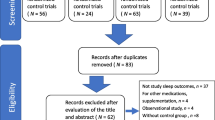
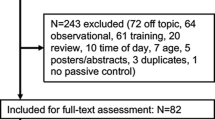
Abstract
A significant body of research has investigated the effects of physical activity on sleep, yet this research has not been systematically aggregated in over a decade. As a result, the magnitude and moderators of these effects are unclear. This meta-analytical review examines the effects of acute and regular exercise on sleep, incorporating a range of outcome and moderator variables. PubMed and PsycINFO were used to identify 66 studies for inclusion in the analysis that were published through May 2013. Analyses reveal that acute exercise has small beneficial effects on total sleep time, sleep onset latency, sleep efficiency, stage 1 sleep, and slow wave sleep, a moderate beneficial effect on wake time after sleep onset, and a small effect on rapid eye movement sleep. Regular exercise has small beneficial effects on total sleep time and sleep efficiency, small-to-medium beneficial effects on sleep onset latency, and moderate beneficial effects on sleep quality. Effects were moderated by sex, age, baseline physical activity level of participants, as well as exercise type, time of day, duration, and adherence. Significant moderation was not found for exercise intensity, aerobic/anaerobic classification, or publication date. Results were discussed with regards to future avenues of research and clinical application to the treatment of insomnia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
References marked with an asterisk indicate studies included in the meta-analysis
*Adamson, L., Hunter, W. M., Ogunremi, O. O., Oswald, I., & Percy-Robb, I. W. (1974). Growth hormone increase during sleep after daytime exercise. Journal of Endocrinology, 62, 473–478.
*Alessi, C. A., Martin, J. L., Webber, A. P., Cynthia Kim, E., Harker, J. O., & Josephson, K. R. (2005). Randomized, controlled trial of a nonpharmacological intervention to improve abnormal sleep/wake patterns in nursing home residents. Journal of the American Geriatriatric Society, 53, 803–810. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53251.x
*Alessi, C. A., Yoon, E. J., Schnelle, J. F., Al-Samarrai, N. R., & Cruise, P. A. (1999). A randomized trial of a combined physical activity and environmental intervention in nursing home residents: do sleep and agitation improve? Journal of the American Geriatriatric Society, 47, 784–791.
American College of Sports Medicine (2013). ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. USA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Astin, J. A., Shapiro, S. L., Eisenberg, D. M., & Forys, K. L. (2003). Mind-body medicine: State of the science, implications for practice. Journal of the American Board of Family Practice, 16, 131–147.
*Baekeland, F. (1970). Exercise deprivation. Sleep and psychological reactions. Archives of General Psychiatry, 22, 365–369.
*Baekeland, F., & Lasky, R. (1966). Exercise and sleep patterns in college athletes. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 23, 1203–1207.
Bastien, C. H., Vallieres, A., & Morin, C. M. (2001). Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index as an outcome measure for insomnia research. Sleep Medicine, 2, 297–307.
*Bevier, W. C., Bliwise, D. L., Bliwise, N. G., Bunnell, D. E., & Horvath, S. M. (1992). Sleep patterns of older adults and the effects of exercise. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Gerontology, 14, 1–15.
Borbély, A. A., Mattmann, P., Loepfe, M., Strauch, I., & Lehmann, D. (1984). Effect of benzodiazepine hypnotics on all-night sleep EEG spectra. Human Neurobiology, 4, 189–194.
Borenstein, Michael, Hedges, Larry, Higgins, Julian, & Rothstein, Hannah. (2005). Comprehensive meta-analysis version 2 (p. 104). Englewood, NJ: Biostat.
*Browman, C. P. (1980). Sleep following sustained exercise. Psychophysiology, 17, 577–580.
*Bulckaert, A., Exadaktylos, V., Haex, B., De Valck, E., Verbraecken, J., & Berckmans, D. (2011). Elevated variance in heart rate during slow-wave sleep after late-night physical activity. Chronobiology International, 28, 282–284. doi:10.3109/07420528.2011.552820
Buman, Matthew P., & King, Abby C. (2010). Exercise as a treatment to enhance sleep. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, 4, 500–514.
