Abstract
Background
It is generally accepted that patients with breast cancer metastases have very poor survival. Metastatic breast cancer patients can be considered a heterogeneous population with a varied clinical course, which underscores the need for accurate prediction of survival based on prognostic factors. The purpose of the present study was to identify factors related to survival in breast cancer patients after diagnosis with metastatic disease.
Populations and methods
A total of 557 patients with breast cancer metastasis diagnosis seen at one large urban practice have been followed up between 1 January, 1999 and 30 June, 2010. Demographic, tumor characteristics, clinical factors as predictors of survival were analyzed using log-rank test and Cox regression model.
Results
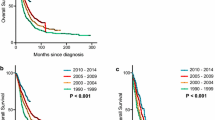
The median survival length was 39 months (range 1–138 months) with 154 (27.7%) alive and 403 (72.3%) dead at the end of follow-up period. This study demonstrated that a history of hypertension, ER/PR status, HER2 status, metastasis-free interval, metastatic location (including brain, bone and liver), and BMI at diagnosis with metastatic breast cancer were the most relevant prognostic factors for survival after metastatic disease diagnosis.
Conclusion
Findings of this study may form a foundation for the growing corpus of knowledge explaining the outcome differences in treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer, potentially helping to create tailored counseling and personalized treatment approaches for this vulnerable group.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program (SEER). SEER Stat Database: SEER Stat Fact Sheets; 2008
Wingo PA, Tong T, Bolden S (1995) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 45(1):8–30
Henderson IC, Harris JR, Kinne DW (1989) Cancer of the breast. In: De Vita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA (eds) Cancer principles & practice of oncology, 3rd edn. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 1197–1268
Chang J, Clark GM, Allred DC, Mohsin S, Chamness G, Elledge RM (2003) Survival of patients with metastatic breast carcinoma: importance of prognostic markers of the primary tumor. Cancer 97(3):545–553
Largillier R, Ferrero JM, Doyen J et al (2008) Prognostic factors in 1, 038 women with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol 19(12):2012–2019
Beslija S, Bonneterre J, Burstein HJ et al (2009) Third consensus on medical treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol 20(11):1771–1785
Vincent MD, Powles TJ, Skeet R et al (1986) An analysis of possible prognostic features of long term and short term survivors of metastatic breast cancer. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 22(9):1059–1065
Hortobagyi GN, Smith TL, Legha SS et al (1983) Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 1(12):776–786
Cluze C, Colonna M, Remontet L et al (2009) Analysis of the effect of age on the prognosis of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 117(1):121–129
Grau AM, Ata A, Foster L et al (2005) Effect of race on long-term survival of breast cancer patients: transinstitutional analysis from an inner city hospital and university medical center. Am Surg 71(2):164–170
Bradley CJ, Given CW, Roberts C (2002) Race, socioeconomic status, and breast cancer treatment and survival. J Natl Cancer Inst 94(7):490–496
Lagerlund M, Bellocco R, Karlsson P, Tejler G, Lambe M (2005) Socio-economic factors and breast cancer survival—a population-based cohort study (Sweden). Cancer Causes Control 16(4):419–430
Dalton SO, During M, Ross L et al (2006) The relation between socioeconomic and demographic factors and tumour stage in women diagnosed with breast cancer in Denmark, 1983–1999. Br J Cancer 95(5):653–659
Rezaianzadeh A, Peacock J, Reidpath D, Talei A, Hosseini SV, Mehrabani D (2009) Survival analysis of 1148 women diagnosed with breast cancer in Southern Iran. BMC Cancer 9:168
Bouchardy C, Verkooijen HM, Fioretta G (2006) Social class is an important and independent prognostic factor of breast cancer mortality. Int J Cancer 119(5):1145–1151
Tao MH, Shu XO, Ruan ZX, Gao YT, Zheng W (2006) Association of overweight with breast cancer survival. Am J Epidemiol 163(2):101–107
Caan BJ, Kwan ML, Hartzell G et al (2008) Pre-diagnosis body mass index, post-diagnosis weight change, and prognosis among women with early stage breast cancer. Cancer Causes Control 19(10):1319–1328
Berclaz G, Li S, Price KN et al (2004) Body mass index as a prognostic feature in operable breast cancer: the International Breast Cancer Study Group experience. Ann Oncol 15(6):875–884
Loi S, Milne RL, Friedlander ML et al (2005) Obesity and outcomes in premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14(7):1686–1691
Whiteman MK, Hillis SD, Curtis KM, McDonald JA, Wingo PA, Marchbanks PA (2005) Body mass and mortality after breast cancer diagnosis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14(8):2009–2014
West DW, Satariano WA, Ragland DR, Hiatt RA (1996) Comorbidity and breast cancer survival: a comparison between black and white women. Ann Epidemiol 6(5):413–419
