Abstract
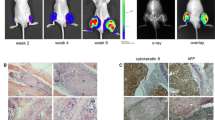
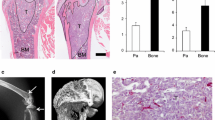
Metastatic bone disease caused by renal cell carcinoma (RCC) occurs frequently and becomes more and more prevalent presumably because survival times among patients with disseminated cancers are increasing. Patients with bone metastases from renal cell carcinoma suffer from severe pain, nerve compression syndromes and pathologic fractures. Very little is known about the mechanisms of skeletal metastases of RCC. Thus, to better understand the molecular mechanism of renal cell cancer (RCC) bone metastasis, it is crucial to develop new animal models. We have established a new animal model of RCC metastasis to bone by inoculation of human 786-O/luciferase cells into the left cardiac ventricle of athymic nude mice. The animals developed aggressive osteolytic bone destruction as monitored by radiography and micro-CT-scans with the mean endpoint at 62 ± 8 days. The extensive bone destruction observed was comparable to the clinical setting and mainly occurred in hind limbs, forelimbs and the spine. The tumors were primarily located within the bone and resulted in destruction of cortical bone. No soft tissue metastases were detected by BLI or histomorphometry. To increase the bone-metastatic potential of the 786-O cell line, an in vivo selection was done yielding a subpopulation causing osteolytic lesions with the mean endpoint of 47 ± 3 days. The selected subline secreted more proangiogenic factors VEGF and bFGF in vitro compared to the parental cell line suggesting that these tumors are highly vascular. This model provides a reliable reproduction of the clinical situation and therefore, is suitable for designing and evaluating more effective treatments for RCC bone metastasis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- bFGF:
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor
- luc:
-
Luciferase
References
Figlin RA (1999) Renal cell carcinoma: management of advanced disease. J Urol 161(2):381–386 (discussion 386-387)
Zekri J et al (2001) The skeletal metastatic complications of renal cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 19(2):379–382
Galasko CS (1981) Bone metastases studied in experimental animals. Clin Orthop Relat Res 155:269–285
Jemal A et al (2004) Cancer statistics, 2004. CA Cancer J Clin 54(1):8–29
Durr HR et al (1999) Surgical treatment of osseous metastases in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Clin Orthop Relat Res 367:283–290
Iwai A et al (2004) Down-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in renal cell carcinoma cells by glucocorticoids. Mol Cell Endocrinol 226(1–2):11–17
Takahashi A et al (1994) Markedly increased amounts of messenger RNAs for vascular endothelial growth factor and placenta growth factor in renal cell carcinoma associated with angiogenesis. Cancer Res 54(15):4233–4237
Motzer RJ, Russo P (2000) Systemic therapy for renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 163(2):408–417
Weber K, Doucet M, Kominsky S (2007) Renal cell carcinoma bone metastasis–elucidating the molecular targets. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26(3–4):691–704
Kominsky SL et al (2007) TGF-beta promotes the establishment of renal cell carcinoma bone metastasis. J Bone Miner Res 22(1):37–44
Mydlo JH et al (1989) Expression of transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor messenger RNA in neoplastic and nonneoplastic human kidney tissue. Cancer Res 49(12):3407–3411
Weber KL et al (2002) Characterization of a renal cell carcinoma cell line derived from a human bone metastasis and establishment of an experimental nude mouse model. J Urol 168(2):774–779
Takahashi N et al (1986) Recombinant human transforming growth factor-alpha stimulates the formation of osteoclast-like cells in long-term human marrow cultures. J Clin Invest 78(4):894–898
Pan J et al (2006) Stromal derived factor-1 (SDF-1/CXCL12) and CXCR4 in renal cell carcinoma metastasis. Mol Cancer 5:56
Rosol TJ et al (2003) Animal models of bone metastasis. Cancer 97(3 Suppl):748–757
Arguello F, Baggs RB, Frantz CN (1988) A murine model of experimental metastasis to bone and bone marrow. Cancer Res 48(23):6876–6881