*Bunnell, D. E., Bevier, W. C., & Horvath, S. M. (1983a). Nocturnal sleep, cardiovascular function, and adrenal activity following maximum-capacity exercise. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 56, 186–189.
*Bunnell, D. E., Bevier, W., & Horvath, S. M. (1983b). Effects of exhaustive exercise on the sleep of men and women. Psychophysiology, 20, 50–58.
Carskadon, Mary A., & Dement, William C. (2000). Normal human sleep: An overview. Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine, 4, 13–23.
*Chen, K. M., Chen, M. H., Chao, H. C., Hung, H. M., Lin, H. S., & Li, C. H. (2009). Sleep quality, depression state, and health status of older adults after silver yoga exercises: Cluster randomized trial. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 46, 154–163. doi:10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2008.09.005
*Chen, K. M., Chen, M. H., Lin, M. H., Fan, J. T., Lin, H. S., & Li, C. H. (2010). Effects of yoga on sleep quality and depression in elders in assisted living facilities. Journal of Nursing Research, 18, 53–61. doi:10.1097/JNR.0b013e3181ce5189
*Chen, M. C., Liu, H. E., Huang, H. Y., & Chiou, A. F. (2012). The effect of a simple traditional exercise programme (Baduanjin exercise) on sleep quality of older adults: A randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 49, 265–273. doi:10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2011.09.009
Cochrane Collaboration (2011). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0. Retrieved from http://handbook.cochrane.org/
Cohen, J. (1977). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (rev). UK: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
*de Jong, J., Lemmink, K. A., Stevens, M., de Greef, M. H., Rispens, P., King, A. C., & Mulder, T. (2006). Six-month effects of the Groningen active living model (GALM) on physical activity, health and fitness outcomes in sedentary and underactive older adults aged 55–65. Patient Education and Counseling, 62, 132–141. doi:10.1016/j.pec.2005.06.017
*Desjardins, J., Healey, T., & Broughton, R. (1974). Early evening exercise and sleep. Sleep Research, 3, 447–450.
Dew, M. A., Hoch, C. C., Buysse, D. J., Monk, T. H., Begley, A. E., Houck, P. R., et al. (2003). Healthy older adults’ sleep predicts all-cause mortality at 4 to 19 years of follow-up. Psychosomatic Medicine, 65, 63–73.
Diekelmann, S., & Born, J. (2010). The memory function of sleep. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 11, 114–126. doi:10.1038/nrn2762
Dixon, E. M., Kamath, M. V., McCartney, N., & Fallen, E. L. (1992). Neural regulation of heart rate variability in endurance athletes and sedentary controls. Cardiovascular Research, 26, 713–719.
*Driver, H. S., Meintjes, A. F., Rogers, G. G., & Shapiro, C. M. (1988). Submaximal exercise effects on sleep patterns in young women before and after an aerobic training programme. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica. Supplementum, 574, 8–13.
*Driver, H. S., Rogers, G. G., Mitchell, D., Borrow, S. J., Allen, M., Luus, H. G., & Shapiro, C. M. (1994). Prolonged endurance exercise and sleep disruption. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 26, 903–907.
Driver, H. S., & Taylor, S. R. (2000). Exercise and sleep. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 4, 387–402. doi:10.1053/smrv.2000.0110
Duval, S., & Tweedie, R. (2000). Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics, 56, 455–463.
Edinger, J. D. (2009). Is it time to step up to stepped care with our cognitive-behavioral insomnia therapies? Sleep, 32, 1539–1541.
Ekkekakis, P., Hall, E. E., & Petruzzello, S. J. (2008). The relationship between exercise intensity and affective responses demystified: To crack the 40-year-old nut, replace the 40-year-old nutcracker! Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 35, 136–149. doi:10.1007/s12160-008-9025-z
*Elavsky, S., & McAuley, E. (2007). Lack of perceived sleep improvement after 4-month structured exercise programs. Menopause, 14, 535–540. doi:10.1097/01.gme.0000243568.70946.d4
Espie, C. A. (2009). “Stepped care”: A health technology solution for delivering cognitive behavioral therapy as a first line insomnia treatment. Sleep, 32, 1549–1558.
