Abstract
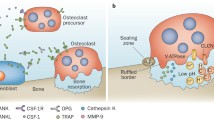
There is emerging interest for osteoclasts as key players in the erosive and inflammatory events leading to joint destruction in chronic arthritis. In fact, chronic inflammatory joint diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are often characterized by destruction of juxta-articular bone and erosions due to the elevated activity of osteoclasts, which are involved in bone resorption. The main step in inflammatory bone erosion is an imbalance between bone resorption and bone formation: osteoclast formation is enhanced by proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-17 and is not balanced by increased activity of bone-forming osteoblasts. T-cells, stromal cells, and synoviocytes enhance osteoclast formation via expression of RANKL and, under pathologic conditions, of proinflammatory cytokines. In rheumatoid arthritis, accumulation of osteoclasts in synovial tissues and their activation associated with osteoclastogenic cytokines and chemokines at cartilage erosion sites suggest that they could be usefully selected as therapeutic target. In particular, in consideration of the primary role of RANKL and TNF-α in osteoclastogenesis, the control of the production of RANKL and the inhibition of TNF-α represent important strategies for reducing bone damage in this disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Redlich K, Hayer S, Ricci R, David JP, Tohidast-Akrad M, Kollias G, Steiner G, Smolen JS, Wagner EF, Schett G (2002) Osteoclasts are essential for TNF-α-mediated joint destruction. J Clin Invest 110:1419–1427
Kotake S, Udagawa N, Hakoda M, Mogi M, Yano K, Tsuda E, Takahashi K, Furuya T, Ishiyama S, Kim KJ, Saito S, Nishikawa T, Takahashi N, Togari A, Tomatsu T, Suda T, Kamatani N (2001) Activated human T cells directly induce osteoclastogenesis from human monocytes: possible role of T cells in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum 44:1003–1012
Suda T, Takahashi N, Martin TJ (1992) Modulation of osteoclast differentiation. Endocr Rev 13:66–80
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E, Gillespie MT, Martin TJ (1999) Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev 20:345–357
Kim HH, Lee DE, Shin JN, Lee YS, Jeon YM, Chung CH, Ni J, Kwon BS, Lee ZH (1999) Receptor activator of NF-kB recruits multiple TRAF family adaptors and activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase. FEBS Lett 443:297–302
Matsumoto M, Sudo T, Saito T, Osada H, Tsujimoto M (2000) Involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in osteoclastogenesis mediated by receptor activator of NF-kB ligand (RANKL). J Biol Chem 275:31155–31161
Kobayashi N, Kadono Y, Naito A, Matsumoto K, Yamamoto T, Tanaka S, Inoue J (2001) Segregation of TRAF6-mediated signaling pathways clarifies its role in osteoclastogenesis. EMBO J 20:1271–1280
Bai S, Kitaura H, Zhao H, Chen J, Müller JM, Schüle R, Darnay B, Novack DV, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL (2005) FHL2 inhibits the activated osteoclast in a TRAF6 dependent manner. J Clin Invest 115:2742–2751
Wada T, Nakashima T, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, Gasser J, Hara H, Schett G, Penninger JM (2005) The molecular scaffold Gab2 is a crucial component of RANK signaling and osteoclastogenesis. Nat Med 11:394–399
David J-P, Sabapathy K, Hoffmann O, Idarraga MH, Wagner EF (2002) JNK1 modulates osteoclastogenesis through both c-Jun phosphorylation-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Cell Sci 115:4317–4325
Jimi E, Akiyama S, Tsurukai T, Okahashi N, Kobayashi K, Udagawa N, Nishihara T, Takahashi N, Suda T (1999) Osteoclast differentiation factor acts as a multifunctional regulator in murine osteoclast differentiation and function. J Immunol 163:434–442
