Abstract
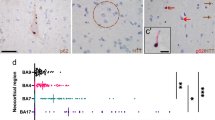
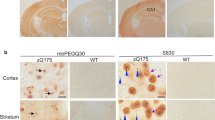
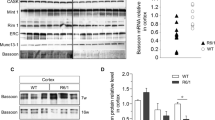
Huntington’s disease (HD) is caused by a polyglutamine repeat expansion in the N-terminus of the huntingtin protein. Huntingtin is normally present in the cytoplasm where it may interact with structural and synaptic elements. The mechanism of HD pathogenesis remains unknown but studies indicate a toxic gain-of-function possibly through aberrant protein interactions. To investigate whether early degenerative changes in HD involve alterations of cytoskeletal and vesicular components, we examined early cellular changes in the frontal cortex of HD presymptomatic (PS), early pathological grade (grade 1) and late-stage (grade 3 and 4) patients as compared to age-matched controls. Morphologic analysis using silver impregnation revealed a progressive decrease in neuronal fiber density and organization in pyramidal cell layers beginning in presymptomatic HD cases. Immunocytochemical analyses for the cytoskeletal markers α -tubulin, microtubule-associated protein 2, and phosphorylated neurofilament demonstrated a concomitant loss of staining in early grade cases. Immunoblotting for synaptic proteins revealed a reduction in complexin 2, which was marked in some grade 1 HD cases and significantly reduced in all late stage cases. Interestingly, we demonstrate that two synaptic proteins, dynamin and PACSIN 1, which were unchanged by immunoblotting, showed a striking loss by immunocytochemistry beginning in early stage HD tissue suggesting abnormal distribution of these proteins. We propose that mutant huntingtin affects proteins involved in synaptic function and cytoskeletal integrity before symptoms develop which may influence early disease onset and/or progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AVILA, J., DOMINGUEZ, J. & DIAZ-NIDO, J. (1994) Regulation of microtubule dynamics by microtubule-associated protein expression and phosphorylation during neuronal development. International Journal of Developmental Biology 38, 13–25.
AYLWARD, E. H., ANDERSON, N. B., BYLSMA, F. W., WAGSTER, M. V., BARTA, P. E., SHERR, M., FEENEY, J., DAVIS, A., ROSENBLATT, A., PEARLSON, G. D. & ROSS, C. A. (1998) Frontal lobe volume in patients with Huntington’s disease. Neurology 50, 252–258.
BEAL, M. F., KOWALL, N. W., ELLISON, D. W., MAZUREK, M. F., SWARTZ, K. J. & MARTIN, J. B. (1986) Replication of the neurochemical characteristics of Huntington’s disease by quinolinic acid. Nature 321, 168–171.
BERRIOS, G. E., WAGLE, A. C., MARKOVA, I. S., WAGLE, S. A., HO, L. W., RUBINSZTEIN, D. C., WHITTAKER, J., FFRENCH-CONSTANT, C., KERSHAW, A., ROSSER, A., BAK, T. & HODGES, J. R. (2001) Psychiatric symptoms and CAG repeats in neurologically asmptomatic Huntington’s disease carriers. Psychiatry Research 102, 217–225.
BLOCK-GALARZA, J., CHASE, K. O., SAPP, E., VAUGHN, K. T., VALLEE, R. B., DIFIGLIA, M. & ARONIN, N. (1997) Fast transport and retrograde movement of huntingtin and HAP 1 in axons. NeuroReport 8, 2247–2251.
BORDELON, Y. M. & CHESSELET, M. F. (1999) Early effects of intrastriatal injections of quinolinic acid on microtubule-associated protein-2 and neuropeptides in rat basal ganglia. Neuroscience 93, 843–853.
BRUGG, B. & MATUS, A. (1991) Phosphorylation determines the binding of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) to microtubules in living cells. Journal of Cell Biology 114, 735–743.
CEPEDA, C., HURST, R. S., CALVERT, C. R., HERNANDEZ-ECHEAGARAY, E., NGUYEN, O. K., JOCOY, E., CHRISTIAN, L. J., ARIANO, M. A. & LEVINE, M. S. (2003) Transient and progressive electrophysiological alterations in the corticostriatal pathway in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Journal of Neuroscience 23, 961–969.