*Esteves, A. M., de Mello, M. T., Pradella-Hallinan, M., & Tufik, S. (2009). Effect of acute and chronic physical exercise on patients with periodic leg movements. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 41, 237–242. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e318183bb22
Field, Andy P. (2003). The problems in using fixed-effects models of meta-analysis on real-world data. Understanding Statistics: Statistical Issues in Psychology, Education, and the Social Sciences, 2, 105–124.
*Flausino, N. H., Da Silva Prado, J. M., de Queiroz, S. S., Tufik, S., & de Mello, M. T. (2012). Physical exercise performed before bedtime improves the sleep pattern of healthy young good sleepers. Psychophysiology, 49, 186–192. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8986.2011.01300.x
Follmann, D., Elliott, P., Suh, I. L., & Cutler, J. (1992). Variance imputation for overviews of clinical trials with continuous response. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 45, 769–773. doi:10.1016/0895-4356(92)90054-Q
*Frye, B., Scheinthal, S., Kemarskaya, T., & Pruchno, R. (2007). Tai chi and low impact exercise: Effects on the physical functioning and psychological well-being of older people. Journal of Applied Gerontology, 26, 433–453. doi:10.1177/0733464807306915
Furlan, R., Piazza, S., Dell’Orto, S., Gentile, E., Cerutti, S., Pagani, M., & Malliani, A. (1993). Early and late effects of exercise and athletic training on neural mechanisms controlling heart rate. Cardiovascular Research, 27, 482–488.
Garber, C. E., Blissmer, B., Deschenes, M. R., Franklin, B. A., Lamonte, M. J., Lee, I. M. et al. (2011). American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: Guidance for prescribing exercise. Medicine Science in Sports and Exercise, 43, 1334–1359. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e318213fefb
Glass, J., Lanctot, K. L., Herrmann, N., Sproule, B. A., & Busto, U. E. (2005). Sedative hypnotics in older people with insomnia: Meta-analysis of risks and benefits. BMJ, 331, 1169. doi:10.1136/bmj.38623.768588.47
Greenland, S., & O’Rourke, K. (2001). On the bias produced by quality scores in meta-analysis, and a hierarchical view of proposed solutions. Biostatistics, 2, 463–471. doi:10.1093/biostatistics/2.4.463
*Griffin, S. J., & Trinder, J. (1978). Physical fitness, exercise, and human sleep. Psychophysiology, 15, 447–450.
*Guilleminault, C., Clerk, A., Black, J., Labanowski, M., Pelayo, R., & Claman, D. (1995). Nondrug treatment trials in psychophysiologic insomnia. Archives of Internal Medicine, 155, 838–844.
*Hague, J. F., Gilbert, S. S., Burgess, H. J., Ferguson, S. A., & Dawson, D. (2003). A sedentary day: Effects on subsequent sleep and body temperatures in trained athletes. Physiology & Behavior, 78, 261–267.
Harvey, A. G. (2002). A cognitive model of insomnia. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 40, 869–893.
Higgins, J. P., Altman, D. G., Gotzsche, P. C., Juni, P., Moher, D., Oxman, A. D., et al. (2011). The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ, 343, d5928. doi:10.1136/bmj.d5928
Hootman, J. M., Macera, C. A., Ainsworth, B. E., Martin, M., Addy, C. L., & Blair, S. N. (2001). Association among physical activity level, cardiorespiratory fitness, and risk of musculoskeletal injury. American Journal of Epidemiology, 154, 251–258.
*Horne, J. A., & Moore, V. J. (1985). Sleep EEG effects of exercise with and without additional body cooling. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 60, 33–38.
*Horne, J. A., & Staff, L. H. (1983). Exercise and sleep: Body-heating effects. Sleep, 6, 36–46.
*Hosseini, H., Esfirizi, M. F., Marandi, S. M., & Rezaei, A. (2011). The effect of Ti Chi exercise on the sleep quality of the elderly residents in Isfahan, Sadeghieh elderly home. Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research, 16, 55–60.
