Abstract
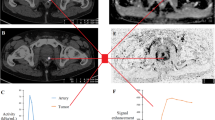
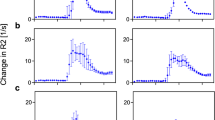
The aim of the present study was to quantify both perfusion and extravasation in the prostate to discriminate tumor from healthy tissue, which might be achieved by dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) using a nonspecific low-molecular-weight contrast medium (CM). To determine extravasation as well as tissue perfusion an inversion-prepared dual-contrast sequence employing a parallel acquisition technique (PAT) was designed for interleaved acquisition of T 1-weighted images for extravasation measurement and T2\( T^{\ast}_{2} \)-weighted images for determination of the highly concentrated bolus with a sufficiently high temporal and spatial resolution at an acceptable signal-to-noise ratio. Thirteen patients with proven prostate cancer were examined with the sequence using a combined body-array prostate coil. Before pharmacokinetic evaluation the images were intensity-corrected and, if required, motion-corrected. The pharmacokinetic model used to calculate perfusion, permeability, blood volume, interstitial volume, transit time, and vessel size index included two compartments and a correction of delay and dispersion of the arterial input function. The information provided by the dual-contrast sequence allowed application of a more elaborate model for evaluation and enabled quantification of all parameters. Peripheral prostate tumors were found to differ from peripheral healthy prostate tissue in perfusion (1.38 mL/(min cm3) vs. 0.23 mL/(min cm3), p = 0.004), mean transit time (2.88 vs. 4.88 s, p = 0.039), and blood volume (1.9 vs. 0.7%, p = 0.019). A inversion-prepared dual-contrast sequence acquiring T 1- and \( T^{\ast}_{2} \)-weighted images with sufficient temporal resolution and signal-to-noise ratio was successfully applied in patients with prostate cancer to quantify all pharmacokinetic parameters of inflow and extravasation of a low-molecular-weight inert tracer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benner T., Heiland S., Erb G., Forsting M., Sartor K. Accuracy of gamma-variate fits to concentration–time curves from dynamic susceptibility-contrast enhanced MRI: influence of time resolution, maximal signal drop and signal-to-noise. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1997;15(3):307–17
Beyersdorff D., Taupitz M., Winkelmann B., Fischer T., Lenk S., Loening S.A., Hamm B. Patients with a history of elevated prostate-specific antigen levels and negative transrectal US-guided quadrant or sextant biopsy results: value of MR imaging. Radiology 2002;224(3):701–6
Bostwick D.G., Wheeler T.M., Blute M., Barrett D.M., MacLennan G.T., Sebo T.J., Scardino P.T., Humphrey P.A., Hudson M.A., Fradet Y., et al. Optimized microvessel density analysis improves prediction of cancer stage from prostate needle biopsies. Urology 1996;48(1):47–57
Brawer M.K., Deering R.E., Brown M., Preston S.D., Bigler S.A. Predictors of pathologic stage in prostatic carcinoma. The role of neovascularity. Cancer 1994;73(3):678–87
Brix G., Kiessling F., Lucht R., Darai S., Wasser K., Delorme S., Griebel J. Microcirculation and microvasculature in breast tumors: pharmacokinetic analysis of dynamic MR image series. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004;52(2):420–9
Buckley D.L., Roberts C., Parker G.J., Logue J.P., Hutchinson C.E. Prostate cancer: evaluation of vascular characteristics with dynamic contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR imaging–initial experience. Radiology 2004;233(3):709–15
Calamante F., Gadian D.G., Connelly A. Delay, dispersion effects in dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI: simulations using singular value decomposition. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000;44(3):466–73
Calamante F., Thomas D.L., Pell G.S., Wiersma J., Turner R. Measuring cerebral blood flow using magnetic resonance imaging techniques. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1999;19(7):701–35
Chandler J.D. Subroutine STEPIT: Finds local minima of a smooth function of several parameters. Behavioral Science 1969;14:81–82
Checkley D., Tessier J.J., Kendrew J., Waterton J.C., Wedge S.R. Use of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI to evaluate acute treatment with ZD6474, a VEGF signalling inhibitor, in PC-3 prostate tumours. Br J Cancer 2003;89(10):1889–95
Daldrup H., Shames D.M., Wendland M., Okuhata Y., Link T.M., Rosenau W., Lu Y., Brasch R.C. Correlation of dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging with histologic tumor grade: comparison of macromolecular and small-molecular contrast media. AJR-Am-J-Roentgenol 1998;171(4):941–9
de Bazelaire C., Rofsky N.M., Duhamel G., Zhang J., Michaelson M.D., George D., Alsop D.C. Combined T2* and T1 measurements for improved perfusion and permeability studies in high field using dynamic contrast enhancement. Eur Radiol 2006;16(9):2083–91
Degani H., Gusis V., Weinstein D., Fields S., Strano S. Mapping pathophysiological features of breast tumors by MRI at high spatial resolution. Nat Med 1997;3(7):780–2
Dennie J., Mandeville J.B., Boxerman J.L., Packard S.D., Rosen B.R., Weisskoff R.M. NMR imaging of changes in vascular morphology due to tumor angiogenesis. Magn. Reson. Med. 1998;40(6):793–9
