Abstract
Purpose
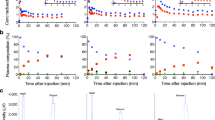
Using the α7-nAChR radiotracer, [18F]ASEM, we present the first successful human positron emission tomography (PET) studies. Rodent occupancy with three clinically employed α7-nAChR drugs confirms the specificity of the radiotracer.
Procedures
Five healthy male subjects were imaged for 90 min following IV [18F]ASEM. Two subjects were scanned for the second time (test/retest; TRV). Mouse biodistribution of [18F]ASEM was carried out in CD1 mice injected with using human equivalent doses of DMXB-A, EVP-6124, and varenicline to block specific binding.
Results
[18F]ASEM readily entered the brain and peaked at 15 min post-injection with reversible kinetics and a peak %SUV of about 400 %. The regional human brain distribution of [18F]ASEM matched previous in vitro data and baboon PET results. The precuneus, parietal, occipital, cingulate cortexes, putamen, and thalamus showed high values of distribution volume (>20 ml/ml) and binding potentials >1 with TRV averaged 10.8 ± 5.1 %. In mouse distribution studies, there was significant dose-dependent blockade in the mouse brain with DMXB-A as well as the other two α7-nAChR drugs.
Conclusions
The characteristics of [18F]ASEM are consistent with the ability to quantify α7-nAChR in the human brain. [18F]ASEM is suitable for imaging neuropsychiatric disorders and target engagement (receptor occupancy) of potential α7-nAChR drugs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albuquerque EX, Pereira EF, Alkondon M, Rogers SW (2009) Mammalian nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 89:73–120
Philip NS, Carpenter LL, Tyrka AR, Price LH (2010) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and depression: a review of the preclinical and clinical literature. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 212:1–12
Ishikawa M, Hashimoto K (2011) alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor as a potential therapeutic target for schizophrenia. Curr Pharm Des 17:121–129
Parri HR, Hernandez CM, Dineley KT (2011) Research update: alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Pharmacol 82:931–942
Woodruff-Pak DS, Gould TJ (2002) Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: involvement in Alzheimer’s disease and schizophrenia. Behav Cogn Neurosci Rev 1:5–20
D’Hoedt D, Bertrand D (2009) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: an overview on drug discovery. Expert Opin Ther Targets 13:395–411
Hoffmeister PG, Donat CK, Schuhmann MU et al (2011) Traumatic brain injury elicits similar alterations in alpha7 nicotinic receptor density in two different experimental models. Neruomol Med 13:44–53
Taly A, Charon S (2012) Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: a therapeutic target in the structure era. Curr Drug Targets 13:695–706
Freedman R, Hall M, Adler LE, Leonard S (1995) Evidence in postmortem brain tissue for decreased numbers of hippocampal nicotinic receptors in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 38:22–33
Marutle A, Zhang X, Court J et al (2001) Laminar distribution of nicotinic receptor subtypes in cortical regions in schizophrenia. J Chem Neuroanat 22:115–126
Thomsen MS, Weyn A, Mikkelsen JD (2011) Hippocampal alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor levels in patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, or major depressive disorder. Bipolar Disord 13:701–707
Thomsen MS, Hansen HH, Timmerman DB, Mikkelsen JD (2010) Cognitive improvement by activation of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: from animal models to human pathophysiology. Curr Pharm Des 16:323–343
Olincy A, Freedman R (2012) Nicotinic mechanisms in the treatment of psychotic disorders: a focus on the alpha7 nicotinic receptor. Handb Exp Pharmacol 213:211–232
Mazurov AA, Speake JD, Yohannes D (2011) Discovery and development of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators. J Med Chem 54:7943–7961
Kulak JM, Schneider JS (2004) Differences in alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor binding in motor symptomatic and asymptomatic MPTP-treated monkeys. Brain Res 999:193–202
Kulak JM, Carroll FI, Schneider JS (2006) [125I]Iodomethyllycaconitine binds to alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in monkey brain. Eur J Neurosci 23:2604–2610
Horti AG, Villemagne VL (2006) The quest for Eldorado: development of radioligands for in vivo imaging of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in human brain. Curr Pharm Des 12:3877–3900
Toyohara J, Wu J, Hashimoto K (2010) Recent development of radioligands for imaging alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain. Curr Top Med Chem 10:1544–1557
Brust P, Peters D, Deuther-Conrad W (2012) Development of radioligands for the imaging of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors with positron emission tomography. Curr Drug Targets 13:594–601
Pomper MG, Phillips E, Fan H et al (2005) Synthesis and biodistribution of radiolabeled alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands. J Nucl Med 46:326–334
Hashimoto K, Nishiyama S, Ohba H et al (2008) [11C]CHIBA-1001 as a novel PET ligand for alpha7 nicotinic receptors in the brain: a PET study in conscious monkeys. PLoS One 3:e3231
Ogawa M, Nishiyama S, Tsukada H et al (2010) Synthesis and evaluation of new imaging agent for central nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subtype. Nucl Med Biol 37:347–355
Dolle F, Valette H, Hinnen F et al (2001) Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of a carbon-11-labelled agonist of the a7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Label Compd Radiopharm 44:785–795
Toyohara J, Ishiwata K, Sakata M et al (2010) In vivo evaluation of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists [11C]A-582941 and [11C]A-844606 in mice and conscious monkeys. PLoS One 5:e8961
Horti AG, Ravert HT, Gao Y et al (2013) Synthesis and evaluation of new radioligands [(11)C]A-833834 and [(11)C]A-752274 for positron-emission tomography of alpha7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nucl Med Biol 40:395–402
