Abstract
Purpose
The cell adhesion molecule integrin αvβ3 is an important player in the process of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Abegrin™, a fully humanized anti-integrin αvβ3 monoclonal antibody, was currently in clinical trials for cancer therapy. Herein, we labeled Abegrin™ with 111In, evaluated the in vitro and in vivo characteristics, and investigated whether the expression of integrin αvβ3 in tumors could be imaged with 111In-labeled Abegrin™.
Methods
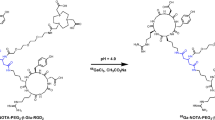
The binding affinity and specificity of Abegrin™ was analyzed using U87MG glioblastoma cells. Abegrin™ was coupled with 1,4,7,10-tetraazadodecane-N,N′,N″,N′″-tetraacetic acid (DOTA) for 111In radiolabeling. γ Imaging of 111In-DOTA–Abegrin™ was carried out in nude mice bearing both integrin αvβ3-positive U87MG and integrin αvβ3-negative HT-29 tumors. Biodistribution and blocking studies of 111In-DOTA–Abegrin™ were investigated in U87MG tumor-bearing nude mice.
Results
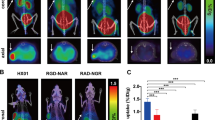
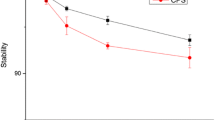
Abegrin™ exhibited high-binding affinity to human integrin αvβ3 expressed on U87MG cells (K d of 0.35 ± 0.06 nM). The antibody retained antigen-binding affinity/specificity after DOTA conjugation. γ Imaging showed that the tumor uptake of 111In-DOTA–Abegrin™ in integrin αvβ3-positive U87MG tumors was much higher than that in integrin αvβ3-negative HT-29 tumors. In the HT-29 tumors, Abegrin™ was mainly nonspecifically accumulated around the blood vessels, while in the U87MG tumors, besides the nonspecific tumor retention, Abegrin™ also specifically bound the human integrin αvβ3 expressed on the tumor cells. Biodistribution and blocking studies exhibited that the U87MG tumor uptake of 111In-DOTA–Abegrin™ decreased from 14.12 ± 0.44 to 6.93 ± 0.94 percentage of injected dose per gram of tissue after coinjection of excess dose of cold Abegrin™, which confirmed the in vivo integrin αvβ3 binding specificity of 111In-DOTA–Abegrin™.
Conclusions
Abegrin™ showed specific binding to human integrin αvβ3 expressed on the tumor cells. 111In-DOTA–Abegrin™ can specifically target the human integrin αvβ3 expression in the nude mouse model. 111In-DOTA–Abegrin™ has a potential for clinical translation as an agent for integrin αvβ3-positive tumor imaging, evaluating tumor angiogenic status and monitoring the therapeutic efficacy of Abegrin™-based cancer therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eble JA, Haier J (2006) Integrins in cancer treatment. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 6:89–105
Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E (1999) Integrin signaling. Science 285:1028
Hynes RO (1992) Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 69:11–25
Seftor RE, Seftor EA, Gehlsen KR, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Brown PD, Ruoslahti E, Hendrix MJ (1992) Role of the alpha v beta 3 integrin in human melanoma cell invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:1557–1561
Eliceiri BP, Cheresh DA (1999) The role of alphav integrins during angiogenesis: insights into potential mechanisms of action and clinical development. J Clin Invest 103:1227–1230
Kumar CC (2003) Integrin alpha v beta 3 as a therapeutic target for blocking tumor-induced angiogenesis. Curr Drug Targets 4:123–131
Brooks PC, Clark RA, Cheresh DA (1994) Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science 264:569–571
Veeravagu A, Liu Z, Niu G, Chen K, Jia B, Cai W, Jin C, Hsu AR, Connolly AJ, Tse V et al (2008) Integrin alphavbeta3-targeted radioimmunotherapy of glioblastoma multiforme. Clin Cancer Res 14:7330–7339
Shi J, Jia B, Liu Z, Yang Z, Yu Z, Chen K, Chen X, Liu S, Wang F (2008) 99mTc-labeled bombesin(7-14)NH2 with favorable properties for SPECT imaging of colon cancer. Bioconjug Chem 19:1170–1178
