Abstract
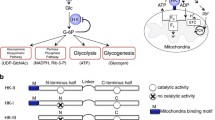
Current thought is that proliferating cells undergo a shift from oxidative to glycolytic metabolism, where the energy requirements of the rapidly dividing cell are provided by ATP from glycolysis. Drawing on the hexokinase–mitochondrial acceptor theory of insulin action, this article presents evidence suggesting that the increased binding of hexokinase to porin on mitochondria of cancer cells not only accelerates glycolysis by providing hexokinase with better access to ATP, but also stimulates the TCA cycle by providing the mitochondrion with ADP that acts as an acceptor for phosphoryl groups. Furthermore, this acceleration of the TCA cycle stimulates protein synthesis via two mechanisms: first, by increasing ATP production, and second, by provision of certain amino acids required for protein synthesis, since the amino acids glutamate, alanine, and aspartate are either reduction products or partially oxidized products of the intermediates of glycolysis and the TCA cycle. The utilization of oxygen in the course of the TCA cycle turnover is relatively diminished even though TCA cycle intermediates are being consumed. With partial oxidation of TCA cycle intermediates into amino acids, there is necessarily a reduction in formation of CO2 from pyruvate, seen as a relative diminution in utilization of oxygen in relation to carbon utilization. This has been assumed to be an inhibition of oxygen uptake and therefore a diminution of TCA cycle activity. Therefore a switch from oxidative metabolism to glycolytic metabolism has been assumed (the Crabtree effect). By stimulating both ATP production and protein synthesis for the rapidly dividing cell, the binding of hexokinase to mitochondrial porin lies at the core of proliferative energy metabolism. This article further reviews literature on the binding of the isozymes of hexokinase to porin, and on the evolution of insulin, proposing that intracellular insulin-like proteins directly bind hexokinase to mitochondrial porin.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bessman, S.P. (1954). In Fat Metabolism (Najjar, V. A., ed.), The Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, p. 133.
Bessman, S. P. (1960). J. Pediatr. 56, 191.
Bessman, S. P. (1966). Am. J. Med. 40, 740.
Golshani, S. (1992). Biochem. Med. Metab. Biol. 47, 108–115.
Mohan, C., Geiger, P. J., and Bessman, S. P. (1989). Curr. Top. Cell. Regul. 30, 105–142.
Bessman, S. P. Mohan, C., and Zaidise, I. (1986). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 5067–5070.
Blachly-Dyson, E., Baldini, A. Litt, M., McCabe, E., and Forte, M. (1994). Genomics 20, 62–67.
Miller, D. S. and Sykes, D. B. (1991). J. Cell. Physiol. 147, 487–494.
Kottke, M., Adams, V. Bosch, W., Bremm, G., Brdiczka, D., Sandri, G., and Panfili, E. (1988). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 935, 87–102.
Adams, V., Bosch, W., Schlegel, J., Wallimann, T., and Brdiczka, D. (1989). Biochim Biophys Acta 981, 213–225.
Katzen, H. M. (1967). In: Advances in Enzyme Regulation (Wever, G., ed.), Pergamon Press, New York, Vol. 5, pp. 335–355.
Katzen, H. M. Soderman, D. D., and Weily, C. E. (1970). J. Biol. Chem. 245, 4081–4096.
Walters, E., and McLean, P. (1968). Biochem. J. 109, 737–741.
Borrebaek, B. (1970). Biochem. Med. 3, 485–497.
DeSchepper, P. J., Toyoda, M., and Bessman, S. P. (1965). J. Biol. Chem. 240, 1670–1674.
Gots, R. E., Gorin, F. A. and Bessman, S. P. (1972). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 49, 1249.
Rapaport, E., Plesner, P., Ullrey, D. B., and Kalckar, H. M. (1983). Carlsberg Res. Commun. 48, 317–320.
Wool, I. G., Stirewalt, W. S., Kurihara, K., Low, R. B., Bailey, P., and Oyer, D. (1968). Recent Prog. Horm Res 24, 139–213.
Rosenwald, I. B. (1996). BioEssays 18, 243–250.
Epifanova, O. I. Setkow, N. A. Polunovsky, V. A., and Terskikh, V. V. (1982). In Cell Function and Differentiation, Part A (Akoyunoglou, G. et al., ed.), Alan Liss, New York, pp. 231–242.
Hershko, A., Mamont P., Shields, R., and Tomkins, G. M. (1971). Nature New. Biol. 232, 206–211.