Jones DH, Nakashima T, Sanchez OH, Kozieradzki I, Komarova SV, Sarosi I, Morony S, Rubin E, Sarao R, Hojilla CV, Komnenovic V, Kong YY, Schreiber M, Dixon SJ, Sims SM, Khokha R, Wada T, Penninger JM (2006) Regulation of cancer cell migration and bone metastasis by RANKL. Nature 440:692–696
Ikeda F, Nishimura R, Matsubara T, Tanaka S, Inoue J, Reddy SV, Hata K, Yamashita K, Hiraga T, Watanabe T, Kukita T, Yoshioka K, Rao A, Yoneda T (2004) Critical roles of c-Jun signaling in regulation of NFAT family and RANKL-regulated osteoclast differentiation. J Clin Invest 114:475–484
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H, Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, Wagner EF, Mak TW, Kodama T, Taniguchi T (2002) Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell 3:889–901
Takayanagi H (2007) Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol 7:292–304
Koga T, Inui M, Inoue K, Kim S, Suematsu A, Kobayashi E, Iwata T, Ohnishi H, Matozaki T, Kodama T, Taniguchi T, Takayanagi H, Takai T (2004) Costimulatory signals mediated by the ITAM motif cooperate with RANKL for bone homeostasis. Nature 428:758–763
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley M, Chang MS, Lüthy R, Nguyen HQ, Wooden S, Bennett L, Boone T, Shimamoto G, DeRose M, Elliott R, Colombero A, Tan HL, Trail G, Sullivan J, Davy E, Bucay N, Renshaw-Gegg L, Hughes TM, Hill D, Pattison W, Campbell P, Sander S, Van G, Tarpley J, Derby P, Lee R, Boyle WJ (1997) Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell 89:309–319
Bromley M, Woolley DE (1984) Chondroclasts and osteoclasts at subchondral sites of erosion in the rheumatoid joint. Arthritis Rheum 27:968–975
Takayanagi H, Oda H, Yamamoto S, Kawaguchi H, Tanaka S, Nishikawa T, Koshihara Y (1997) A new mechanism of bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis: synovial fibroblasts induce osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 240:279–286
Gravallese EM, Manning C, Tsay A, Naito A, Pan C, Amento E, Goldring SR (2000) Synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis is a source of osteoclast differentiation factor. Arthritis Rheum 43:250–258
Takayanagi H, Iizuka H, Juji T, Nakagawa T, Yamamoto A, Miyazaki T, Koshihara Y, Oda H, Nakamura K, Tanaka S (2000) Involvement of receptor activator of nuclear factor kB ligand/osteoclast differentiation factor in osteoclastogenesis from synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:259–269
Pettit AR, Ji H, von Stechow D, Müller R, Goldring SR, Choi Y, Benoist C, Gravallese EM (2001) TRANCE/RANKL knockout mice are protected from bone erosion in a serum transfer model of arthritis. Am J Pathol 159:1689–1699
Colucci S, Brunetti G, Cantatore FP, Oranger A, Mori G, Quarta L, Cirulli N, Mancini L, Corrado A, Grassi FR, Grano M (2007) Lymphocytes and synovial fluid fibroblasts support osteoclastogenesis through RANKL, TNFalpha, and IL-7 in an in vitro model derived from human psoriatic arthritis. J Pathol 212:47–55
Schwarz EM, Looney RJ, Drissi MH, O’Keefe RJ, Boyce BF, Xing L, Ritchlin CT (2006) Autoimmunity and bone. Ann NY Acad Sci 1068:275–283
Weitzmann MN, Pacifici R (2005) The role of T lymphocytes in bone metabolism. Immunol Rev 208:154–168
Teitelbaum S (2006) Osteoclasts; culprits in inflammatory osteolysis. Arthritis Res Ther 8:201
Lam J, Takeshita S, Barker JE, Kanagawa O, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL (2000) TNF-α induces osteoclastogenesis by direct stimulation of macrophages exposed to permissive levels of RANK ligand. J Clin Invest 106:1481–1488
Kim N, Kadono Y, Takami M, Lee J, Lee SH, Okada F, Kim JH, Kobayashi T, Odgren PR, Nakano H, Yeh WC, Lee SK, Lorenzo JA, Choi Y (2005) Osteoclast differentiation independent of the TRANCE-RANKTRAF6 axis. J Exp Med 202:589–595