CHA, J. H. (2000) Transcriptional dysregulation in Huntington’s disease. Trends in Neuroscience 23, 387–392.
CUDKOWICZ, M. & KOWALL, N. W. (1990) Degeneration of pyramidal projection neurons in Huntington’s disease cortex. Annals of Neurology 27, 200–204.
DE LA MONTE, S. M., VONSATTEL, J. P. & RICHARDSON, E. P., JR. (1988) Morphometric demonstration of atrophic changes in the cerebral cortex, white matter, and neostriatum in Huntington’s disease. Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology 47, 516–525.
DESAI, A. & MITCHISON, T. J. (1997) Microtubule polymerization dynamics. Annual Review of Cell & Developmental Biology 13, 83–117.
DEWHURST, K. (1969) Neuro-psychiatric aspects of Huntington’s disease. Confinia Neurologica 31, 258–268.
DIAZ-NIDO, J., MONTORO, R. J., LOPEZ-BARNEO, J. & AVILA, J. (1993) High external potassium induces an increase in the phosphorylation of the cytoskeletal protein MAP2 in rat hippocampal slices. European Journal of Neuroscience 5, 818–824.
DIFIGLIA, M., SAPP, E., CHASE, K., SCHWARZ, C., MELONI, A., YOUNG, C., MARTIN, E., VONSATTEL, J. P., CARRAWAY, R., & REEVES, S. A. (1995) Huntingtin is a cytoplasmic protein associated with vesicles in human and rat brain neurons. Neuron 14, 1075–1081.
DIFIGLIA, M., SAPP, E., CHASE, K. O., DAVIES, S. W., BATES, G. P., VONSATTEL, J. P. & ARONIN, N. (1997) Aggregation of huntingtin in neuronal intranuclear inclusions and dystrophic neurites in brain. Science 277, 1990–1993.
DOM, R., MALFROID, M. & BARO, F. (1976) Neuropathology of Huntington’s chorea. Studies of the ventrobasal complex of the thalamus. Neurology 26, 64–68.
ELDER, G. A., FRIEDRICH, V. L., JR., BOSCO, P., KANG, C., GOUROV, A., TU, P. H., LEE, V. M. & LAZZARINI, R. A. (1998a) Absence of the mid-sized neurofilament subunit decreases axonal calibers, levels of light neurofilament (NF-L), and neurofilament content. Journal of Cell Biology 141, 727–739.
ELDER, G. A., FRIEDRICH, V. L., JR., KANG, C., BOSCO, P., GOUROV, A., TU, P. H., ZHANG, B., LEE, V. M. & LAZZARINI, R. A. (1998b) Requirement of heavy neurofilament subunit in the development of axons with large calibers. Journal of Cell Biology 143, 195–205.
ENGQVIST-GOLDSTEIN, A. E., WARREN, R. A., KESSELS, M. M., KEEN, J. H., HEUSER, J. & DRUBIN, D. G. (2001) The actin-binding protein Hip1R associates with clathrin during early stages of endocytosis and promotes clathrin assembly in vitro. Journal of Cell Biology 154, 1209–1223.
FOLSTEIN, S. E. (1983) Psychiatric features of Huntington’s disease: Recent approaches and findings. Psychiatric Developments 1, 193–205.
FOROUD, T., SIEMERS, E., KLEINDORFER, D., BILL, D. J., HODES, M. E., NORTON, J. A., CONNEALLY, P. M. & CHRISTIAN, J. C. (1995) Cognitive scores in carriers of Huntington’s disease gene compared to noncarriers. Annals of Neurology 37, 657–664.
GUIDETTI, P., CHARLES, V., CHEN, E.-Y., REDDY, P. H., KORDOWER, J. H., WHETSELL, W. O., JR., SCHWARCZ, R. & TAGLE, D. A. (2001) Early degenerative changes in transgenic mice expressing mutant huntingtin involve dendritic abnormalities but no impairment of mitochondrial energy production. Experimental Neurology 169, 340–350.
