Abstract
Purpose
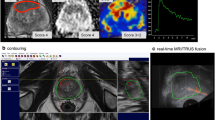
Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided random prostate biopsy is, in spite of its low sensitivity, the gold standard for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. The recent advent of PET imaging using a novel dedicated radiotracer, \(^{68}\hbox {Ga}\)-labeled prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), combined with MRI provides improved pre-interventional identification of suspicious areas. This work proposes a multimodal fusion image-guided biopsy framework that combines PET-MRI images with TRUS, using automatic segmentation and registration, and offering real-time guidance.
Methods
The prostate TRUS images are automatically segmented with a Hough transform-based random forest approach. The registration is based on the Coherent Point Drift algorithm to align surfaces elastically and to propagate the deformation field calculated from thin-plate splines to the whole gland.
Results
The method, which has minimal requirements and temporal overhead in the existing clinical workflow, is evaluated in terms of surface distance and landmark registration error with respect to the clinical ground truth. Evaluations on agar–gelatin phantoms and clinical data of 13 patients confirm the validity of this approach.
Conclusion
The system is able to successfully map suspicious regions from PET/MRI to the interventional TRUS image.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Available online: http://www.slicerigt.org.
Computational Geometry Algorithms Library, available online: http://www.cgal.org.
Available online: https://code.google.com/p/gmmreg/.
References
Worldwide Cancer Key Facts (2014) Cancer Research UK. http://publications.cancerresearchuk.org/downloads/Product/CS_KF_WORLDWIDE.pdf
Cool DW, Bax J, Romagnoli C, Ward AD, Gardi L, Karnik V, Izawa J, Chin J, Fenster A (2011) Fusion of MRI to 3D TRUS for mechanically-assisted targeted prostate biopsy: system design and initial clinical experience. In: Prostate cancer imaging. Image analysis and image-guided interventions. Springer, Berlin, pp 121–133
Criminisi A, Shotton J (2013) Decision forests for computer vision and medical image analysis. Springer, Berlin
Dang J, Frisch B, Lasaygues P, Zhang D, Tavernier S, Felix N, Lecoq P, Auffray E, Varela J, Mensah S, Mingxi W (2011) Development of an anthropomorphic breast phantom for combined pet, b-mode ultrasound and elastographic imaging. IEEE Trans Nuclear Sci 58(3):660–667
Delongchamps NB, Peyromaure M, Schull A, Beuvon F, Bouazza N, Flam T, Zerbib M, Muradyan N, Legman P, Cornud F (2013) Prebiopsy magnetic resonance imaging and prostate cancer detection: comparison of random and targeted biopsies. J Urol 189(2):493–499
Eiber M, Nekolla SG, Maurer T, Weirich G, Wester HJ, Schwaiger M (2014) 68Ga-PSMA PET/MR with multimodality image analysis for primary prostate cancer. Abdom Imaging, 1–3. doi:10.1007/s00261-014-0301-z
Erikson AP, Åström K (2012) On the bijectivity of thin-plate splines. In: Analysis for science, engineering and beyond. Springer, pp 93–141
Ghose S, Oliver A, Martí R, Lladó X, Vilanova JC, Freixenet J, Mitra J, Sidibé D, Meriaudeau F (2012) A survey of prostate segmentation methodologies in ultrasound, magnetic resonance and computed tomography images. Comput Methods Progr Biomed 108(1):262–287
Grady L (2006) Random walks for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28(11):1768–1783
Hu Y, Ahmed HU, Taylor Z, Allen C, Emberton M, Hawkes D, Barratt D (2012) MR to ultrasound registration for image-guided prostate interventions. Med Image Anal 16(3):687–703
Jian B, Vemuri BC (2011) Robust point set registration using Gaussian mixture models. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(8):1633–1645
Kaplan I, Oldenburg NE, Meskell P, Blake M, Church P, Holupka EJ (2002) Real time MRI-ultrasound image guided stereotactic prostate biopsy. Magn Reson Imaging 20(3):295–299
Lasso A, Heffter T, Rankin A, Pinter C, Ungi T, Fichtinger G (2014) PLUS: open-source toolkit for ultrasound-guided intervention systems. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 10:2527–2537
Marks L, Young S, Natarajan S (2013) MRI-ultrasound fusion for guidance of targeted prostate biopsy. Curr Opin Urol 23(1):43
Maurer T, Beer AJ, Wester HJ, Kübler H, Schwaiger M, Eiber M (2014) Positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging with 68gallium-labeled ligand of prostate-specific membrane antigen: promising novel option in prostate cancer imaging? Int J Urol 21(12):1286–1288