Fuller K, Kirstein B, Chambers TJ (2006) Murine osteoclast formation and function: differential regulation by humoral agents. Endocrinology 147:1979–1985
Ochi S, Shinohara M, Sato K, Gober HJ, Koga T, Kodama T, Takai T, Miyasaka N, Takayanagi H (2007) Pathological role of osteoclast costimulation in arthritis-induced bone loss. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 27:11394–11399
Abu-Amer Y, Erdmann J, Kollias G, Alexopoulou L, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL (2000) Tumor necrosis factor receptors types 1 and 2 differentially regulate osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem 275:27307–27310
Wei S, Kitaura H, Zhou P, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL (2005) IL-1 mediates TNF-induced osteoclastogenesis. J Clin Invest 115:282–290
Yoshida H, Hayashi S, Kunisada T, Ogawa M, Nishikawa S, Okamura H, Sudo T, Shultz LD, Nishikawa S (1990) The murine mutation osteopetrosis is in the coding region of the macrophage colony stimulating factor gene. Nature 345:442–444
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL (2003) Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 423:337–342
Faccio R, Takeshita S, Zallone A, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL (2003) c-Fms and the αvβ3 integrin collaborate during osteoclast differentiation. J Clin Invest 111:749–758
Quinn JM, Itoh K, Udagawa N, Hausler K, Yasuda H, Shima N, Mizuno A, Higashio K, Takahashi N, Suda T, Martin TJ, Gillespie MT (2001) Transforming growth factor-β affects osteoclast differentiation via direct and indirect actions. J Bone Miner Res 16:1787–1794
Takai H, Kanematsu M, Yano K, Tsuda E, Higashio K, Ikeda K, Watanabe K, Yamada Y (1998) Transforming growth factor-β stimulates the production of osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor by bone marrow stromal cells. J Biol Chem 273:27091–27096
Hase H, Kanno Y, Kojima H, Sakurai D, Kobata T (2008) Coculture of osteoclast precursors with rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts induces osteoclastogenesis via transforming growth factor-β mediated down-regulation of osteoprotegerin. Arthritis Rheum 58:3356–3365
Kotake S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Matsuzaki K, Itoh K, Ishiyama S, Saito S, Inoue K, Kamatani N, Gillespie MT, Martin TJ, Suda T (1999) IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis is a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis. J Clin Invest 103:1345–1352
Sato K, Takayanagi H (2006) Osteoclasts, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoimmunology. Curr Opin Rheumatol 18:419–426
Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, Smolen JS, Weisman M, Emery P, Feldmann M, Harriman GR, Maini RN (2000) Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-tumor necrosis factor trial in rheumatoid arthritis with concomitant therapy study group. N Engl J Med 343:1594–1602
Redlich K, Schett G, Steiner G, Hayer S, Wagner EF, Smolen JS (2003) Rheumatoid arthritis therapy after tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 blockade. Arthritis Rheum 48:3308–3319
Lange U, Teichmann J, Muller-Ladner U, Strunk J (2005) Increase in bone mineral density of patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF-α antibody: a prospective open-label pilot study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 44:1546–1548
Catrina AI, Trollmo C, af Klint E, Engstrom M, Lampa J, Hermansson Y, Klareskog L, Ulfgren AK (2005) Evidence that anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy with both etanercept and infliximab induces apoptosis in macrophages, but not lymphocytes, in rheumatoid arthritis joints: extended report. Arthritis Rheum 52:61–72