Ives, J. C., & Sosnoff, J. (2000). Beyond the mind-body exercise hype. The Physician and Sportsmedicine, 28, 67–81. doi:10.3810/psm.2000.03.776
*Jennings, S. E. (1981). The Effects of a 9-week conditioning program on slow wave sleep and mood states of physically inactive women. (Doctor of Philosophy), Pennsylvania State University. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com.ezp-prod1.hul.harvard.edu/docview/303122521?accountid=11311
Juni, P., Witschi, A., Bloch, R., & Egger, M. (1999). The hazards of scoring the quality of clinical trials for meta-analysis. JAMA, 282, 1054–1060.
*Kalak, N., Gerber, M., Kirov, R., Mikoteit, T., Yordanova, J., Puhse, U., et al. (2012). Daily morning running for 3 weeks improved sleep and psychological functioning in healthy adolescents compared with controls. Journal of Adolescent Health, 51, 615–622. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2012.02.020
Kanaley, J. A., Weltman, J. Y., Veldhuis, J. D., Rogol, A. D., Hartman, M. L., & Weltman, A. (1997). Human growth hormone response to repeated bouts of aerobic exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology (1985), 83, 1756–1761.
*King, A. C., Baumann, K., O’Sullivan, P., Wilcox, S., & Castro, C. (2002). Effects of moderate-intensity exercise on physiological, behavioral, and emotional responses to family caregiving: A randomized controlled trial. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 57, M26–M36.
*King, A. C., Oman, R. F., Brassington, G. S., Bliwise, D. L., & Haskell, W. L. (1997). Moderate-intensity exercise and self-rated quality of sleep in older adults. A randomized controlled trial. JAMA, 277, 32–37.
*King, A. C., Pruitt, L. A., Woo, S., Castro, C. M., Ahn, D. K., Vitiello, M. V., et al. (2008). Effects of moderate-intensity exercise on polysomnographic and subjective sleep quality in older adults with mild to moderate sleep complaints. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 63, 997–1004.
*Kline, C. E., Sui, X., Hall, M. H., Youngstedt, S. D., Blair, S. N., Earnest, C. P., & Church, T. S. (2012). Dose-response effects of exercise training on the subjective sleep quality of postmenopausal women: Exploratory analyses of a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open, 2. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2012-001044
Kripke, D. F., Garfinkel, L., Wingard, D. L., Klauber, M. R., & Marler, M. R. (2002). Mortality associated with sleep duration and insomnia. Archives of General Psychiatry, 59, 131–136.
Kubitz, K. A., Landers, D. M., Petruzzello, S. J., & Han, M. (1996). The effects of acute and chronic exercise on sleep. A meta-analytic review. Sports Medicine, 21, 277–291.
*Kupfer, D. J., Sewitch, D. E., Epstein, L. H., Bulik, C., McGowen, C. R., & Robertson, R. J. (1985). Exercise and subsequent sleep in male runners: Failure to support the slow wave sleep-mood-exercise hypothesis. Neuropsychobiology, 14, 5–12.
Lattal, K. A. (2010). Delayed reinforcement of operant behavior. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 93, 129–139. doi:10.1901/jeab.2010.93-129
Lauderdale, D. S., Knutson, K. L., Yan, L. L., Liu, K., & Rathouz, P. J. (2008). Self-reported and measured sleep duration: How similar are they? Epidemiology, 19, 838–845. doi:10.1097/EDE.0b013e318187a7b0
*Littman, A. J., Vitiello, M. V., Foster-Schubert, K., Ulrich, C. M., Tworoger, S. S., Potter, J. D., et al. (2007). Sleep, ghrelin, leptin and changes in body weight during a 1-year moderate-intensity physical activity intervention. Int J Obes (Lond), 31, 466–475. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0803438
Lucidi, F., Devoto, A., Violani, C., De Gennaro, L., Mastracci, P., & Bertini, M. (1996). Rapid eye movements density as a measure of sleep need: REM density decreases linearly with the reduction of prior sleep duration. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 99, 556–561. doi:10.1016/S0013-4694(96)95671-0
Madden, G. J., & Bickel, W. K. (2010). Impulsivity: The behavioral and neurological science of discounting: Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Mallon, L., Broman, J. E., & Hetta, J. (2000). Relationship between insomnia, depression, and mortality: A 12-year follow-up of older adults in the community. International Psychogeriatrics, 12, 295–306.
