Abstract
Objective
We investigated the whole-body biodistributions and radiation dosimetry of five 11C-labeled and one 18F-labeled radiotracers in human subjects, and compared the results to those obtained from murine biodistribution studies.
Methods
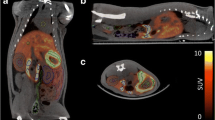
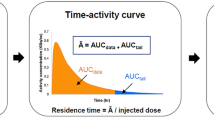
The radiotracers investigated were 11C-SA4503, 11C-MPDX, 11C-TMSX, 11C-CHIBA-1001, 11C-4DST, and 18F-FBPA. Dynamic whole-body positron emission tomography (PET) was performed in three human subjects after a single bolus injection of each radiotracer. Emission scans were collected in two-dimensional mode in five bed positions. Regions of interest were placed over organs identified in reconstructed PET images. The OLINDA program was used to estimate radiation doses from the number of disintegrations of these source organs. These results were compared with the predicted human radiation doses on the basis of biodistribution data obtained from mice by dissection.
Results
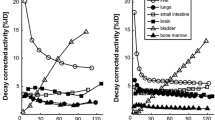
The ratios of estimated effective doses from the human-derived data to those from the mouse-derived data ranged from 0.86 to 1.88. The critical organs that received the highest absorbed doses in the human- and mouse-derived studies differed for two of the six radiotracers. The differences between the human- and mouse-derived dosimetry involved not only the species differences, including faster systemic circulation of mice and differences in the metabolism, but also measurement methodologies.
Conclusions
Although the mouse-derived effective doses were roughly comparable to the human-derived doses in most cases, considerable differences were found for critical organ dose estimates and pharmacokinetics in certain cases. Whole-body imaging for investigation of radiation dosimetry is desirable for the initial clinical evaluation of new PET probes prior to their application in subsequent clinical investigations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zanotti-Fregonara P, Innis RB. Suggested pathway to assess radiation safety of 11C-labeled PET tracers for first-in-human studies. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;39:544–7.
van der Aart J, Hallett WA, Rabiner EA, Passchier J, Comley RA. Radiation dose estimates for carbon-11-labelled PET tracers. Nucl Med Biol. 2012;39:305–14.
Santens P, De Vos F, Thierens H, et al. Biodistribution and dosimetry of carbon-11-methoxyprogabidic acid, a possible ligand for GABA-receptors in the brain. J Nucl Med. 1998;39:307–10.
Bencherif B, Endres CJ, Musachio JL, et al. PET imaging of brain acetylcholinesterase using [11C]CP-126,998, a brain selective enzyme inhibitor. Synapse. 2002;45:1–9.
Tolvanen T, Yli-Kerttula T, Ujula T, et al. Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of [11C]choline: a comparison between rat and human data. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:874–83.
Sakata M, Wu J, Toyohara J, et al. Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligand [11C]CHIBA-1001 in humans. Nucl Med Biol. 2011;38:443–8.
Toyohara J, Nariai T, Sakata M, et al. Whole-body distribution and brain tumor imaging with 11C–4DST: a pilot study. J Nucl Med. 2011;52:1322–8.
Kawamura K, Ishiwata K, Shimada Y, et al. Preclinical evaluation of [11C]SA4503: radiation dosimetry, in vivo selectivity and PET imaging of sigma1 receptors in the cat brain. Ann Nucl Med. 2000;14:285–92.
Ishiwata K, Nariai T, Kimura Y, et al. Preclinical studies on [11C]MPDX for mapping adenosine A1 receptors by positron emission tomography. Ann Nucl Med. 2002;16:377–82.
Ishiwata K, Wang WF, Kimura Y, Kawamura K, Ishii K. Preclinical studies on [11C]TMSX for mapping adenosine A2A receptors by positron emission tomography. Ann Nucl Med. 2003;17:205–11.
Ishiwata K, Ido T, Mejia AA, Ichihashi M, Mishima Y. Synthesis and radiation dosimetry of 4-borono-2-[18F]fluoro-d, l-phenylalanine: a target compound for PET and boron neutron capture therapy. Appl Radiat Isot. 1991;42:325–8.
Kawamura K, Ishiwata K, Tajima H, et al. In vivo evaluation of [11C]SA4503 as a PET ligand for mapping CNS sigma1 receptors. Nucl Med Biol. 2000;27:255–61.