Kotake S, Sato K, Kim KJ, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Nakamura I, Yamaguchi A, Kishimoto T, Suda T, Kashiwazaki S (1996) Interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6 receptors in the synovial fluids from rheumatoid arthritis patients are responsible for osteoclast like cell formation. J Bone Miner Res 11:88–95
Jovanovic DV, Martel-Pelletier J, Di Battista JA, Mineau F, Jolicoeur FC, Benderdour M, Pelletier JP (2000) Stimulation of 92-kd gelatinase (matrix metalloproteinase 9) production by interleukin-17 in human monocyte/macrophages: a possible role in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:1134–1144
Chabaud M, Lubberts E, Joosten L, van Den Berg W, Miossec P (2001) IL-17 derived from juxta-articular bone and synovium contributes to joint degradation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res 3:168–177
Yago T, Nanke Y, Kawamoto M, Furuya T, Kobashigawa T, Kamatani N, Kotake S (2007) IL-23 induces human osteoclastogenesis via IL-17 in vitro, and anti-IL-23 antibody attenuates collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Arthritis Res Ther 9:R96
Weitzmann MN, Cenci S, Rifas L, Brown C, Pacifici R (2000) Interleukin-7 stimulates osteoclast formation by up-regulating the T-cell production of soluble osteoclastogenic cytokines. Blood 96:1873–1878
Kawai T, Matsuyama T, Hosokawa Y, Makihira S, Seki M, Karimbux NY, Goncalves RB, Valverde P, Dibart S, Li YP, Miranda LA, Ernst CW, Izumi Y, Taubman MA (2006) B and T lymphocytes are the primary sources of RANKL in the bone resorptive lesion of periodontal disease. Am J Pathol 169:987–998
Bodolay E, Koch AE, Kim J, Szegedi G, Szekanecz Z (2002) Angiogenesis and chemokines in rheumatoid arthritis and other systemic inflammatory rheumatic diseases. J Cell Mol Med 6:357–376
Murphy PM, Baggiolini M, Charo IF, Hébert CA, Horuk R, Matsushima K, Miller LH, Oppenheim JJ, Power CA (2000) International union of pharmacology. XXII. Nomenclature for chemokine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 52:145–176
Abe M, Hiura K, Wilde J, Moriyama K, Hashimoto T, Ozaki S, Wakatsuki S, Kosaka M, Kido S, Inoue D, Matsumoto T (2002) Role for macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1α and MIP-1β in the development of osteolytic lesions in multiple myeloma. Blood 100:2195–2202
Kwak HB, Lee SW, Jin HM, Ha H, Lee SH, Takeshita S, Tanaka S, Kim HM, Kim HH, Lee ZH (2005) Monokine induced by interferon-γ is induced by receptor activator of nuclear factor kB ligand and is involved in osteoclast adhesion and migration. Blood 105:2963–2969
Kwak HB, Ha H, Kim HN, Lee JH, Kim HS, Lee S, Kim HM, Kim JY, Kim HH, Song YW, Lee ZH (2008) Reciprocal cross-talk between RANKL and interferon-γ–inducible protein 10 is responsible for bone-erosive experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58:1332–1342
Taub DD, Lloyd AR, Conlon K, Wang JM, Ortaldo JR, Harada A, Matsushima K, Kelvin DJ, Oppenheim JJ (1993) Recombinant human interferon-inducible protein 10 is a chemoattractant for human monocytes and T lymphocytes and promotes T cell adhesion to endothelial cells. J Exp Med 177:1809–1814
Jinquan T, Jing C, Jacobi HH, Reimert CM, Millner A, Quan S, Hansen JB, Dissing S, Malling HJ, Skov PS, Poulsen LK (2000) CXCR3 expression and activation of eosinophils: role of IFN-γ-inducible protein-10 and monokine induced by IFN-γ. J Immunol 165:1548–1556
Hanaoka R, Kasama T, Muramatsu M, Yajima N, Shiozawa F, Miwa Y, Negishi M, Ide H, Miyaoka H, Uchida H, Adachi M (2003) A novel mechanism for the regulation of IFN-γ inducible protein-10 expression in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 5:R74–R81
Coelho LF, Magno de Freitas Almeida G, Mennechet FJ, Blangy A, Uzé G (2005) Interferon-alpha and -beta differentially regulate osteoclastogenesis: role of differential induction of chemokine CXCL11 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11917–11922