*Manzaneque, J. M., Vera, F. M., Rodriguez, F. M., Garcia, G. J., Leyva, L., & Blanca, M. J. (2009). Serum cytokines, mood and sleep after a qigong program: is qigong an effective psychobiological tool? Journal of Health Psychology, 14, 60–67. doi:10.1177/1359105308097946
*Matsumoto, K., Saito, Y., Abe, M., & Furumi, K. (1984). The effects of daytime exercise on night sleep. Journal of Human Ergology (Tokyo), 13, 31–36.
McGinty, D., & Szymusiak, R. (1990). Keeping cool: A hypothesis about the mechanisms and functions of slow-wave sleep. Trends in Neurosciences, 13, 480–487.
Mellinger, G. D., Balter, M. B., & Uhlenhuth, E. H. (1985). Insomnia and its treatment. Prevalence and correlates. Archives of General Psychiatry, 42, 225–232.
*Montgomery, I., Trinder, J., Paxton, S., Fraser, G., Meaney, M., & Koerbin, G. L. (1985). Sleep disruption following a marathon. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness, 25, 69–74.
*Montgomery, I., Trinder, J., Paxton, S., Harris, D., Fraser, G., & Colrain, I. (1988). Physical exercise and sleep: the effect of the age and sex of the subjects and type of exercise. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica. Supplementum, 574, 36–40.
Montgomery, P., & Dennis, J. (2003). Cognitive behavioural interventions for sleep problems in adults aged 60+. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 1, CD003161. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd003161
*Montmayeur, A., Buguet, A., Sollin, H., & Lacour, J. R. (1994). Exercise and sleep in four African sportsmen living in the Sahel. A pilot study. International Journal of Sports Medicine, 15, 42–45. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1021018
Morin, C. M., Hauri, P. J., Espie, C. A., Spielman, A. J., Buysse, D. J., & Bootzin, R. R. (1999). Nonpharmacologic treatment of chronic insomnia. An American Academy of Sleep Medicine review. Sleep, 22, 1134–1156.
Morin, C. M., LeBlanc, M., Daley, M., Gregoire, J. P., & Merette, C. (2006). Epidemiology of insomnia: Prevalence, self-help treatments, consultations, and determinants of help-seeking behaviors. Sleep Medicine, 7, 123–130. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2005.08.008
*Morita, E., Imai, M., Okawa, M., Miyaura, T., & Miyazaki, S. (2011). A before and after comparison of the effects of forest walking on the sleep of a community-based sample of people with sleep complaints. Biopsychosoc Med, 5, 13. doi:10.1186/1751-0759-5-13
Morselli, L. L., Guyon, A., & Spiegel, K. (2012). Sleep and metabolic function. Pflugers Archiv, 463, 139–160. doi:10.1007/s00424-011-1053-z
*Myllymaki, T., Kyrolainen, H., Savolainen, K., Hokka, L., Jakonen, R., Juuti, T., et al. (2011). Effects of vigorous late-night exercise on sleep quality and cardiac autonomic activity. Journal of Sleep Research, 20, 146–153. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2869.2010.00874.x
*Myllymaki, T., Rusko, H., Syvaoja, H., Juuti, T., Kinnunen, M. L., & Kyrolainen, H. (2012). Effects of exercise intensity and duration on nocturnal heart rate variability and sleep quality. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 112, 801–809. doi:10.1007/s00421-011-2034-9
National Sleep Foundation (n.d.). Sleep aids and insomnia. Retrieved 2014, from http://sleepfoundation.org/sleep-disorders-problems/insomnia/sleep-aids-and-insomnia/page/0,1/.