Nagel G, Wedding U, Rohrig B, Katenkamp D (2004) The impact of comorbidity on the survival of postmenopausal women with breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130(11):664–670
Cronin-Fenton DP, Norgaard M, Jacobsen J et al (2007) Comorbidity and survival of Danish breast cancer patients from 1995 to 2005. Br J Cancer 96(9):1462–1468
Gordon NH, Silverman P, Lasheen W, Meinert J, Siminoff LA (2007) Thirty-year follow-up of chemo/hormonal therapy in node-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 102(3):301–312
Braithwaite D, Tammemagi CM, Moore DH et al (2009) Hypertension is an independent predictor of survival disparity between African-American and white breast cancer patients. Int J Cancer 124(5):1213–1219
Ahern TP, Lash TL, Thwin SS, Silliman RA (2009) Impact of acquired comorbidities on all-cause mortality rates among older breast cancer survivors. Med Care 47(1):73–79
Ruiterkamp J, Ernst MF, van de Poll-Franse LV, Bosscha K, Tjan-Heijnen VC, Voogd AC (2009) Surgical resection of the primary tumour is associated with improved survival in patients with distant metastatic breast cancer at diagnosis. Eur J Surg Oncol 35(11):1146–1151
Census 2000 summary file 3 (SF 3): U.S. Census Bureau; 2000
American Heart Association. What Is High Blood Pressure? http://www.americanheart.org/presenter.jhtml?identifier=2114. Accessed August 1, 2009
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR (1987) A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis 40(5):373–383
Deyo RA, Cherkin DC, Ciol MA (1992) Adapting a clinical comorbidity index for use with ICD-9-CM administrative databases. J Clin Epidemiol 45(6):613–619
Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB (1977) Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Methodological) 39(1):1–38
Hosmer DW Jr, Lemeshow S (1999) Applied survival analysis. Wiley Interscience, London
Swenerton KD, Legha SS, Smith T et al (1979) Prognostic factors in metastatic breast cancer treated with combination chemotherapy. Cancer Res 39(5):1552–1562
Falkson G, Gelman R, Falkson CI, Glick J, Harris J (1991) Factors predicting for response, time to treatment failure, and survival in women with metastatic breast cancer treated with DAVTH: a prospective Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 9(12):2153–2161
Insa A, Lluch A, Prosper F, Marugan I, Martinez-Agullo A, Garcia-Conde J (1999) Prognostic factors predicting survival from first recurrence in patients with metastatic breast cancer: analysis of 439 patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 56(1):67–78
Cutler SJ, Ardyce JA, Taylor SG III (1969) Classification of patients with disseminated cancer of the breast. Cancer 24(5):861–869
Ryberg M, Nielsen D, Osterlind K, Skovsgaard T, Dombernowsky P (2001) Prognostic factors and long-term survival in 585 patients with metastatic breast cancer treated with epirubicin-based chemotherapy. Ann Oncol 12(1):81–87
Robain M, Pierga JY, Jouve M et al (2000) Predictive factors of response to first-line chemotherapy in 1426 women with metastatic breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 36(18):2301–2312
Andre F, Slimane K, Bachelot T et al (2004) Breast cancer with synchronous metastases: trends in survival during a 14-year period. J Clin Oncol 22(16):3302–3308
Yamamoto N, Watanabe T, Katsumata N et al (1998) Construction and validation of a practical prognostic index for patients with metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 16(7):2401–2408
Vogel CL, Azevedo S, Hilsenbeck S, East DR, Ayub J (1992) Survival after first recurrence of breast cancer The Miami experience. Cancer 70(1):129–135
Solomayer EF, Diel IJ, Meyberg GC, Gollan C, Bastert G (2000) Metastatic breast cancer: clinical course, prognosis and therapy related to the first site of metastasis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 59(3):271–278
Goldhirsch A, Gelber RD, Castiglione M (1988) Relapse of breast cancer after adjuvant treatment in premenopausal and perimenopausal women: patterns and prognoses. J Clin Oncol 6(1):89–97
Hortobagyi GN, Kau S-W, Buzdar AU, et al. (2004) What is the prognosis of patients with operable breast cancer (BC) five years after diagnosis? [Abstract]. J Clin Oncol, In: ASCO annual meeting proceedings (Post-Meeting Edition), vol 22(14S, July 15 Supplement), p 585
Grasic-Kuhar C, Bracko M, Zakotnik B (2008) Risk factors for late relapse and death in patients with early breast cancer. Neoplasma 55(5):416–420
EBCTCG (2005) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 365(9472):1687–1717
Hamet P (1996) Cancer and hypertension. An unresolved issue. Hypertension 28(3):321–324
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, S.Y., Rosenzweig, M., Sereika, S.M. et al. Factors associated with mortality after breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Causes Control 23, 103–112 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-011-9859-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-011-9859-8