Yoneda T et al (1997) Inhibition of osteolytic bone metastasis of breast cancer by combined treatment with the bisphosphonate ibandronate and tissue inhibitor of the matrix metalloproteinase-2. J Clin Invest 99(10):2509–2517
Yin JJ et al (1999) TGF-beta signaling blockade inhibits PTHrP secretion by breast cancer cells and bone metastases development. J Clin Invest 103(2):197–206
Coleman RE (1997) Skeletal complications of malignancy. Cancer 80(8 Suppl):1588–1594
Milowsky MI, Nanus DM (2003) Chemotherapeutic strategies for renal cell carcinoma. Urol Clin North Am 30(3):601–609
Motzer RJ et al (1997) Renal cell carcinoma. Curr Probl Cancer 21(4):185–232
Vuky J et al (2006) Phase II trial of imatinib (Gleevec) in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Invest New Drugs 24(1):85–88
Leibovich BC, Blute ML (2006) Surgical management of renal cell carcinoma. Semin Oncol 33(5):552–562
Lorincz T, Timar J, Szendroi M (2004) Alterations of microvascular density in bone metastases of adenocarcinomas. Pathol Oncol Res 10(3):149–153
Fidler IJ, Kripke ML (1977) Metastasis results from preexisting variant cells within a malignant tumor. Science 197(4306):893–895
Kang Y et al (2003) A multigenic program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Cell 3(6):537–549
Ling V et al (1985) Quantitative genetic analysis of tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 4(2):173–192
Dvorak HF (2002) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a critical cytokine in tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and therapy. J Clin Oncol 20(21):4368–4380
Rini BI, Small EJ (2005) Biology and clinical development of vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy in renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 23(5):1028–1043
Gorospe M et al (1999) Protective function of von Hippel-Lindau protein against impaired protein processing in renal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 19(2):1289–1300
Semenza G (2002) Signal transduction to hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Biochem Pharmacol 64(5–6):993–998
van Spronsen DJ et al (2005) Novel treatment strategies in clear-cell metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Drugs 16(7):709–717
Iguchi H et al (2002) A possible role of VEGF in osteolytic bone metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 21(3):309–313
Yang Q et al (2008) VEGF enhancement of osteoclast survival and bone resorption involves VEGF receptor-2 signaling and beta3-integrin. Matrix Biol 27(7):589–599
Hurley MM et al (1998) Basic fibroblast growth factor induces osteoclast formation in murine bone marrow cultures. Bone 22(4):309–316
Guise TA et al (2002) Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP)-(1-139) isoform is efficiently secreted in vitro and enhances breast cancer metastasis to bone in vivo. Bone 30(5):670–676
Kakonen SM, Mundy GR (2003) Mechanisms of osteolytic bone metastases in breast carcinoma. Cancer 97(3 Suppl):834–839
Paule B (2001) Interleukin-6 and bone metastasis of renal cancer: molecular bases and therapeutic implications. Prog Urol 11(2):368–375
Manolagas SC (1995) Role of cytokines in bone resorption. Bone 17(2 Suppl):63S–67S
Bendre MS et al (2003) Interleukin-8 stimulation of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption is a mechanism for the increased osteolysis of metastatic bone disease. Bone 33(1):28–37
Girasole G et al (1994) Interleukin-11: a new cytokine critical for osteoclast development. J Clin Invest 93(4):1516–1524
Yoneda T, Sasaki A, Mundy GR (1994) Osteolytic bone metastasis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 32(1):73–84
Acknowledgements
We thank Bernd Hartmann, Ina Neumann, Christine Morgenroth, Meike Fehder, Wilhelm Ebel, Andreas Jung and Julia Meier for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strube, A., Stepina, E., Mumberg, D. et al. Characterization of a new renal cell carcinoma bone metastasis mouse model. Clin Exp Metastasis 27, 319–330 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-010-9329-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-010-9329-9