Abraham AK, Ramanathan M, Weinstock-Guttman B, Mager DE (2009) Mechanisms of interferon-beta effects on bone homeostasis. Biochem Pharmacol 77:1757–1762
Takayanagi H, Sato K, Takaoka A, Taniguchi T (2005) Interplay between interferon and other cytokine systems in bone metabolism. Immunol Rev 208:181–193
Schneider GB, Relfson M (1994) Effects of interleukin-2 on bone resorption and natural immunity in osteopetrotic (ia) rats. Lymphokine Cytokine Res 13:335–341
Park-Min KH, Ji JD, Antoniv T, Reid AC, Silver RB, Humphrey MB, Nakamura M, Ivashkiv LB (2009) IL-10 suppresses calcium-mediated costimulation of RANK signaling during human osteoclast differentiation by inhibiting TREM-2 expression. J Immunol 183:2444–2455
Kalliolias GD, Zhao B, Triantafyllopoulou A, Park-Min KH, Ivashkiv LB (2010) Interleukin-27 inhibits human osteoclastogenesis by abrogating RANKL-mediated induction of nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 and suppressing proximal RANK signaling. Arthritis Rheum 62:402–413
Hiasa M, Abe M, Nakano A, Oda A, Amou H, Kido S, Takeuchi K, Kagawa K, Yata K, Hashimoto T, Ozaki S, Asaoka K, Tanaka E, Moriyama K, Matsumoto T (2009) GM-CSF and IL-4 induce dendritic cell differentiation and disrupt osteoclastogenesis through M-CSF receptor shedding by up-regulation of TNF-alpha converting enzyme (TACE). Blood 114:4517–4526
Zhao B, Takami M, Yamada A, Wang X, Koga T, Hu X, Tamura T, Ozato K, Choi Y, Ivashkiv LB, Takayanagi H, Kamijo R (2009) Interferon regulatory factor 8 regulates bone metabolism by suppressing osteoclastogenesis. Nat Med 15:1066–1071
Ji JD, Park-Min KH, Shen Z, Fajardo RJ, Goldring SR, McHugh KP, Ivashkiv LB (2009) Inhibition of RANK expression and osteoclastogenesis by TLRs and IFN-gamma in human osteoclast precursors. J Immunol 183:7223–7233
Kim N, Takami M, Rho J, Josien R, Choi Y (2002) A novel member of the leukocyte receptor complex regulates osteoclast differentiation. J Exp Med 195:201–209
Kim GS, Koh JM, Chang JS, Park BL, Kim LH, Park EK, Kim SY, Shin HD (2005) Association of the OSCAR promoter polymorphism with BMD in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res 20:1342–1348
Merck E, Gaillard C, Scuiller M, Scapini P, Cassatella MA, Trinchieri G, Bates EE (2006) Ligation of the FcR_ chain-associated human osteoclast-associated receptor enhances the proinflammatory responses of human monocytes and neutrophils. J Immunol 176:3149–3156
So H, Rho J, Jeong D, Park R, Fisher DE, Ostrowski MC, Choi Y, Kim N (2003) Microphthalmia transcription factor and PU.1 synergistically induce the leukocyte receptor osteoclast-associated receptor gene expression. J Biol Chem 278:24209–24216
Lee J, Kim K, Kim JH, Jin HM, Choi HK, Lee SH, Kook H, Kim KK, Yokota Y, Lee SY, Choi Y, Kim N (2006) Id helix-loop-helix proteins negatively regulate TRANCE-mediated osteoclast differentiation. Blood 107:2686–2693
Kim K, Kim JH, Lee J, Jin HM, Kook H, Kim KK, Lee SY, Kim N (2007) MafB negatively regulates RANKL-mediated osteoclast differentiation. Blood 109:3253–3259
Herman S, Müller RB, Krönke G, Zwerina J, Redlich K, Hueber AJ, Gelse H, Neumann E, Müller-Ladner U, Schett G (2008) Induction of osteoclast-associated receptor, a key osteoclast costimulation molecule, in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58:3041–3050
Koga T, Inui M, Inoue K, Kim S, Suematsu A, Kobayashi E, Iwata T, Ohnishi H, Matozaki T, Kodama T, Taniguchi T, Takayanagi H, Takai T (2004) Costimulatory signals mediated by the ITAM motif cooperate with RANKL for bone homeostasis. Nature 428:758–763
Mocsai A, Humphrey MB, Van Ziffle JA, Hu Y, Burghardt A, Spusta SC, Majumdar S, Lanier LL, Lowell CA, Nakamura MC (2004) The immunomodulatory adapter proteins DAP12 and Fc receptor gammachain (FcRgamma) regulate development of functional osteoclasts through the Syk tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6158–6163