GUNAWARDENA, S., HER, L. S., BRUSCH, R. G., LAYMON, R. A., NIESMAN, I. R., GORDESKY-GOLD, B., SINTASATH, L., BONINI, N. M. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (2003) Disruption of axonal transport by loss of huntingtin or expression of pathogenic polyQ proteins in Drosophila.[see comment]. Neuron 40, 25–40.
GUTEKUNST, C. A., LEVEY, A. I., HEILMAN, C. J., WHALEY, W. L., YI, H., NASH, N. R., REES, H. D., MADDEN, J. J. & HERSCH, S. M. (1995) Identification and localization of huntingtin in brain and human lymphoblastoid cell lines with anti-fusion protein antibodies. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 92, 8710–8714.
HALPAIN, S. & GREENGARD, P. (1990) Activation of NMDA receptors induces rapid dephosphorylation of the cytoskeletal protein MAP2. Neuron 5, 237–246.
HARJES, P. & WANKER, E. E. (2003) The hunt for huntingtin function: Interaction partners tell many different stories. Trends in Biochemical Science 28, 425–433.
HARMS, L., MEIERKORD, H., TIMM, G., PFEIFFER, L. & LUDOLPH, A. C. (1997) Decreased N-acetyl-aspartate/choline ratio and increased lactate in the frontal lobe of patients with Huntington’s disease: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry 62, 27–30.
HARPER, P. S. (1992) The epidemiology of Huntington’s disease. Human Genetics 89, 365–376.
HARRISON, P. J. & EASTWOOD, S. L. (1998) Preferential involvement of excitatory neurons in medial temporal lobe in schizophrenia. Lancet 352, 1669–1673.
HENZE, D. A., CAMERON, W. E. & BARRIONUEVO, G. (1996) Dendritic morphology and its effects on the amplitude and rise-time of synaptic signals in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells. Journal of Comparative Neurology 369, 331–344.
HICKS, R. R., SMITH, D. H. & MCINTOSH, T. K. (1995) Temporal response and effects of excitatory amino acid antagonism on microtubule-associated protein 2 immunoreactivity following experimental brain injury in rats. Brain Research 678, 151–160.
HUNTINGTON’S DISEASE COLLABORATIVE RESEARCH GROUP (1993) A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington’s disease chromosomes. Cell 72, 971–983.
JACKSON, M., GENTLEMAN, S., LENNOX, G., WARD, L., GRAY, T., RANDALL, K., MORRELL, K. & LOWE, J. (1995) The cortical neuritic pathology of Huntington’s disease. Neuropathology & Applied Neurobiology 21, 18–26.
JASON, G. W., SUCHOWERSKY, O., PAJURKOVA, E. M., GRAHAM, L., KLIMEK, M. L., GARBER, A. T. & POIRIER-HEINE, D. (1997) Cognitive manifestations of Huntington disease in relation to genetic structure and clinical onset. Archives of Neurology 54, 1081–1088.
JIAO, Y., SUN, Z., LEE, T., FUSCO, F. R., KIMBLE, T. D., MEADE, C. A., CUTHBERTSON, S. & REINER, A. (1999) A simple and sensitive antigen retrieval method for free-floating and slide-mounted tissue sections. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 93, 149–162.
JOHNSON, G. V. & JOPE, R. S. (1992) The role of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP-2) in neuronal growth, plasticity, and degeneration. Journal of Neuroscience Research 33, 505–512.
KAECH, S., LUDIN, B. & MATUS, A. (1996) Cytoskeletal plasticity in cells expressing neuronal microtubule-associated proteins. Neuron 17, 1189–1199.
LAFORET, G. A., SAPP, E., CHASE, K., MCINTYRE, C., BOYCE, F. M., CAMPBELL, M., CADIGAN, B. A., WARZECKI, L., TAGLE, D., REDDY, P. H., CEPEDA, C., CALVERT, C. R., JOKEL, E. S., KLAPSTEIN, G. J., ARIANO, M. A., LEVINE, M. S., DIFIGLIA, M. & ARONIN, N. (2001) Changes in cortical and striatal neurons predict behavioral and electrophysiological abnormalities in a transgenic murine model of Huntington’s disease. Journal of Neuroscience 21, 9112–9123.
