Abstract
Purpose
RGD peptide-based radiotracers are well established as integrin αvβ3 imaging probes to evaluate tumor angiogenesis or tissue remodeling after ischemia or infarction. In order to optimize the labeling process and pharmacokinetics of the imaging probes, we synthesized three dimeric RGD peptides with or without PEGylation and performed in vivo screening.
Procedures
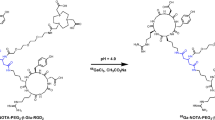
Radiolabeling was achieved through the reaction of F-18 aluminum–fluoride complex with the cyclic chelator, 1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid (NOTA). Three imaging probes were synthesized as 18F-AlF-NOTA-E[c(RGDfK)]2, 18F-AlF-NOTA-PEG4-E[c(RGDfK)]2, and 18F-AlF-NOTA-E[PEG4-c(RGDfk)]2. The receptor binding affinity was determined by competitive cell binding assay, and the stability was evaluated by mouse serum incubation. Tumor uptake and whole body distribution of the three tracers were compared through direct tissue sampling and PET quantification of U87MG tumor-bearing mice.
Results
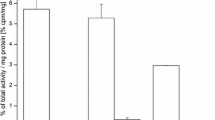
All three compounds remained intact after 120 min incubation with mouse serum. They all had a rapid and relatively high tracer uptake in U87MG tumors with good target-to-background ratios. Compared with the other two tracers, 18F-AlF-NOTA-E[PEG4-c(RGDfk)]2 had the highest tumor uptake and the lowest accumulation in the liver. The integrin receptor specificity was confirmed by co-injection of unlabeled dimeric RGD peptide.
Conclusion
The rapid one-step radiolabeling strategy by the complexation of 18F-aluminum fluoride with NOTA-peptide conjugates was successfully applied to synthesize three dimeric RGD peptides. Among the three probes developed, 18F-AlF-NOTA-E[PEG4-c(RGDfk)]2 with relatively low liver uptake and high tumor accumulation appears to be a promising candidate for further translational research.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang M, Gao H, Yan Y et al (2011) PET imaging of early response to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD4190. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38:1237–1247
Niu G, Chen X (2011) Why integrin as a primary target for imaging and therapy. Theranostics 1:30–47
Brooks PC, Montgomery AM, Rosenfeld M et al (1994) Integrin alpha v beta 3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell 79:1157–1164
Cai W, Chen X (2008) Multimodality molecular imaging of tumor angiogenesis. J Nucl Med 49(Suppl 2):113S–128S
Backer MV, Backer JM (2012) Imaging key biomarkers of tumor angiogenesis. Theranostics 2:502–515
Noiri E, Goligorsky MS, Wang GJ et al (1996) Biodistribution and clearance of 99mTc-labeled Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptide in rats with ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 7:2682–2688
Ahmadi M, Sancey L, Briat A et al (2008) Chemical and biological evaluations of an (111)in-labeled RGD-peptide targeting integrin alpha(V) beta(3) in a preclinical tumor model. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 23:691–700
Jeong JM, Hong MK, Chang YS et al (2008) Preparation of a promising angiogenesis PET imaging agent: 68Ga-labeled c(RGDyK)-isothiocyanatobenzyl-1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid and feasibility studies in mice. J Nucl Med 49:830–836
Li ZB, Chen K, Chen X (2008) (68)Ga-labeled multimeric RGD peptides for microPET imaging of integrin alpha(v)beta (3) expression. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 35:1100–1108
Chen X, Park R, Shahinian AH et al (2004) 18F-labeled RGD peptide: initial evaluation for imaging brain tumor angiogenesis. Nucl Med Biol 31:179–189
Chen X, Liu S, Hou Y et al (2004) MicroPET imaging of breast cancer alphav-integrin expression with 64Cu-labeled dimeric RGD peptides. Mol Imaging Biol 6:350–359
Lang L, Li W, Jia HM et al (2011) New methods for labeling RGD peptides with bromine-76. Theranostics 1:341–353
Jacobson O, Zhu L, Niu G et al (2011) MicroPET imaging of integrin alpha(v)beta (3) expressing tumors using (89)Zr-RGD peptides. Mol Imaging Biol 13(6):1224–1233
Zhang X, Xiong Z, Wu Y et al (2006) Quantitative PET imaging of tumor integrin alphavbeta3 expression with 18F-FRGD2. J Nucl Med 47:113–121
Sun X, Yan Y, Liu S et al (2011) 18F-FPPRGD2 and 18F-FDG PET of response to Abraxane therapy. J Nucl Med 52:140–146
Liu S, Liu Z, Chen K et al (2010) 18F-labeled galacto and PEGylated RGD dimers for PET imaging of alphavbeta3 integrin expression. Mol Imaging Biol 12:530–538
Chin FT, Shen B, Liu S et al (2012) First experience with clinical-grade [(18)F]FPP(RGD) (2): an automated multi-step radiosynthesis for clinical PET studies. Mol Imaging Biol 14(1):88–95
Mittra ES, Goris ML, Iagaru AH et al (2011) Pilot pharmacokinetic and dosimetric studies of (18)F-FPPRGD2: a PET radiopharmaceutical agent for imaging alpha(v)beta(3) integrin levels. Radiology 260:182–191