Liu Z, Wang F, Chen X (2008) Integrin alpha v beta 3-targeted cancer therapy. Drug Development Research 69:329–339
Beer AJ, Grosu AL, Carlsen J, Kolk A, Sarbia M, Stangier I, Watzlowik P, Wester HJ, Haubner R, Schwaiger M (2007) [18F]galacto-RGD positron emission tomography for imaging of alphavbeta3 expression on the neovasculature in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin Cancer Res 13:6610–6616
Beer AJ, Haubner R, Wolf I, Goebel M, Luderschmidt S, Niemeyer M, Grosu AL, Martinez MJ, Wester HJ, Weber WA et al (2006) PET-based human dosimetry of 18F-galacto-RGD, a new radiotracer for imaging alpha v beta3 expression. J Nucl Med 47:763–769
Morrison MS, Ricketts SA, Barnett J, Cuthbertson A, Tessier J, Wedge SR (2009) Use of a novel Arg-Gly-Asp radioligand, 18F-AH111585, to determine changes in tumor vascularity after antitumor therapy. J Nucl Med 50:116–122
Liu Z, Niu G, Shi J, Liu S, Wang F, Liu S, Chen X (2009) (68)Ga-labeled cyclic RGD dimers with Gly(3) and PEG (4) linkers: promising agents for tumor integrin alpha (v)beta (3) PET imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36:947–957
Tucker GC (2006) Integrins: molecular targets in cancer therapy. Curr Oncol Rep 8:96–103
Gutheil JC, Campbell TN, Pierce PR, Watkins JD, Huse WD, Bodkin DJ, Cheresh DA (2000) Targeted antiangiogenic therapy for cancer using Vitaxin: a humanized monoclonal antibody to the integrin alphavbeta3. Clin Cancer Res 6:3056–3061
Wu H, Beuerlein G, Nie Y, Smith H, Lee BA, Hensler M, Huse WD, Watkins JD (1998) Stepwise in vitro affinity maturation of Vitaxin, an alphav beta3-specific humanized mAb. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6037
Cai W, Chen X (2006) Anti-angiogenic cancer therapy based on integrin alphavbeta3 antagonism. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 6:407–428
Delbaldo C, Raymond E, Vera K, Hammershaimb L, Kaucic K, Lozahic S, Marty M, Faivre S (2008) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of etaracizumab (Abegrin), a humanized monoclonal antibody against alphavbeta3 integrin receptor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 26:35–43
Posey JA, Khazaeli MB, DelGrosso A, Saleh MN, Lin CY, Huse W, LoBuglio AF (2001) A pilot trial of Vitaxin, a humanized anti-vitronectin receptor (anti alpha v beta 3) antibody in patients with metastatic cancer. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 16:125–132
Cai W, Wu Y, Chen K, Cao Q, Tice DA, Chen X (2006) In vitro and in vivo characterization of 64Cu-labeled Abegrin, a humanized monoclonal antibody against integrin alpha v beta 3. Cancer Res 66:9673–9681
Scheer MG, Stollman TH, Boerman OC, Verrijp K, Sweep FC, Leenders WP, Ruers TJ, Oyen WJ (2008) Imaging liver metastases of colorectal cancer patients with radiolabelled bevacizumab: Lack of correlation with VEGF-A expression. Eur J Cancer 44:1835–1840
Iagaru A, Gambhir SS, Goris ML (2008) 90Y-ibritumomab therapy in refractory non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: observations from 111In-ibritumomab pretreatment imaging. J Nucl Med 49:1809–1812
Pandit-Taskar N, O'Donoghue JA, Morris MJ, Wills EA, Schwartz LH, Gonen M, Scher HI, Larson SM, Divgi CR (2008) Antibody mass escalation study in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer using 111In-J591: lesion detectability and dosimetric projections for 90Y radioimmunotherapy. J Nucl Med 49:1066–1074
Behr TM, Behe M, Wormann B (2001) Trastuzumab and breast cancer. N Engl J Med 345:995–996
Banning A, Kipp A, Schmitmeier S, Lowinger M, Florian S, Krehl S, Thalmann S, Thierbach R, Steinberg P, Brigelius-Flohe R (2008) Glutathione Peroxidase 2 Inhibits Cyclooxygenase-2-Mediated Migration and Invasion of HT-29 Adenocarcinoma Cells but Supports Their Growth as Tumors in Nude Mice. Cancer Res 68:9746–9753