*Naylor, E., Penev, P. D., Orbeta, L., Janssen, I., Ortiz, R., Colecchia, E. F., et al. (2000). Daily social and physical activity increases slow-wave sleep and daytime neuropsychological performance in the elderly. Sleep, 23, 87–95.
*Nguyen, M. H., & Kruse, A. (2012). A randomized controlled trial of Tai chi for balance, sleep quality and cognitive performance in elderly Vietnamese. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 7, 185–190. doi:10.2147/cia.s32600
*O’Connor, P. J., Breus, M. J., & Youngstedt, S. D. (1998). Exercise-induced increase in core temperature does not disrupt a behavioral measure of sleep. Physiology & Behavior, 64, 213–217.
*Oda, S. (2001). The effects of recreational underwater exercise in early evening on sleep for physically untrained male subjects. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 55, 179–181. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1819.2001.00816.x
Ohayon, M. M. (2002). Epidemiology of insomnia: What we know and what we still need to learn. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 6, 97–111.
Ohayon, M. M., Caulet, M., & Guilleminault, C. (1997). How a general population perceives its sleep and how this relates to the complaint of insomnia. Sleep, 20, 715–723.
Ohayon, M. M., Carskadon, M. A., Guilleminault, C., & Vitiello, M. V. (2004). Meta-analysis of quantitative sleep parameters from childhood to old age in healthy individuals: Developing normative sleep values across the human lifespan. Sleep, 27, 1255–1274.
Ohayon, M. M., & Roth, T. (2003). Place of chronic insomnia in the course of depressive and anxiety disorders. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 37, 9–15.
*Oudegeest-Sander, M. H., Eijsvogels, T. H., Verheggen, R. J., Poelkens, F., Hopman, M. T., Jones, H., & Thijssen, D. H. (2013). Impact of physical fitness and daily energy expenditure on sleep efficiency in young and older humans. Gerontology, 59, 8–16. doi:10.1159/000342213
*Passos, G. S., Poyares, D., Santana, M. G., Garbuio, S. A., Tufik, S., & Mello, M. T. (2010). Effect of acute physical exercise on patients with chronic primary insomnia. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 6, 270–275.
*Paxton, S. J., Montgomery, I., Trinder, J., Newman, J., & Bowling, A. (1982). Sleep after exercise of variable intensity in fit and unfit subjects. Australian Journal of Psychology, 34, 289–296. doi:10.1080/00049538208254724
*Paxton, S. J., Trinder, J., & Montgomery, I. (1983). Does aerobic fitness affect sleep? Psychophysiology, 20, 320–324.
Peigneux, P., Laureys, S., Fuchs, S., Collette, F., Perrin, F., Reggers, J., et al. (2004). Are spatial memories strengthened in the human hippocampus during slow wave sleep? Neuron, 44, 535–545. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2004.10.007
Pilcher, J. J., Ginter, D. R., & Sadowsky, B. (1997). Sleep quality versus sleep quantity: Relationships between sleep and measures of health, well-being and sleepiness in college students. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 42, 583–596.
*Pinniger, R., Thorsteinsson, E. B., Brown, R. F., & McKinley, P. (2013). Tango dance can reduce distress and insomnia in people with self-referred affective symptoms. American Journal of Dance Therapy, 35, 60–77. doi:10.1007/s10465-012-9141-y
Prentice, A. M., & Jebb, S. A. (2001). Beyond body mass index. Obesity Reviews, 2, 141–147.
Quera-Salva, M. A., Orluc, A., Goldenberg, F., & Guilleminault, C. (1991). Insomnia and use of hypnotics: Study of a French population. Sleep, 14, 386–391.
*Reid, K. J., Baron, K. G., Lu, B., Naylor, E., Wolfe, L., & Zee, P. C. (2010). Aerobic exercise improves self-reported sleep and quality of life in older adults with insomnia. Sleep Medicine, 11, 934–940. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2010.04.014
Requa, R. K., DeAvilla, L. N., & Garrick, J. G. (1993). Injuries in recreational adult fitness activities. American Journal of Sports Medicine, 21, 461–467.