Rinker-Schaeffer, C. W., Austin, V., Zimmer, S., and Rhoads, R. E. (1992). J. Biol. Chem. 267, 10659–10664.
Greiner, E. F., Guppy, M., and Brand, K. (1994). J. Biol. Chem. 269, 31484–31490.
Mohan, C., and Bessman, S. P. (1986). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 248, 190–199.
Warburg, O. (1956). Science 123, 309–314.
Crabtree, H. C. (1929). Biochem. J. 23, 536–545
Arora, K. K., and Pederson, P. L. (1988). J. Biol. Chem. 263, 17422–17428.
Eigenbrodt, E., and Glossmann, H. (1980). Trends Pharmacol. Sci. May 1980, 240–245.
Cohen, P., Parker, P. J., and Woodgett, J. R. (1985). In Molecular Basis of Insulin Action (Czech, M., ed.), Plenum, New York, pp 213–233.
Pederson, P. L. (1978). Prog. Exp. Tumor Res 22, 190–274.
Chen, L. B., Weiss, M. J., Davis, S., Bleday, R. S., Wong, J. R., Song, J., Terasaki, M., Shepherd, E. L., Walker, E. S., and Steele, G. D. In Cancer Cells, Vol. 3, Growth Factors and Transformation (Feramisco, J., Ozanne, B., and Stiles, C., eds.), Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1985, pp. 333–343.
Antaniades, H. N., Pantazis, P., Graves, D. T., Owen, A. J., and Tempst, P. In Cancer Cells, Vol. 3, Growth Factors and Transformation (Feramisco, J., Ozanne, B., and Stiles, C., eds.), Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1985, pp. 145–151.
Rempel, A., Bannasch, P., and Mayer, D. (1994). Biochem. J. 303, 269–274.
Printz, R. L., Koch, S., Potter, L. R., O'Doherty, R. M., Tiesinga, J. J., Moritz, S., and Granner, D. K. (1993). J. Biol. Chem. 268, 5209–5219.
Salotra, P. T., and Singh, V. M. (1982). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 216, 758–764.
Preller, A., and Wilson, J. (1992). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 294, 482–492.
Goncharova, N. Y., and Zelenina, E. V. (1991). Biokhimiya 56, 913–922.
Russell, R. R., Mrus, J. M., Mormmessin, J. I., and Taegtmeyer, H. (1992). J. Clin. Invest. 90, 1972–1977.
Wilson, J. E. (1980). Curr. Top. Cell. Regul. 16, 1–54.
Arora, K. K., Filburn, C. R., and Pederson, P. (1993). J. Biol. Chem. 268, 18259–18266.
Koranyi, L. I., Tanizawa, Y., Welling, C. M., Rabin, D.U., and Permutt, M. A. (1992). Diabetes 41, 807–811.
Seino, S., Blackstone, C. D., Chan, S.J., Whittaker, J., Bell, G. I., and Steiner, D. F. (1988). Horm. Metab. Res. 20, 430–435.
Steiner, D. F., and Chan, S. J. (1988). Horm. Metab. Res. 20, 443–444.
Le Roith, D., Adamo, M., Shemer, J., Waldbillig, R., Lesniak, M. A., DePablo, F., Hart, C., and Roth, J. (1988). Horm. Metab. Res. 20, 411–420.
Chan, S. J., Kwok, S. C. M., and Steiner, D. F. (1981). Diabetes Care. 4, 4–10.
Wozniak, M., Rydzewski, B., Baker, S. P., and Raizada, M. K. (1993). Neurochem. Int. 22, 1–10.
Pal, N., and Bessman, S. P. (1988). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 154, 450–454.
Bessman, S. P., and Geiger, P. J. (1980). Curr. Top. Cell. Regul. 16, 55–86.
Chen, L. B. (1988). Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 4, 155–181.
Krajewski, I., Tanaka, S., Takayama, S., Schibler, M. J., Fenton, W, and Reed, J. C. (1993). Cancer Res. 53, 4701–4714.
Nguyen, M., Millar, D. G. Yong, V. W., Korsmeyer, S. J., and Shore, G. C. (1993). J Biol. Chem. 268, 25265–25268.
Smets, L. A., Van den Berg, J., Acton, D., Top, B., Van Rooij, H., and Verwijs-Janssen, M. (1994). Blood 84, 1613–1619.
Richter, C. (1993). FEBS Lett. 325, 104–107.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golshani-Hebroni, S.G., Bessman, S.P. Hexokinase Binding to Mitochondria: A Basis for Proliferative Energy Metabolism. J Bioenerg Biomembr 29, 331–338 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022442629543
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022442629543