Gao Y, Ravert HT, Valentine H et al (2012) 5-(5-(6-[(11)C]methyl-3,6-diazabicyclo[3.2.0]heptan-3-yl)pyridin-2-yl)-1H-indole as a potential PET radioligand for imaging cerebral alpha7-nAChR in mice. Bioorg Med Chem 20:3698–3702
Toyohara J, Sakata M, Wu J et al (2009) Preclinical and the first clinical studies on [11C]CHIBA-1001 for mapping alpha7 nicotinic receptors by positron emission tomography. Ann Nucl Med 23:301–309
Peters D, Timmerman DB, Roenn LC, Nielsen EB (2009) Preparation of labeled indolyl-pyridazinyl-diazabicyclononane derivatives and their use in diagnostic methods, particularly receptor imaging
Deuther-Conrad W, Fischer S, Hiller A et al (2011) Assessment of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor availability in juvenile pig brain with [18F]NS10743. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38:1541–1549
Ettrup A, Mikkelsen JD, Lehel S et al (2011) 11C–NS14492 as a novel PET radioligand for imaging cerebral alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: in vivo evaluation and drug occupancy measurements. J Nucl Med 52:1449–1456
Tanibuchi Y, Wu J, Toyohara J et al (2010) Characterization of [(3)H]CHIBA-1001 binding to alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain from rat, monkey, and human. Brain Res 1348:200–208
Ding M, Ghanekar S, Elmore CS et al (2012) [3H]Chiba-1001 (methyl-SSR180711) has low in vitro binding affinity and poor in vivo selectivity to nicotinic alpha-7 receptor in rodent brain. Synapse 66:315–322
Gao Y, Kellar KJ, Yasuda RP et al (2013) Derivatives of dibenzothiophene for positron emission tomography imaging of alpha7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Med Chem 56:7574–7589
Horti AG, Gao Y, Kuwabara H et al (2014) 18F-ASEM, a radiolabeled antagonist for imaging the alpha7-Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor with PET. J Nucl Med 55:672–677
Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Smith SM (2012) Fsl. Neuroimage 62:782–790
Patenaude B, Smith SM, Kennedy DN, Jenkinson M (2011) A Bayesian model of shape and appearance for subcortical brain segmentation. Neuroimage 56:907–922
Fischl B, van der Kouwe A, Destrieux C et al (2004) Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex 14:11–22
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2004) Rigid body registration. In: Frackowiak R, Ashburner J, Penny WD et al (eds) Human brain function. Academic, San Diego, pp 635–654
Keller SH, Sibomana M, Olesen OV et al (2012) Methods for motion correction evaluation using 18F-FDG human brain scans on a high-resolution PET scanner. J Nucl Med 53:495–504
Logan J, Fowler JS, Volkow ND et al (1996) Distribution volume ratios without blood sampling from graphical analysis of PET data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:834–840
Foster DM (1998) Developing and testing integrated multicompartment models to describe a single-input multiple-output study using the SAAM II software system. Adv Exp Med Biol 445:59–78
Stabin MG, Siegel JA (2003) Physical models and dose factors for use in internal dose assessment. Health Phys 85:294–310
Stabin MG, Sparks RB, Crowe E (2005) OLINDA/EXM: the second-generation personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med 46:1023–1027
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M, Ahmad N (2008) Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J 22:659–661
Prickaerts J, van Goethem NP, Chesworth R et al (2012) EVP-6124, a novel and selective alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, improves memory performance by potentiating the acetylcholine response of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuropharmacology 62:1099–1110
Rollema H, Shrikhande A, Ward KM et al (2010) Pre-clinical properties of the alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonists varenicline, cytisine and dianicline translate to clinical efficacy for nicotine dependence. Br J Pharmacol 160:334–345
Court JA, Martin-Ruiz C, Graham A, Perry E (2000) Nicotinic receptors in human brain: topography and pathology. J Chem Neuroanat 20:281–298
Breese CR, Adams C, Logel J et al (1997) Comparison of the regional expression of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 mRNA and [125I]-alpha-bungarotoxin binding in human postmortem brain. J Comp Neurol 387:385–398
Akaike H (1974) A new look at statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Autom Control AU-19:716–722
Innis RB, Cunningham VJ, Delforge J et al (2007) Consensus nomenclature for in vivo imaging of reversibly binding radioligands. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1533–1539
Kranz M, Sattler B, Deuther-Conrad W et al (2014) Preclinical dose assessment and biodistribution of [18F]DBT10, a new α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7-nAChR) imaging ligand. J Nucl Med 55(Suppl 1):1143
Wallace TL, Bertrand D (2013) Alpha7 neuronal nicotinic receptors as a drug target in schizophrenia. Expert Opin Ther Targets 17:139–155
Freedman R, Olincy A, Buchanan RW et al (2008) Initial phase 2 trial of a nicotinic agonist in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 165:1040–1047
Olincy A, Harris JG, Johnson LL et al (2006) Proof-of-concept trial of an alpha7 nicotinic agonist in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:630–638
Acknowledgments
The authors received NIH grants MH079017 and AG037298 and funds from the Department of Radiology. Special thanks to Ali Kargbo, MS; Rebecca Mellinger Pilgram, BS; and Anil Mathur, MD, MIS for the HPLC metabolite analysis; Paige Finley, BS for the mouse experiments; the JHU PET technologists and PET radiochemists and Andrew Crabb, MS and Arman Rahmim, PhD for the computer-related and HRRT PET assistance. Thanks to Michael Stabin, PhD for assisting in radiation dosimetry estimates and Julia Buchanan for the editorial assistance.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 180 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wong, D.F., Kuwabara, H., Pomper, M. et al. Human Brain Imaging of α7 nAChR with [18F]ASEM: a New PET Radiotracer for Neuropsychiatry and Determination of Drug Occupancy. Mol Imaging Biol 16, 730–738 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-014-0779-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-014-0779-3