Rhodes, R. E., Mark, R. S., & Temmel, C. P. (2012). Adult sedentary behavior: A systematic review. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 42, 3–28. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2011.10.020
*Richards, K. C., Lambert, C., Beck, C. K., Bliwise, D. L., Evans, W. J., Kalra, G. K., et al. (2011). Strength training, walking, and social activity improve sleep in nursing home and assisted living residents: Randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 59, 214–223. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.03246.x
Rosenthal, R. (1991). Meta-analytic procedures for social research (Vol. 6). Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Rosenthal, R., & Rubin, D. B. (1988). [Selection models and the file drawer problem]: Comment: Assumptions and procedures in the file drawer problem. Statistical Science, 3, 120–125.
Roth, T. (2007). Insomnia: Definition, prevalence, etiology, and consequences. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 3, S7–S10.
Routledge, F. S., Campbell, T. S., McFetridge-Durdle, J. A., & Bacon, S. L. (2010). Improvements in heart rate variability with exercise therapy. Canadian Journal of Cardiology, 26, 303–312.
Sandercock, G. R., Bromley, P. D., & Brodie, D. A. (2005). Effects of exercise on heart rate variability: Inferences from meta-analysis. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 37, 433–439.
Santos, R. V., Tufik, S., & De Mello, M. T. (2007). Exercise, sleep and cytokines: Is there a relation? Sleep Medicine Reviews, 11, 231–239. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2007.03.003
Sarris, J., & Byrne, G. J. (2011). A systematic review of insomnia and complementary medicine. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 15, 99–106. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2010.04.001
Schroeder, J. (2012). Mind/body exercise: What is it? American College of Sports Medicine. Retrieved from http://www.acsm.org/access-public-information/articles/2012/01/19/mind-body-exercise-what-is-it-
Schwartz, S., McDowell Anderson, W., Cole, S. R., Cornoni-Huntley, J., Hays, J. C., & Blazer, D. (1999). Insomnia and heart disease: A review of epidemiologic studies. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 47, 313–333.
Semler, C. N., & Harvey, A. G. (2005). Misperception of sleep can adversely affect daytime functioning in insomnia. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 43, 843–856. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2004.06.016
*Shapiro, C. M., Bortz, R., Mitchell, D., Clarke, R. A. I., & Jooste, P. L. (1985). Effect of exercise in a hot environment on human sleep patterns. South African Journal of Science, 81, 624–627.
Shapiro, C. M., Warren, P. M., Trinder, J., Paxton, S. J., Oswald, I., Flenley, D. C., & Catterall, J. R. (1984). Fitness facilitates sleep. European Journal of Applied Physiology and Occupational Physiology, 53, 1–4.
Shochat, T., Umphress, J., Israel, A. G., & Ancoli-Israel, S. (1999). Insomnia in primary care patients. Sleep, 22, S359–S365.
Simon, G. E., & VonKorff, M. (1997). Prevalence, burden, and treatment of insomnia in primary care. American Journal of Psychiatry, 154, 1417–1423.
Smith, M. T., Perlis, M. L., Park, A., Smith, M. S., Pennington, J., Giles, D. E., & Buysse, D. J. (2002). Comparative meta-analysis of pharmacotherapy and behavior therapy for persistent insomnia. American Journal of Psychiatry, 159, 5–11.
Stepanski, E. J., & Wyatt, J. K. (2003). Use of sleep hygiene in the treatment of insomnia. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 7, 215–225.
*Trinder, J., Bruck, D., Paxton, S. J., Montgomery, I., & Bowling, A. (1982). Physical-fitness, exercise, age and human sleep. Australian Journal of Psychology, 34, 131–138. doi:10.1080/00049538208257806
*Tworoger, S. S., Yasui, Y., Vitiello, M. V., Schwartz, R. S., Ulrich, C. M., Aiello, E. J., et al. (2003). Effects of a yearlong moderate-intensity exercise and a stretching intervention on sleep quality in postmenopausal women. Sleep, 26, 830–836.