Lang L, Li W, Guo N et al (2011) Comparison study of [18F]FAl-NOTA-PRGD2, [18F]FPPRGD2, and [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-PRGD2 for PET imaging of U87MG tumors in mice. Bioconjugate chemistry 22:2415–2422
McBride WJ, D’Souza CA, Sharkey RM et al (2010) Improved F-18 labeling of peptides with a fluoride-aluminum-chelate complex. Bioconjugate chemistry 21:1331–1340
McBride WJ, Sharkey RM, Karacay H et al (2009) A novel method of F-18 radiolabeling for PET. J Nucl Med 50:991–998
Lang L, Li W, Guo N et al (2011) Comparison study of [18F]FAl-NOTA-PRGD2, [18F]FPPRGD2, and [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-PRGD2 for PET imaging of U87MG tumors in mice. Bioconjugate chemistry 22:2415–2422
Gao H, Lang L, Guo N et al (2012) PET imaging of angiogenesis after myocardial infarction/reperfusion using a one-step labeled integrin-targeted tracer 18F-AlF-NOTA-PRGD2. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39:683–692
Guo N, Lang L, Li W et al (2012) Quantitative analysis and comparison study of [18F]AlF-NOTA-PRGD2, [18F]FPPRGD2 and [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-PRGD2 using a reference tissue model. PLoS One 7:e37506
Haubner R, Wester HJ, Burkhart F et al (2001) Glycosylated RGD-containing peptides: tracer for tumor targeting and angiogenesis imaging with improved biokinetics. J Nucl Med 42:326–336
Beer AJ, Kessler H, Wester HJ, Schwaiger M (2011) PET imaging of integrin alphaVbeta3 expression. Theranostics 1:48–57
Shi J, Kim YS, Zhai S, Liu Z, Chen X, Liu S (2009) Improving tumor uptake and pharmacokinetics of (64)Cu-labeled cyclic RGD peptide dimers with Gly(3) and PEG(4) linkers. Bioconjugate chemistry 20:750–759
Liu Z, Niu G, Shi J, Liu S, Wang F, Chen X (2009) (68)Ga-labeled cyclic RGD dimers with Gly3 and PEG4 linkers: promising agents for tumor integrin alphavbeta3 PET imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36:947–957
Zhou Y, Shao G, Liu S (2012) Monitoring breast tumor lung metastasis by U-SPECT-II/CT with an integrin alpha(v)beta(3)-targeted radiotracer(99m)Tc-3P-RGD(2). Theranostics 2:577–588
Shi J, Zhou Y, Chakraborty S et al (2011) Evaluation of in-labeled cyclic RGD peptides: effects of peptide and linker multiplicity on their tumor uptake, excretion kinetics and metabolic stability. Theranostics 1:322–340
Zhou Y, Chakraborty S, Liu S (2011) Radiolabeled cyclic RGD peptides as radiotracers for imaging tumors and thrombosis by SPECT. Theranostics 1:58–82
Liu S, Liu H, Ren G, Kimura RH, Cochran JR, Cheng Z (2011) PET imaging of integrin positive tumors using F labeled knottin peptides. Theranostics 1:403–412
Tomayko MMRC (1989) Determination of subcutaneous tumor size in athymic (nude) mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 24:148–154
Euhus DMHC, LaRegina MC, Johnson FE (1986) Tumor measurement in the nude mouse. J Surg Oncol 31:229–234
Kenny LM, Coombes RC, Oulie I et al (2008) Phase I trial of the positron-emitting Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptide radioligand 18F-AH111585 in breast cancer patients. Journal of nuclear medicine 49:879–886
Beer AJ, Haubner R, Goebel M et al (2005) Biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of the alphavbeta3-selective tracer 18F-galacto-RGD in cancer patients. Journal of nuclear medicine 46:1333–1341
Harris JM, Chess RB (2003) Effect of pegylation on pharmaceuticals. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:214–221
Gagnon MK, Hausner SH, Marik J, Abbey CK, Marshall JF, Sutcliffe JL (2009) High-throughput in vivo screening of targeted molecular imaging agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:17904–17909
Bass LA, Wang M, Welch MJ, Anderson CJ (2000) In vivo transchelation of copper-64 from TETA-octreotide to superoxide dismutase in rat liver. Bioconjugate chemistry 11:527–532
Deshpande SV, Subramanian R, McCall MJ, DeNardo SJ, DeNardo GL, Meares CF (1990) Metabolism of indium chelates attached to monoclonal antibody: minimal transchelation of indium from benzyl-EDTA chelate in vivo. Journal of nuclear medicine 31:218–224
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2013CB733800, 2013CB733802, 2014CB744503), the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (81201129, 81371596, 51373144 and 81101068), and the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jinxia Guo and Lixin Lang contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 85.5 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Lang, L., Hu, S. et al. Comparison of Three Dimeric 18F-AlF-NOTA-RGD Tracers. Mol Imaging Biol 16, 274–283 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-013-0668-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-013-0668-1