Milletari F, Yigitsoy M, Navab N, Ahmadi SA (2014) Left ventricle segmentation in cardiac ultrasound using hough-forests with implicit shape and appearance priors. MIDAS J. http://hdl.handle.net/10380/3485
Mitra J, Kato Z, Martí R, Oliver A, Lladó X, Sidibé D, Ghose S, Vilanova JC, Comet J, Meriaudeau F (2012) A spline-based non-linear diffeomorphism for multimodal prostate registration. Med Image Anal 16(6):1259–1279
Myronenko A, Song X (2010) Point set registration: coherent point drift. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 32(12):2262–2275
Narayanan R, Kurhanewicz J, Shinohara K, Crawford E, Simoneau A, Suri JS (2009) MRI-ultrasound registration for targeted prostate biopsy. In: IEEE international symposium on biomedical imaging: from nano to macro, 2009. ISBI’09, pp 991–994
Natarajan S, Marks LS, Margolis DJ, Huang J, Macairan ML, Lieu P, Fenster A (2011) Clinical application of a 3d ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy system. In: Urologic oncology: seminars and original investigations, vol 29, pp 334–342. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Qiu W, Yuan J, Ukwatta E, Sun Y, Rajchl M, Fenster A (2014) Prostate segmentation: an efficient convex optimization approach with axial symmetry using 3D TRUS and MR images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging
Reif DM, Motsinger AA, McKinney BA, Crowe JE, Moore JH (2006) Feature selection using a random forests classifier for the integrated analysis of multiple data types. In: IEEE symposium on computational intelligence and bioinformatics and computational biology, 2006. CIBCB’06, pp 1–8
Rematas K, Leibe B (2011) Efficient object detection and segmentation with a cascaded Hough Forest ISM. In: 2011 IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops (ICCV workshops), pp 966–973
Reynier C, Troccaz J, Fourneret P, Dusserre A, Gay-Jeune C, Descotes JL, Bolla M, Giraud JY (2004) MRI/TRUS data fusion for prostate brachytherapy. Preliminary results. Med Phys 31(6):1568–1575
Shah A, Zettinig O, Maurer T, Precup C, Schulte zu Berge C, Weiss J, Frisch B, Navab N (2014) An open source multimodal image-guided prostate biopsy framework. In: MICCAI workshop on clinical image-based procedures (CLIP). LNCS, vol 8680. Springer, Berlin
Sonn GA, Margolis DJ, Marks LS (2013) Target detection: magnetic resonance imaging-ultrasound fusion-guided prostate biopsy. In: Urologic oncology: seminars and original investigations. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Sparks R, Bloch BN, Feleppa E, Barratt D, Madabhushi A (2013) Fully automated prostate magnetic resonance imaging and transrectal ultrasound fusion via a probabilistic registration metric. In: SPIE medical imaging. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 86,710A
Sperling D (2014) MRI-ultrasound fusion imaging. In: Image guided prostate cancer treatments. Springer, Berlin, pp 115–123
Turkbey B, Pinto PA, Choyke PL (2009) Imaging techniques for prostate cancer: implications for focal therapy. Nat Rev Urol 6(4):191–203
Umeyama S (1991) Least-squares estimation of transformation parameters between two point patterns. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 13(4):376–380
Xu S, Kruecker J, Guion P, Glossop N, Neeman Z, Choyke P, Singh AK, Wood BJ (2007) Closed-loop control in fused MR-TRUS image-guided prostate biopsy. In: MICCAI 2007. LNCS. Springer, Berlin, pp 128–135
Acknowledgments
We thank Wolfgang Wein, ImFusion GmbH, for providing his image processing framework, and the teams of radiology and nuclear medicine departments at our clinic for various phantom MRI scans. This work is partially supported by the EU 7th Framework Program projects Marie Curie Early Initial Training Network Fellowship (PITN-GA-2011-289355-PicoSEC-MCNet), EndoTOFPET-US (GA-FP7/2007-2013-256984), and SoftwareCampus program of the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF, Förderkennzeichen 01IS12057). The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committees.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zettinig, O., Shah, A., Hennersperger, C. et al. Multimodal image-guided prostate fusion biopsy based on automatic deformable registration. Int J CARS 10, 1997–2007 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-015-1233-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-015-1233-y