Abstract
Purpose
Fatty acid synthase (FAS) is an emerging target for anticancer therapy with a variety of new FAS inhibitors being explored in preclinical models. The aim of this study was to use positron emission tomography with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG-PET) to monitor the effects of the FAS inhibitor C75 on tumor glucose metabolism in a rodent model of human A549 lung cancer.
Materials and Methods
After a baseline FDG-PET scan, C75 was administered and post-treatment scans were performed serially. FAS activity was measured in treated animals ex vivo by [14C]acetate incorporation in animals euthanized in parallel to those imaged.
Results
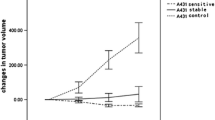
Longitudinally measured metabolic volumes of interest and tumor/background ratios demonstrated a transient, reversible decrease in glucose metabolism and tumor metabolic volume after treatment, with the peak effect seen at 4 h. FDG-PET measurements correlated with changes in tumor FAS activity measured ex vivo.
Conclusions
Because C75 causes an effect that is shorter in duration than expected, modification of the current weekly dosing regimen should be considered. These results demonstrate the utility of small animal FDG-PET in assessing the pharmacodynamics of new anticancer agents in preclinical models.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Lupuand and J. A. Menendez. Targeting fatty acid synthase in breast and endometrial cancer: an alternative to selective estrogen receptor modulators? Endocrinology 147:4056–4066 (2006).
E. S. Pizer, J. Thupari, W. F. Han, M. L. Pinn, F. J. Chrest, G. L. Frehywot, C. A. Townsend, and F. P. Kuhajda. Malonyl-coenzyme-A is a potential mediator of cytotoxicity induced by fatty-acid synthase inhibition in human breast cancer cells and xenografts. Cancer Res. 60:213–218 (2000).
J. M. McFadden, S. M. Medghalchi, J. N. Thupari, M. L. Pinn, A. Vadlamudi, K. I. Miller, F. P. Kuhajda, and C. A. Townsend. Application of a flexible synthesis of (5R)-thiolactomycin to develop new inhibitors of type I fatty acid synthase. J. Med. Chem. 48:946–961 (2005).
F. P. Kuhajda. Fatty acid synthase and cancer: new application of an old pathway. Cancer Res. 66:5977–5980 (2006).
F. P. Kuhajda. Fatty-acid synthase and human cancer: new perspectives on its role in tumor biology. Nutrition 16:202–208 (2000).
E. W. Gabrielson, M. L. Pinn, J. R. Testa, and F. P. Kuhajda. Increased fatty acid synthase is a therapeutic target in mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 7:153–157 (2001).
S. H. Cha, Z. Hu, S. Chohnan, and M. D. Lane. Inhibition of hypothalamic fatty acid synthase triggers rapid activation of fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102:14557–14562 (2005).
F. P. Kuhajda, L. E. Landree, and G. V. Ronnett. The connections between C75 and obesity drug-target pathways. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 26:541–544 (2005).
T. H. March, P. G. Marron-Terada, and S. A. Belinsky. Refinement of an orthotopic lung cancer model in the nude rat. Vet. Pathol. 38:483–490 (2001).
J. Seidel, J. J. Vaquero, J. Pascau, and M. Desco. Features of the NIH atlas small animal PET scanner and its use with a coaxial small animal volume CT scanner. In Conference Proceeding of IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, 2002, pp. 545–548.
J. Seidel, J. J. Vaquero, and M. V. Green. Resolution uniformity and sensitivity of the NIH ATLAS small animal PET scanner: comparison to simulated LSO scanners without depth-of-interaction capability. IEEE Nucl. Sci. Symp. Conf. Rec. 3:1555–1558 (2001).
R. Yao, J. Seidel, C. A. Johnson, M. E. Daube-Witherspoon, M. V. Green, and R. E. Carson. Performance characteristics of the 3-D OSEM algorithm in the reconstruction of small animal PET images. Ordered-subsets expectation-maximixation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 19:798–804 (2000).
J. S. Lee, R. L. Hagemann, Y. Wang, B. M. Tsui, and M. G. Pomper. Performance evaluation of the NIH ATLAS II small animal PET scanner. In Annual Meeting of Society for Molecular Imaging, San Francisco, CA (2003).
J. Seidel, J. J. Vaquero, and M. V. Green. Resolution uniformity and sensitivity of the NIH ATLAS small animal PET scanner: Comparison to simulated LSO scanners without depth-of-interaction capability. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 50:1347–1350 (2003).
M. E. Juweid and B. D. Cheson. Positron–emission tomography and assessment of cancer therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 354:496–507 (2006).
G. D. Demetri, M. von Mehren, C. D. Blanke, A. D. Van den Abbeele, B. Eisenberg, P. J. Roberts, M. C. Heinrich, D. A. Tuveson, S. Singer, M. Janicek, J. A. Fletcher, S. G. Silverman, S. L. Silberman, R. Capdeville, B. Kiese, B. Peng, S. Dimitrijevic, B. J. Druker, C. Corless, C. D. Fletcher, and H. Joensuu. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 347:472–480 (2002).
A. Saleem, N. Charnley, and P. Price. Clinical molecular imaging with positron emission tomography. Eur. J. Cancer 42:1720–1727 (2006).
R. Weissleder. Molecular imaging in cancer. Science 312:1168–1171 (2006).
W. A. Weber. Chaperoning drug development with PET. J. Nucl. Med. 47:735–737 (2006).
V. Sebastiani, P. Visca, C. Botti, G. Santeusanio, G. M. Galati, V. Piccini, B. Capezzone de Joannon, U. Di Tondo, and P. L. Alo. Fatty acid synthase is a marker of increased risk of recurrence in endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 92:101–105 (2004).
M. Mamede, T. Higashi, M. Kitaichi, K. Ishizu, T. Ishimori, Y. Nakamoto, K. Yanagihara, M. Li, F. Tanaka, H. Wada, T. Manabe, and T. Saga. [18F]FDG uptake and PCNA, Glut-1, and Hexokinase-II expressions in cancers and inflammatory lesions of the lung. Neoplasia 7:369–379 (2005).
J. N. Li, M. Gorospe, F. J. Chrest, T. S. Kumaravel, M. K. Evans, W. F. Han, and E. S. Pizer. Pharmacological inhibition of fatty acid synthase activity produces both cytostatic and cytotoxic effects modulated by p53. Cancer Res. 61:1493–1499 (2001).
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the suggestions and comments of Dr. Jurgen Seidel and Michael Green of the National Institutes of Health, Clinical Center. This work was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute (P50 CA058184, R01 CA101232 and U24 CA92871).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jae Sung Lee and Hajime Orita contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.S., Orita, H., Gabrielson, K. et al. FDG-PET for Pharmacodynamic Assessment of the Fatty Acid Synthase Inhibitor C75 in an Experimental Model of Lung Cancer. Pharm Res 24, 1202–1207 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9264-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9264-x