Dennis L.K., Resnick M.I. Analysis of recent trends in prostate cancer incidence and mortality. Prostate 2000;42(4):247–52
Donahue K.M., Weisskoff R.M., Parmelee D.J., Callahan R.J., Wilkinson R.A., Mandeville J.B., Rosen B.R. Dynamic Gd-DTPA enhanced MRI measurement of tissue cell volume fraction. Magn-Reson-Med 1995;34(3):423–32
Fritz Hansen T., Rostrup E., Sondergaard L., Ring P.B., Amtorp O., Larsson H.B. Capillary transfer constant of Gd-DTPA in the myocardium at rest and during vasodilation assessed by MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1998;40(6):922–9
Gleason D.F., Mellinger G.T. Prediction of prognosis for prostatic adenocarcinoma by combined histological grading and clinical staging. J-Urol 1974;111(1):58–64
Griswold M.A., Jakob P.M., Heidemann R.M., Nittka M., Jellus V., Wang J., Kiefer B., Haase A. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn. Reson. Med. 2002;47(6):1202–10
Hara N., Okuizumi M., Koike H., Kawaguchi M., Bilim V. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) is a useful modality for the precise detection and staging of early prostate cancer. Prostate 2005;62(2):140–7
Harrer J.U., Parker G.J., Haroon H.A., Buckley D.L., Embelton K., Roberts C., Baleriaux D., Jackson A. Comparative study of methods for determining vascular permeability and blood volume in human gliomas. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004;20(5):748–57
Heverhagen J.T., von Tengg-Kobligk H., Baudendistel K.T., Jia G., Polzer H., Henry H., Levine A.L., Rosol T.J., Knopp M.V. Benign prostate hyperplasia: evaluation of treatment response with DCE MRI. Magma 2004;17(1):5–11
Hricak H., White S., Vigneron D., Kurhanewicz J., Kosco A., Levin D., Weiss J., Narayan P., Carroll P.R. Carcinoma of the prostate gland: MR imaging with pelvic phased-array coils versus integrated endorectal–pelvic phased-array coils. Radiology 1994;193(3):703–9
Inaba T. Quantitative measurements of prostatic blood flow and blood volume by positron emission tomography. J Urol 1992;148(5):1457–60
Jenkinson M., Smith S. A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med Image Anal 2001;5(2):143–56
Jiang L., Zhao D., Constantinescu A., Mason R.P. Comparison of BOLD contrast and Gd-DTPA dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging in rat prostate tumor. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004;51(5):953–60
Johnson G., Wetzel S.G., Cha S., Babb J., Tofts P.S. Measuring blood volume and vascular transfer constant from dynamic, T(2)*-weighted contrast-enhanced MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004;51(5):961–8
Kershaw L.E., Buckley D.L. Precision in measurements of perfusion and microvascular permeability with T1-weighted dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006;56(5):986–92
Kety S.S., Axel L., Hoop B. Principles of conventional techniques. In: Bihan-D L. editor. Diffusion and Perfusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging. New York: Raven Press; 1995. p 201–215
Kiessling F., Huber P.E., Grobholz R., Heilmann M., Meding J., Lichy M.P., Fink C., Krix M., Peschke P., Schlemmer H.P. Dynamic magnetic resonance tomography and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of prostate cancers in rats treated by radiotherapy. Invest Radiol 2004;39(1):34–44
Kiselev V.G., Strecker R., Ziyeh S., Speck O., Hennig J. Vessel size imaging in humans. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005;53(3):553–63
Larsson H.B., Fritz Hansen T., Rostrup E., Sondergaard L., Ring P., Henriksen O. Myocardial perfusion modeling using MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996;35(5):716–26
Lüdemann L., Grieger W., Wurm R., Wust P., Zimmer C. Quantitative measurement of leakage volume and permeability in gliomas, meningiomas and brain metastases with dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2005;23(8):833–41
Mullerad M., Hricak H., Wang L., Chen H.N., Kattan M.W., Scardino P.T. Prostate cancer: detection of extracapsular extension by genitourinary and general body radiologists at MR imaging. Radiology 2004;232(1):140–6
Ostergaard L., Weisskoff R.M., Chesler D.A., Gyldensted C., Rosen B.R. High resolution measurement of cerebral blood flow using intravascular tracer bolus passages. Part I: Mathematical approach and statistical analysis. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996;36(5):715–25
Padhani A.R., Gapinski C.J., Macvicar D.A., Parker G.J., Suckling J., Revell P.B., Leach M.O., Dearnaley D.P., Husband J.E. Dynamic contrast enhanced MRI of prostate cancer: correlation with morphology and tumour stage, histological grade and PSA. Clin Radiol 2000;55(2):99–109
Pradel C., Siauve N., Bruneteau G., Clement O., de Bazelaire C., Frouin F., Wedge S.R., Tessier J.L., Robert P.H., Frija G., et al. Reduced capillary perfusion and permeability in human tumour xenografts treated with the VEGF signalling inhibitor ZD4190: an in vivo assessment using dynamic MR imaging and macromolecular contrast media. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2003;21(8):845–51
Pruessmann K.P., Weiger M., Scheidegger M.B., Boesiger P. SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999;42(5):952–62
Pschyrembel, W. Blutbild. In: Klinisches Wörterbuch, 256th edn, edited by C. Zink. Berlin, New York: de Gruyter, 1990, p. 217.
