono-PEGylation of recombinant human epidermal growth factor (EGF) was accomplished using polyethyleneglycol (PEG) derivatives (Mw = 2000 and 5000) through a reactive terminal aldehyde group.
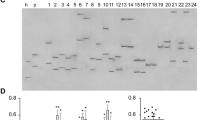
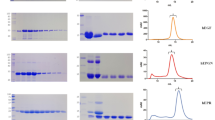
Methods. The site-specific PEG conjugation was conducted at a slightly acidic pH condition (pH 5.5). The mono-PEGylation was targeted to an α-amine group at the N-terminal end of EGF to minimize reduction of biologic activity. Tryptic digestion mapping and MALDI-TOF MS techniques were applied to show the occurrence of mono-PEGylation at the N-terminus of EGF.
Results. The site-specific mono-PEGylated EGF, when compared with native EGF, fully retained its in vitro biologic activities such as cell proliferation and intracellular signal transduction. This revealed that although a synthetic polymer of a PEG was covalently conjugated to EGF, the internalized complex of PEGylated EGF-receptor within cells did not hamper the intracellular signal transduction events. The PEGylated EGF also exhibited a prolonged circulation in blood stream in vivo and markedly enhanced physical stability when incubated with tissue homogenate.
Conclusion. N-terminally mono-PEGylated EGF shows increased physical stability while retaining its biologic activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J. M. Harris and S. Zilpsky. Poly(ethylene glycol): Chemistry and Biological Applications. ACS Symposium Series 680, American Chemical Society, Washington DC (1997).
K. Kartre. The conjugation of proteins with poly(ethylene glycol) and other polymers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 10:91-114 (1993).
A. Abuchowski, J. R. McCoy, N. C. Palczuk, T. van Es, and F. F. David. Effect of covalent attachment of polyethylene glycol on immunogenicity and circulating life of bovine liver catalase. J. Biol. Chem. 252:3582-3586 (1977).
R. Clark, K. Olson, G. Fuh, M. Marian, D. Mortensen, G. Teshima, S. Chang, H. Chu, V. Mukku, and E. C. Davis. T. Somers, M. Cronin, M. Winkler, J. A. Wells. Long-acting growth hormone produced by conjugation with polyethylene glycol. J. Biol. Chem. 271:21969-21977 (1996).
I. B. Lee and H. Dong. Na, C. J. Park, B. H. Lee, S. S. Lee, S. D. Lee, and K. C. Lee. Increased stability of PEGylated recombinant human epidermal growth factor. AAPS Annual Meeting Abstract # M2232, Denver, Colorado. (2001).
P. Bailon, and W. Berthold. Polyethylene glycol-conjugated pharmaceutical proteins. Pharm. Sci. Tech. Today 1:352-356 (1998).
S. Zalipsky. Chemistry of polyethylene glycol conjugates with bioactive molecules. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 16:157-182 (1995).
Y. Tsutsumi, M. Onda, S. Nagata, B. Lee, R. J. Kreitman, and I. Pastan. Site-specific chemical modification with polyethylene glycol of recombinant immunotoxin anti-Tac(Fv)-PE38 (LMB-2) improves antitumor activity and reduces animal toxicity and immunogenicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:8548-8553 (2000).
O. B. Kinstler, D. N. Brems, S. L. Lauren, A. G. Paige, J. B. Hamburger, and M. J. Treuheit. Characterization and stability of N-terminally PEGylated rhG-CSF. Pharm. Res. 13:996-1002 (1996).
S. S. Wong. Chemistry of protein conjugation and cross-linking. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida (1991).
G. Carpenter, L. King, and S. Cohen. Epidermal growth factor stimulates phosphorylation in membrane preparations in vitro. Nature 276:409-410 (1978).
G. N. Gill and C. S. Lazar. Increased phosphotyrosine content and inhibition of proliferation in EGF-treated A431 cells. Nature 293:305-307 (1981).
D. W. Barnes. Epidermal growth factor inhibits growth of A431 human epidermoid carcinoma in serum-free cell culture. J. Cell Biol. 93:1-4 (1982).
K. Han and K.-D. Lee, Z-G, Gao, and J-S. Park. Preparation and evaluation of poly(L-lactic acid) microspheres containing rhEGF for chronic gastric ulcer healing. J. Control. Release 75:259-269 (2001).
J. N. Mansbridge, K. Liu, R. E. Pinney, R. Patch, A. Ratcliffe, and G. K. Naughton. Growth factors secreted by fibroblasts: role in healing diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 1:265-269 (1999).
R. Kircheis, T. Blessing, S. Brunner, L. Wightman, and E. Wagner. Tumor targeting with surface-shielded ligand-polycation DNA complexes. J. Control. Release 72:165-170 (2001).
H. Lee, T. H. Kim, and T. G. Park. Receptor-mediated gene delivery system using streptavidin and biotin-derivatized and pegylated epidermal growth factor. J. Control. Release 83:109-119 (2002).