LAWRENCE, A. D., HODGES, J. R., ROSSER, A. E., KERSHAW, A., FFRENCH-CONSTANT, C., RUBINSZTEIN, D. C., ROBBINS, T. W. & SAHAKIAN, B. J. (1998) Evidence for specific cognitive deficits in preclinical Huntington’s disease. Brain 121, 1329–1341.
LAWRENCE, A. D., SAHAKIAN, B. J., HODGES, J. R., ROSSER, A. E., LANGE, K. W. & ROBBINS, T. W. (1996) Executive and mnemonic functions in early Huntington’s disease. Brain 119, 1633–1645.
LEE, W. C., YOSHIHARA, M. & LITTLETON, J. T. (2004) Cytoplasmic aggregates trap polyglutamine-containing proteins and block axonal transport in a Drosophila model of Huntington’s disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 101, 3224–3229.
LI, H., LI, S. H., JOHNSTON, H., SHELBOURNE, P. F. & LI, X. J. (2000) Amino-terminal fragments of mutant huntingtin show selective accumulation in striatal neurons and synaptic toxicity [see comments]. Nature Genetics 25, 385–389.
LI, H., LI, S. H., YU, Z. X., SHELBOURNE, P. & LI, X. J. (2001) Huntingtin aggregate-associated axonal degeneration is an early pathological event in Huntington’s disease mice. Journal of Neuroscience 21, 8473–8481.
LI, M., SOBUE, G., DOYU, M., MUKAI, E., HASHIZUME, Y. & MITSUMA, T. (1995a) Primary sensory neurons in X-linked recessive bulbospinal neuropathy: Histopathology and androgen receptor gene expression. Muscle & Nerve 18, 301–308.
LI, X. J., LI, S. H., SHARP, A. H., NUCIFORA, F. C., JR., SCHILLING, G., LANAHAN, A., WORLEY, P., SNYDER, S. H. & ROSS, C. A. (1995b) A huntingtin-associated protein enriched in brain with implications for pathology. Nature 378, 398–402.
LUTHI-CARTER, R., STRAND, A., PETERS, N. L., SOLANO, S. M., HOLLINGSWORTH, Z. R., MENON, A. S., FREY, A. S., SPEKTOR, B. S., PENNEY, E. B., SCHILLING, G., ROSS, C. A., BORCHELT, D. R., TAPSCOTT, S. J., YOUNG, A. B., CHA, J. H. & OLSON, J. M. (2000) Decreased expression of striatal signaling genes in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Human Molecular Genetics 9, 1259–1271.
MANN, D. M., OLIVER, R. & SNOWDEN, J. S. (1993) The topographic distribution of brain atrophy in Huntington’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathologica 85, 553–559.
MATUS, A., BERNHARDT, R., BODMER, R. & ALAIMO, D. (1986) Microtubule-associated protein 2 and tubulin are differently distributed in the dendrites of developing neurons. Neuroscience 17, 371–389.
MCMURRAY, C. T. (2000) Neurodegeneration: Diseases of the cytoskeleton? Cell Death & Differentiation 7, 861–865.
METZLER, M., LEGENDRE-GUILLEMIN, V., GAN, L., CHOPRA, V., KWOK, A., MCPHERSON, P. S. & HAYDEN, M. R. (2001) HIP1 functions in clathrin-mediated endocytosis through binding to clathrin and adaptor protein 2. Journal of Biological Chemistry 276, 39271–39276.
MODREGGER, J., DIPROSPERO, N. A., CHARLES, V., TAGLE, D. A. & PLOMANN, M. (2002) PACSIN 1 interacts with huntingtin and is absent from synaptic varicosities in presymptomatic Huntington’s disease brains. Human Molecular Genetics 11, 2547–2558.
MORTON, A. J. & EDWARDSON, J. M. (2001) Progressive depletion of complexin II in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Journal of Neurochemistry 76, 166–172.