Uchida, S., Shioda, K., Morita, Y., Kubota, C., Ganeko, M., & Takeda, N. (2012). Exercise effects on sleep physiology. Frontiers in Neurology, 3, 48. doi:10.3389/fneur.2012.00048
Vanhees, L., Lefevre, J., Philippaerts, R., Martens, M., Huygens, W., Troosters, T., & Beunen, G. (2005). How to assess physical activity? How to assess physical fitness? European Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation, 12, 102–114.
*Vein, A. M., Sidorov, A. A., Murtazaev, M. S., Karlov, A. V., et al. (1991). Physical exercise and nocturnal sleep in healthy humans. Human Physiology, 17, 391–397.
Vevea, Jack L., & Woods, Carol M. (2005). Publication bias in research synthesis: Sensitivity analysis using a priori weight functions. Psychological Methods, 10, 428.
*Viana, V. A., Esteves, A. M., Boscolo, R. A., Grassmann, V., Santana, M. G., Tufik, S., & de Mello, M. T. (2012). The effects of a session of resistance training on sleep patterns in the elderly. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 112, 2403–2408. doi:10.1007/s00421-011-2219-2
*Walker, J. M., Floyd, T. C., Fein, G., Cavness, C., Lualhati, R., & Feinburg, I. (1978). Effects of exercise on sleep. Journal of Applied Physiology: Respiratory, Environmental and Exercise Physiology, 44, 945–951.
Walker, M. P., & van der Helm, E. (2009). Overnight therapy? The role of sleep in emotional brain processing. Psychological Bulletin, 135, 731–748. doi:10.1037/a0016570
*Wong, S. N., Halaki, M., & Chow, C. M. (2013). The effects of moderate to vigorous aerobic exercise on the sleep need of sedentary young adults. Journal of Sports Sciences, 31, 381–386. doi:10.1080/02640414.2012.733823
Yang, P. Y., Ho, K. H., Chen, H. C., & Chien, M. Y. (2012). Exercise training improves sleep quality in middle-aged and older adults with sleep problems: A systematic review. Journal of Physiotherapy, 58, 157–163. doi:10.1016/s1836-9553(12)70106-6
*Yeh, S. C., & Chang, M. Y. (2012). The effect of Qigong on menopausal symptoms and quality of sleep for perimenopausal women: A preliminary observational study. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 18, 567–575. doi:10.1089/acm.2011.0133
Youngstedt, S. D., O’Connor, P. J., & Dishman, R. K. (1997). The effects of acute exercise on sleep: A quantitative synthesis. Sleep, 20, 203–214.
Zagaar, M., Dao, A., Alhaider, I., & Alkadhi, K. (2013). Regular treadmill exercise prevents sleep deprivation-induced disruption of synaptic plasticity and associated signaling cascade in the dentate gyrus. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 56, 375–383. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2013.07.011
Zeitlhofer, J., Schmeiser-Rieder, A., Tribl, G., Rosenberger, A., Bolitschek, J., & Kapfhammer, G. (2000). Sleep and quality of life in the Austrian population. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 102, 249–257.
*Zir, L. M., Smith, R. A., & Parker, D. C. (1971). Human growth hormone release in sleep: Effect of daytime exercise. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 32, 662–665. doi:10.1210/jcem-32-5-6
Conflict of interest
M. Alexandra Kredlow, Michelle C. Capozzoli, Bridget A. Hearon and Amanda W. Calkins declare that they have no conflicts of interest. In the past 2 years, Michael W. Otto has served as a paid consultant for MicroTransponder Inc., Concert Pharmaceuticals, and ProPhase; provided expert consensus opinion for Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, received royalty support for use of the SIGH-A from ProPhase, and received book royalties from Oxford University Press, Routledge, and Springer.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
The authors of this manuscript conform to the Helsinki Declaration concerning informed consent and human rights and follow correct procedures concerning experimental studies involving humans.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kredlow, M.A., Capozzoli, M.C., Hearon, B.A. et al. The effects of physical activity on sleep: a meta-analytic review. J Behav Med 38, 427–449 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-015-9617-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-015-9617-6