T. H. Kim, H. Lee, and T. G. Park. PEGylated recombinant human epidermal growth factor (rhEGF) for sustained release from biodegradable PLGA microspheres. Biomaterials 23:2311-2317 (2002).
H. Lee and T. G. Park. Preparation and characterization of mono-PEGylated epidermal growth factor: evaluation of in vitro biological activity. Pharm. Res. 19:845-851 (2002).
S. S. Bae, Y. H. Lee, J.-S. Chang, S. H. Galadari, Y. S. Kim, S. H. Ryu, and P.-G. Suh. Src homology domains of phospholipase C gamma1 inhibit nerve growth factor-induced differentiation of PC12 cells. J. Neurochem. 71:178-185 (1998).
U. K. Laemmli. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680-685 (1970).
Y. B. Lim, S. O. Han, H. U. Kong, Y. Lee, J. S. Park, B. Jeong, and S. W. Kim. Biodegradable polyester, poly[α-(4-aminobutyl)-l-glycolic acid], as a non-toxic gene carrier. Pharm. Res. 17:811-816 (2000).
S. Saito, M. Yoshida, M. Ichijo, S. Ishizaka, and T. Tsujii. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) in human milk. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 94:220-224 (1993).
J. Schlessinger. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinase. Cell 103:211-225 (2000).
B. A. Keel and J. S. Davis. Epidermal growth factor activates extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) in freshly isolated porcine granulose cells. Steroids 64:654-658 (1999).
C. Monfardini and F. M. Veronese. Stabilization of substances in circulation. Bioconjug. Chem. 9:418-450 (1998).
E. Boccu, G. P. Velo, and F. M. Veronese. Pharmcokinetic properties of polyethylene glycol derivatized superoxide dismutase. Pharmacol. Res. Commun. 14:113-120 (1982).
D. A. Engler, G. T. Montelione, and S. K. Niyogi. Human epidermal growth factor: distinct roles of tyrosine 37 and arginine 41 in receptor binding as determined by site-directed mutagenesis and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 271:47-50 (1990).
U. Hommel, T. J. Dudgeon, A. Fallon, R. M. Edwards, and I. D. Campbell. Structure-function relationships in human epidermal growth factor studied by site-directed mutagenesis and 1H NMR. Biochemistry 30:8891-8898 (1991).
P. C. Baass, G. M. DiGuglielmo, F. Authier, B. I. Posner, and J. J. M. Bergeron. Compartmentalized signal transduction by receptor tyrosine kinases. Trends Cell Biol. 5:465-470 (1995).
A. V. Vieira, C. Lamaze, and S. L. Schmid. Control of EGF receptor signaling by clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Science 274:2086-2089 (1996).
G. M. Di Guglielmo, P. C. Baass, W. J. Ou, B. I. Posner, and J. J. Bergeron. Compartmentalization of SHC, GRB2, and mSOS, and hyperphosphorylation of Raf-1 by EGF but not insulin in liver parenchyma. EMBO J. 13:4269-4277 (1994).
L. E. Johannessen, T. Ringerike, J. Molnes, and I. H. Madshus. Epidermal growth factor receptor efficiently activates mitogen-activated protein kinase in HeLa cells and HepG2 cells conditionally defective in clathrin-dependent endocytosis. Exp. Cell Res. 260:136-145 (2000).
K. L. Pierce, S. Maudsley, Y. Daaka, L. M. Luttrell, and R. J. Lefkowitz. Role of endocytosis in the activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade by sequestering and nonsequestering G protein-coupled receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:1489-1494 (2000).
M. R. Sherman, L. D. William, M. G. P. Saifer, J. A. French, L. W. Kwak, and J. J. Oppenheim. Conjugation of high-molecular weight poly(ethylene glycol) to cytokines: granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factors as model substrates. Poly(ethylene) glycol. Chemistry and biological application. ACS Symposium Series 680:155-169 (1997).
T. Maack, V. Johnson, S. T. Kau, J. Figueiredo, and D. Sigulem. Renal filtration, transport, and metabolism of low-molecular-weight proteins: a review. Kidney Int. 16:251-270 (1979).
A. Abuchowski and F. F. Davis. Preparation and properties of polyethylene glycol-trypsin adducts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 578:41-46 (1979).
K. C. Lee, S. C. Moon, M. O. Park, J. T. Lee, D. H. Na, S. D. Yoo, H. S. Lee, and P. P. DeLuca. Isolation, characterization, and stability of positional isomers of mono-PEGylated salmon calcitonins. Pharm. Res. 16:813-818 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, H., Jang, I.H., Ryu, S.H. et al. N-Terminal Site-Specific Mono-PEGylation of Epidermal Growth Factor. Pharm Res 20, 818–825 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023402123119
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023402123119