MORTON, A. J., FAULL, R. L. & EDWARDSON, J. M. (2001) Abnormalities in the synaptic vesicle fusion machinery in Huntington’s disease. Brain Research Bulletin 56, 111–117.
MURPHY, K. P., CARTER, R. J., LIONE, L. A., MANGIARINI, L., MAHAL, A., BATES, G. P., DUNNETT, S. B. & MORTON, A. J. (2000) Abnormal synaptic plasticity and impaired spatial cognition in mice transgenic for exon 1 of the human Huntington’s disease mutation. Journal of Neuroscience 20, 5115–5123.
NAGAI, Y., ONODERA, O., CHUN, J., STRITTMATTER, W. J. & BURKE, J. R. (1999) Expanded polyglutamine domain proteins bind neurofilament and alter the neurofilament network. Experimental Neurology 155, 195–203.
NICNIOCAILL, B., HARALDSSON, B., HANSSON, O., O’CONNOR, W. T. & BRUNDIN, P. (2001) Altered striatal amino acid neurotransmitter release monitored using microdialysis in R6/1 Huntington transgenic mice. European Journal of Neuroscience 13, 206–210.
ONO, S., BAUX, G., SEKIGUCHI, M., FOSSIER, P., MOREL, N. F., NIHONMATSU, I., HIRATA, K., AWAJI, T., TAKAHASHI, S. & TAKAHASHI, M. (1998) Regulatory roles of complexins in neurotransmitter release from mature presynaptic nerve terminals. European Journal of Neuroscience 10, 2143–2152.
PAULSON, H. L. & FISCHBECK, K. H. (1996) Trinucleotide repeats in neurogenetic disorders. Annual Review of Neuroscience 19, 79–107.
PLOMANN, M., LANGE, R., VOPPER, G., CREMER, H., HEINLEIN, U. A., SCHEFF, S., BALDWIN, S. A., LEITGES, M., CRAMER, M., PAULSSON, M. & BARTHELS, D. (1998) PACSIN, a brain protein that is upregulated upon differentiation into neuronal cells. European Journal of Biochemistry 256, 201–211.
SAPP, E., PENNEY, J., YOUNG, A., ARONIN, N., VONSATTEL, J. P. & DIFIGLIA, M. (1999) Axonal transport of N-terminal huntingtin suggests early pathology of corticostriatal projections in Huntington disease. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 58, 165–173.
SAPP, E., SCHWARZ, C., CHASE, K., BHIDE, P. G., YOUNG, A. B., PENNEY, J., VONSATTEL, J. P., ARONIN, N. & DIFIGLIA, M. (1997) Huntingtin localization in brains of normal and Huntington’s disease patients. Annals of Neurology 42, 604–612.
SCHNELL, S. A., STAINES, W. A. & WESSENDORF, M. W. (1999) Reduction of lipofuscin-like autofluorescence in fluorescently labeled tissue. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry 47, 719–730.
SHARP, A. H., LOEV, S. J., SCHILLING, G., LI, S. H., LI, X. J., BAO, J., WAGSTER, M. V., KOTZUK, J. A., STEINER, J. P., LO, A., ET AL. (1995) Widespread expression of Huntington’s disease gene (IT15) protein product. Neuron 14, 1065–1074.
SOLLNER, T. H. (2003) Regulated exocytosis and SNARE function (Review) Molecular Membrane Biology 20, 209–220.
SOLLNER, T., WHITEHEART, S. W., BRUNNER, M., ERDJUMENT-BROMAGE, H., GEROMANOS, S., TEMPST, P. & ROTHMAN, J. E. (1993) SNAP receptors implicated in vesicle targeting and fusion. Nature 362, 318–324.
SOTREL, A., PASKEVICH, P. A., KIELY, D. K., BIRD, E. D., WILLIAMS, R. S. & MYERS, R. H. (1991) Morphometric analysis of the prefrontal cortex in Huntington’s disease. Neurology 41, 1117–1123.
SOTREL, A., WILLIAMS, R. S., KAUFMANN, W. E. & MYERS, R. H. (1993) Evidence for neuronal degeneration and dendritic plasticity in cortical pyramidal neurons of Huntington’s disease: A quantitative Golgi study. Neurology 43, 2088–2096.