Ishiwata K, Noguchi J, Wakabayashi S, et al. 11C-labeled KF18446: a potential central nervous system adenosine A2a receptor ligand. J Nucl Med. 2000;41:345–54.
Toyohara J, Sakata M, Wu J, et al. Preclinical and the first clinical studies on [11C]CHIBA-1001 for mapping α7 nicotinic receptors by positron emission tomography. Ann Nucl Med. 2009;23:301–9.
Ishiwata K, Ishii S, Senda M, Tsuchiya Y, Tomimoto K. Electrophilic synthesis of 6-[18F]fluoro-L-DOPA: use of 4-O-pivaloyl-L-DOPA as a suitable precursor for routine production. Appl Radiat Isot. 1993;44:755–9.
Fujiwara T, Watanuki S, Yamamoto S, et al. Performance evaluation of a large axial field-of-view PET scanner: SET-2400 W. Ann Nucl Med. 1997;11:307–13.
Meikle SR, Bailey DL, Hooper PK, et al. Simultaneous emission and transmission measurements for attenuation correction in whole-body PET. J Nucl Med. 1995;36:1680–8.
Stabin MG, Sparks RB, Crowe E. OLINDA/EXM: the second generation personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med. 2005;46:1023–7.
Kirschner AS, Ice RD, Beierwaltes WH. Radiation dosimetry of 131I–19-iodocholesterol: the pitfalls of using tissue concentration data—reply. J Nucl Med. 1975;16:248–9.
International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP Publication 60: 1990 recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. Ann ICRP. 1991;21:493–502.
Hirvonen J, Roivainen A, Virta J, Helin S, Nagren K, Rinne JO. Human biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of 11C-(R)-PK11195, the prototypic PET ligand to image inflammation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:606–12.
Pauleit D, Floeth F, Herzog H, et al. Whole-body distribution and dosimetry of O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003;30:519–24.
Brown WD, Oakes TR, DeJesus OT, et al. Fluorine-18-fluoro-L-DOPA dosimetry with carbidopa pretreatment. J Nucl Med. 1998;39:1884–91.
Deloar HM, Fujiwara T, Shidahara M, et al. Estimation of absorbed dose for 2-[F-18]fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose using whole-body positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Nucl Med. 1998;25:565–74.
Mejia AA, Nakamura T, Itoh M, et al. Absorbed dose estimates in positron emission tomography studies based on the administration of 18F-labeled radiopharmaceuticals. J Radiat Res. 1991;32:243–61.
Lin JH. Species similarities and differences in pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab Dispos. 1995;23:1008–21.
Toyohara J, Okada M, Toramatsu C, Suzuki K, Irie T. Feasibility studies of 4′-[methyl-11C]thiothymidine as a tumor proliferation imaging agent in mice. Nucl Med Biol. 2008;35:67–74.
Chiu SH, Huskey SW. Species differences in N-glucuronidation. Drug Metab Dispos. 1998;26:838–47.
Luoto P, Laitinen I, Suilamo S, Någren K, Roivainen A. Human dosimetry of carbon-11 labeled N-butan-2-yl-1-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-methylisoquinoline-3-carboxamide extrapolated from whole-body distribution kinetics and radiometabolism in rats. Mol Imaging Biol. 2010;12:435–42.
Harvey J, Firnau G, Garnett ES. Estimation of the radiation dose in man due to 6-[18F]fluoro-L-dopa. J Nucl Med. 1985;26:931–5.
Tang G, Wang M, Tang X, Luo L, Gan M. Pharmacokinetics and radiation dosimetry estimation of O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine as oncologic PET tracer. Appl Radiat Isot. 2003;58:219–25.
International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP Publication 80. Recalculated dose data for 19 frequently used radiopharmaceuticals from ICRP Publication 53. Ann ICRP. 1998;28:47–83.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) No. 19591665 (Tadashi Nariai), (B) No. 22390241 (Jun Toyohara), and (B) No. 20390334 (Kiichi Ishiwata) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, and a Grant from the National Center for Global Health and Medicine (Jun Toyohara, Tadashi Nariai, and Kiichi Ishiwata).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakata, M., Oda, K., Toyohara, J. et al. Direct comparison of radiation dosimetry of six PET tracers using human whole-body imaging and murine biodistribution studies. Ann Nucl Med 27, 285–296 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-013-0685-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-013-0685-9