Abstract
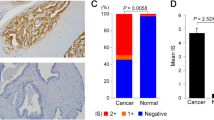
SHARPIN emerges higher expression in prostate cancerous tissues than in benign prostate hyperplasia by means of immunohistochemistry in our previous study. In this work, we performed the gain of function assay and find that overexpression of SHARPIN in LNCaP, DU145 and PC-3 cells promoted cell proliferation, invasiveness and reduced apoptosis. Furthermore, SHARPIN overexpression displayed elevated Bcl-2 and Survivin expression and reduced levels of Bax, cleaved caspase-3. Meanwhile, entropic expression of SHARPIN increased the levels of phosphorylated p65, IkBα, ERK and Akt, were selectively increased in these cells. Collectively, our study unraveled the ability of SHARPIN overexpression to induce tumorigenesis of prostate cancer cells through the NF-kB/ERK/Akt pathway and transformation of apoptosis-associated proteins.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
31 July 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-021-01545-3
References
Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, Stein K, Mariotto A, Smith T, Cooper D, Gansler T, Lerro C, Fedewa S, Lin C, Leach C, Cannady RS, Cho H, Scoppa S, Hachey M, Kirch R, Jemal A, Ward E. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:220–41.
Sheng M, Kim E. The Shank family of scaffold proteins. J Cell Sci. 2000;113:1851–6.
Lim S. Sharpin, a novel postsynaptic density protein that directly interacts with the shank family of proteins. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2001;17:385–97.
Ikeda F, Deribe YL, Skånland SS, Stieglitz B, Grabbe C, Franz-Wachtel M, van Wijk SJL, Goswami P, Nagy V, Terzic J, Tokunaga F, Androulidaki A, Nakagawa T, Pasparakis M, Iwai K, Sundberg JP, Schaefer L, Rittinger K, Macek B, Dikic I. SHARPIN forms a linear ubiquitin ligase complex regulating NF-κB activity and apoptosis. Nature. 2011;471:637–41.
Tokunaga F, Iwai K. LUBAC, a novel ubiquitin ligase for linear ubiquitination, is crucial for inflammation and immune responses. Microbes Infect. 2012;14:563–72.
Jung J, Kim JM, Park B, Cheon Y, Lee B, Choo SH, Koh SS, Lee S. Newly identified tumor-associated role of human Sharpin. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010;340:161–7.
Zhang Y, Huang H, Zhou H, Du T, Zeng L, Cao Y, Chen J, Lai Y, Li J, Wang G, Guo Z. Activation of nuclear factor κB pathway and downstream targets survivin and livin by SHARPIN contributes to the progression and metastasis of prostate cancer. Cancer 2014;120:3208–18.
Ali AS, Ali S, El-Rayes BF, Philip PA, Sarkar FH. Exploitation of protein kinase C: a useful target for cancer therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 2009;35:1–8.
DiDonato JA, Mercurio F, Karin M. NF-κB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol Rev. 2012;246(1):379–400.
Jin R, Yi Y, Yull FE, Blackwell TS, Clark PE, Koyama T, Smith JA, Matusik RJ. NF-κb gene signature predicts prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2014;74(10):2763–72.
Nguyen DP, Li J, Yadav SS, Tewari AK. Recent insights into NF-κB signalling pathways and the link between inflammation and prostate cancer. Bju Int. 2014;114(2):168–76.
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26(22):3279–90.
Altomare DA, Testa JR. Perturbations of the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24(5):7455–64.
He L, Ingram A, Rybak AP, Tang D. Shank-interacting protein–like 1 promotes tumorigenesis via PTEN inhibition in human tumor cells. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(6):2094–108.
Toulany M, Minjgee M, Saki M, Holler M, Meier F, Eicheler W, Rodemann HP. ERK2-dependent reactivation of Akt mediates the limited response of tumor cells with constitutive K-RAS activity to PI3 K inhibition. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014;15(3):317–28.
Suire S, Hawkins P, Stephens L. Activation of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase γ by Ras. Curr Biol. 2002;12(13):1068–75.
Zimmermann S. Phosphorylation and regulation of raf by akt (Protein kinase b). Science. 1999;286(5445):1741–4.
Deschenes-Simard X, Kottakis F, Meloche S, Ferbeyre G. ERKs in Cancer: friends or Foes? Cancer Res. 2014;74(2):412–9.
Pommier Y, Sordet O, Antony S, Hayward RL, Kohn KW. Apoptosis defects and chemotherapy resistance: molecular interaction maps and networks. Oncogene. 2004;23(16):2934–49.
Strasser A, Cory S, Adams JM. Deciphering the rules of programmed cell death to improve therapy of cancer and other diseases. EMBO J. 2011;30(18):3667–83.
Fernald K, Kurokawa M. Evading apoptosis in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2013;23(12):620–33.
Liu C, Yang J, Fu W, Qi S, Wang C, Quan C, Yang K. Coactivation of the PI3 K/Akt and ERK signaling pathways in PCB153-induced NF-κB activation and caspase inhibition. Toxicol Appl Pharm. 2014;277(3):270–8.
Liu Y, He J, Chen X, Li J, Shen M, Yu W, Yang Y, Xiao Z. The proapoptotic effect of formononetin in human osteosarcoma cells: involvement of inactivation of ERK and akt pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34(3):637–45.
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y, Sakuragi N. Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in cancer. BioMed Res Int. 2014;2014:150845.
Ye Q, Cai W, Zheng Y, Evers BM, She Q. ERK and AKT signaling cooperate to translationally regulate survivin expression for metastatic progression of colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2013;33(14):1828–39.
Tyagi N, Bhardwaj A, Singh AP, McClellan S, Carter JE, Singh S. P-21 activated kinase 4 promotes proliferation and survival of pancreatic cancer cells through AKT- and ERK-dependent activation of NF-kappaB pathway. Oncotarget. 2014;5(18):8778–89.
Andersen MH, Svane IM, Becker JC, Straten PT. The universal character of the tumor-associated antigen survivin. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(20):5991–4.
Kanwar JR, Kamalapuram SK, Kanwar RK. Survivin signaling in clinical oncology: a multifaceted dragon. Med Res Rev. 2013;33(4):765–89.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China [No. 81272807, 81472382], the National Natural Science Foundation of China for Young Scientists Grant [No. 81101947], Science and Technology Development Program of Guangdong Province [No. 2013B021800107].
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jin Li, Yiming Lai and Yi Cao have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Lai, Y., Cao, Y. et al. SHARPIN overexpression induces tumorigenesis in human prostate cancer LNCaP, DU145 and PC-3 cells via NF-κB/ERK/Akt signaling pathway. Med Oncol 32, 1 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0444-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0444-3