STRONG, T. V., TAGLE, D. A., VALDES, J. M., ELMER, L. W., BOEHM, K., SWAROOP, M., KAATZ, K. W., COLLINS, F. S. & ALBIN, R. L. (1993) Widespread expression of the human and rat Huntington’s disease gene in brain and nonneural tissues. Nature Genetics 5, 259–265.
SUHR, S. T., SENUT, M. C., WHITELEGGE, J. P., FAULL, K. F., CUIZON, D. B. & GAGE, F. H. (2001) Identities of sequestered proteins in aggregates from cells with induced polyglutamine expression. Journal of Cell Biology 153, 283–294.
SZEBENYI, G., MORFINI, G. A., BABCOCK, A., GOULD, M., YOUNG, M., FABER, P. W., MACDONALD, M. E., MCPHAUL, M. J. & BRADY, S. T. (2003) Neuropathic forms of huntingtin and androgen receptor inhibit fast axonal transport. Neuron 40, 41–52.
TAKAHASHI, S., UJIHARA, H., HUANG, G. Z., YAGYU, K. I., SANBO, M., KABA, H. & YAGI, T. (1999) Reduced hippocampal LTP in mice lacking a presynaptic protein: Complexin II. European Journal of Neuroscience 11, 2359–2366.
TROTTIER, Y., DEVYS, D., IMBERT, G., SAUDOU, F., AN, I., LUTZ, Y., WEBER, C., AGID, Y., HIRSCH, E. C. & MANDEL, J. L. (1995) Cellular localization of the Huntington’s disease protein and discrimination of the normal and mutated form [see comments]. Nature Genetics 10, 104–110.
TUKAMOTO, T., NUKINA, N., IDE, K. & KANAZAWA, I. (1997) Huntington’s disease gene product, huntingtin, associates with microtubules in vitro. Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research 51, 8–14.
USDIN, M. T., SHELBOURNE, P. F., MYERS, R. M. & MADISON, D. V. (1999) Impaired synaptic plasticity in mice carrying the Huntington’s disease mutation. Human Molecular Genetics 8, 839–846.
VELIER, J., KIM, M., SCHWARZ, C., KIM, T. W., SAPP, E., CHASE, K., ARONIN, N. & DIFIGLIA, M. (1998) Wild-type and mutant huntingtins function in vesicle trafficking in the secretory and endocytic pathways. Experimental Neurology 152, 34–40.
VONSATTEL, J. P., MYERS, R. H., STEVENS, T. J., FERRANTE, R. J., BIRD, E. D. & RICHARDSON, E. P., JR. (1985) Neuropathological classification of Huntington’s disease. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 44, 559–577.
WANKER, E. E., ROVIRA, C., SCHERZINGER, E., HASENBANK, R., WALTER, S., TAIT, D., COLICELLI, J. & LEHRACH, H. (1997) HIP-I: A huntingtin interacting protein isolated by the yeast two-hybrid system. Human Molecular Genetics 6, 487–495.
WOOLF, N. J. (1998) A structural basis for memory storage in mammals. Progress in Neurobiology 55, 59–77.
ZOGHBI, H. Y. & ORR, H. T. (2000) Glutamine repeats and neurodegeneration. Annual Review of Neuroscience 23, 217–247.
ZUCCATO, C., CIAMMOLA, A., RIGAMONTI, D., LEAVITT, B. R., GOFFREDO, D., CONTI, L., MACDONALD, M. E., FRIEDLANDER, R. M., SILANI, V., HAYDEN, M. R., TIMMUSK, T., SIPIONE, S. & CATTANEO, E. (2001) Loss of huntingtin-mediated BDNF gene transcription in Huntington’s disease. Science 293, 493–498.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DiProspero, N.A., Chen, EY., Charles, V. et al. Early changes in Huntington’s disease patient brains involve alterations in cytoskeletal and synaptic elements. J Neurocytol 33, 517–533 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11068-004-0514-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11068-004-0514-8