Rohlfing T., Denzler J., Grassl C., Russakoff D.B., Maurer C.R. Jr. Markerless real-time 3-D target region tracking by motion backprojection from projection images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2005;24(11):1455–68
Rosen B.R., Belliveau J.W., Vevea J.M., Brady T.J. Perfusion imaging with NMR contrast agents. Magn-Reson-Med 1990;14(2):249–65
Sodickson D.K., Manning W.J. Simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics (SMASH): fast imaging with radiofrequency coil arrays. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997;38(4):591–603
Stanisz G.J., Henkelman R.M. Gd-DTPA relaxivity depends on macromolecular content. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000;44(5):665–7
St Lawrence K.S., Lee T.Y. An adiabatic approximation to the tissue homogeneity model for water exchange in the brain: II. Experimental validation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1998;18(12):1378–85
Studholme C., Hill D.L.G. An overlap invariant entropy measure of 3D medical image alignment. Pattern Recognition 1999;32(1):71–86
Taillieu F., Salomon L.J., Siauve N., Clement O., Faye N., Balvay D., Vayssettes C., Frija G., Ville Y., Cuenod C.A. Placental perfusion and permeability: simultaneous assessment with dual-echo contrast-enhanced MR imaging in mice. Radiology 2006;241(3):737–45
Thompson H.K. Jr., Starmer C.F., Whalen R.E., McIntosh H.D. Indicator Transit Time Considered as a Gamma Variate. Circ Res 1964;14:502–15
Tofts P.S., Brix G., Buckley D.L., Evelhoch J.L., Henderson E., Knopp M.V., Larsson H.B., Lee T.Y., Mayr N.A., Parker G.J., et al. Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced T(1)-weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: standardized quantities and symbols. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1999;10(3):223–32
Tropres I., Grimault S., Vaeth A., Grillon E., Julien C., Payen J.F., Lamalle L., Decorps M. Vessel size imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2001;45(3):397–408
Vallee J.P., Sostman H.D., MacFall J.R., Coleman R.E. Quantification of myocardial perfusion with MRI and exogenous contrast agents. Cardiology 1997;88(1):90–105
van Lin E.N., Futterer J.J., Heijmink S.W., van der Vight L.P., Hoffmann A.L., van Kollenburg P., Huisman H.J., Scheenen T.W., Witjes J.A., Leer J.W., et al. IMRT boost dose planning on dominant intraprostatic lesions: gold marker-based three-dimensional fusion of CT with dynamic contrast-enhanced and 1H-spectroscopic MRI. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;65(1):291–303
Vonken E.P., van Osch M.J., Bakker C.J., Viergever M.A. Simultaneous quantitative cerebral perfusion and Gd-DTPA extravasation measurement with dual-echo dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000;43(6):820–7
Zhu X.P., Li K.L., Kamaly Asl I.D., Checkley D.R., Tessier J.J., Waterton J.C., Jackson A. Quantification of endothelial permeability, leakage space, and blood volume in brain tumors using combined T1 and T2* contrast-enhanced dynamic MR imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000;11(6):575–85
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lüdemann, L., Prochnow, D., Rohlfing, T. et al. Simultaneous Quantification of Perfusion and Permeability in the Prostate Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging with an Inversion-Prepared Dual-Contrast Sequence. Ann Biomed Eng 37, 749–762 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-009-9645-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-009-9645-x