Liu Z, Yu Z, He W, Ma S, Sun L, Wang F (2009) In-vitro internalization and in-vivo tumor uptake of anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody LA22 in A549 lung cancer cells and animal model. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 24:15–24
Shao W, Zhao S, Liu Z, Zhang J, Ma S, Sato JD, Zhang P, Tong M, Han J, Wang Y et al (2006) Inhibition of human tumor xenograft growth in nude mice by a conjugate of monoclonal antibody LA22 to epidermal growth factor receptor with anti-tumor antibiotics mitomycin C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 349:816–824
Liu Z, Yan Y, Chin FT, Wang F, Chen X (2009) Dual Integrin and Gastrin-Releasing Peptide Receptor Targeted Tumor Imaging Using (18)F-labeled PEGylated RGD-Bombesin Heterodimer (18)F-FB-PEG(3)-Glu-RGD-BBN. J Med Chem 52:425–432
He Q, Liu Z, Jia B, Li X, Shi J, Zhang J, Lan F, Yang Z, Liu Y, Shen L et al (2008) In vivo gamma imaging of the secondary tumors of transplanted human fetal striatum neural stem cells-derived primary tumor cells. Neuroreport 19:1009–1014
Maeda H, Fang J, Inutsuka T, Kitamoto Y (2003) Vascular permeability enhancement in solid tumor: various factors, mechanisms involved and its implications. Int Immunopharmacol 3:319–328
Boswell CA, Sun X, Niu W, Weisman GR, Wong EH, Rheingold AL, Anderson CJ (2004) Comparative in vivo stability of copper-64-labeled cross-bridged and conventional tetraazamacrocyclic complexes. J Med Chem 47:1465–1474
Liu Z, Li Z, Cao Q, Liu S, Wang F, Chen X (2009) Small-Animal PET of Tumors with 64Cu-Labeled RGD-Bombesin Heterodimer. J Nucl Med 50:1168–1177
Sprague JE, Peng Y, Sun X, Weisman GR, Wong EH, Achilefu S, Anderson CJ (2004) Preparation and biological evaluation of copper-64-labeled tyr3-octreotate using a cross-bridged macrocyclic chelator. Clin Cancer Res 10:8674–8682
Prasanphanich AF, Nanda PK, Rold TL, Ma L, Lewis MR, Garrison JC, Hoffman TJ, Sieckman GL, Figueroa SD, Smith CJ (2007) [64Cu-NOTA-8-Aoc-BBN(7-14)NH2] targeting vector for positron-emission tomography imaging of gastrin-releasing peptide receptor-expressing tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:12462–12467
Gladson CL (1996) Expression of integrin alpha v beta 3 in small blood vessels of glioblastoma tumors. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:1143–1149
Maeda H (2001) The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect in tumor vasculature: the key role of tumor-selective macromolecular drug targeting. Adv Enzyme Regul 41:189–207
Aerts HJ, Dubois L, Perk L, Vermaelen P, van Dongen GA, Wouters BG, Lambin P (2009) Disparity between in vivo EGFR expression and 89Zr-labeled cetuximab uptake assessed with PET. J Nucl Med 50:123–131
McLarty K, Cornelissen B, Scollard DA, Done SJ, Chun K, Reilly RM (2009) Associations between the uptake of 111In-DTPA-trastuzumab, HER2 density and response to trastuzumab (Herceptin) in athymic mice bearing subcutaneous human tumour xenografts. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36:81–93
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Zhi Yang and Mr. Cunjing Jin for their excellent technical assistance with γ-imaging and biodistribution studies. This work is jointly supported by NSFC projects (30930030, 30870728, 30900373, and 20820102035), an 863 project (2007AA02Z467), and grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2009ZX09103-733, 2009ZX09301-010, and 2009ZX09103-746).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Jia, B., Zhao, H. et al. Specific Targeting of Human Integrin αvβ3 with 111In-Labeled Abegrin™ in Nude Mouse Models. Mol Imaging Biol 13, 112–120 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-010-0302-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-010-0302-4