Zou W, Kitaura H, Reeve J, Long F, Tybulewicz VL, Shattil SJ, Ginsberg MH, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL (2007) Syk, c-Src, the alphavbeta3 integrin, and ITAM immunoreceptors, in concert, regulate osteoclastic bone resorption. J Cell Biol 176:877–888
Humphrey MB, Lanier LL, Nakamura MC (2005) Role of ITAM-containing adapter proteins and their receptors in the immune system and bone. Immunol Rev 208:50–65
Hamerman JA, Jarjoura JR, Humphrey MB, Nakamura MC, Seaman WE, Lanier LL (2006) Cutting edge: inhibition of TLR and FcR responses in macrophages by triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells (TREM)-2 and DAP12. J Immunol 177:2051–2055
Kong YY, Feige U, Sarosi I, Bolon B, Tafuri A, Morony S, Capparelli C, Li J, Elliott R, McCabe S, Wong T, Campagnuolo G, Moran E, Bogoch ER, Van G, Nguyen LT, Ohashi PS, Lacey DL, Fish E, Boyle WJ, Penninger JM (1999) Activated T cells regulate bone loss and joint destruction in adjuvant arthritis through osteoprotegerin ligand. Nature 402:304–309
Horwood NJ, Kartsogiannis V, Quinn JM, Romas E, Martin TJ, Gillespie MT (1999) Activated T lymphocytes support osteoclast formation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 265:144–150
Nakashima T, Takayanagi H (2008) The dynamic interplay between osteoclasts and the immune system. Arch Biochem Biophys 473:166–171
Takayanagi H, Ogasawara K, Hida S, Chiba T, Murata S, Sato K, Takaoka A, Yokochi T, Oda H, Tanaka K, Nakamura K, Taniguchi T (2000) T-cell-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis by signalling cross-talk between RANKL and IFN-gamma. Nature 408:600–605
Miranda-Carús ME, Benito-Miguel M, Balsa A, Cobo-Ibáñez T, Pérez de Ayala C, Pascual-Salcedo D, Martín-Mola E (2006) Peripheral blood T lymphocytes from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis express RANKL and interleukin-15 on the cell surface and promote osteoclastogenesis in autologous monocytes. Arthritis Rheum 54:1151–1164
Mori G, Cantatore FP, Brunetti G, Oranger A, Colaianni G, Quarta L, Corrado A, Colucci S, Grano M (2007) Synovial fluid fibroblasts and lymphocytes support the osteoclastogenesis in human psoriatic arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1117:159–164
González-Álvaro I, Domínguez-Jiménez C, Ortiz AM, Núñez-González V, Roda-Navarro P, Fernández-Ruiz E, Sancho D, Sánchez-Madrid F (2006) Interleukin-15 and interferon-γ participate in the cross-talk between natural killer and monocytic cells required for tumour necrosis factor production. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R88
Choi Y, Kim JJ (2003) B cells activated in the presence of Th1 cytokines inhibit osteoclastogenesis. Exp Mol Med 35:385–392
Weitzmann MN, Cenci S, Haug J, Brown C, DiPersio J, Pacifici R (2000) B lymphocytes inhibit human osteoclastogenesis by secretion of TGFbeta. J Cell Biochem 78:318–324
Li Y, Toraldo G, Li A, Yang X, Zhang H, Qian WP, Weitzmann MN (2007) B cells and T cells are critical for the preservation of bone homeostasis and attainment of peak bone mass in vivo. Blood 109:3839–3848
Sato T, Shibata T, Ikeda K, Watanabe K (2001) Generation of bone-resorbing osteoclasts from B220+ cells: Its role in accelerated osteoclastogenesis due to estrogen deficiency. J Bone Miner Res 16:2215–2221
Choi Y, Woo KM, Ko SH, Lee YJ, Park SJ, Kim HM, Kwon BS (2001) Osteoclastogenesis is enhanced by activated B cells but suppressed by activated CD8(+) T cells. Eur J Immunol 31:2179–2188
Manabe N, Kawaguchi H, Chikuda H, Miyaura C, Inada M, Nagai R, Nabeshima Y, Nakamura K, Sinclair AM, Scheuermann RH, Kuro-o M (2001) Connection between B lymphocyte and osteoclast differentiation pathways. J Immunol 167:2625–2631
Giuliani N, Colla S, Sala R, Moroni M, Lazzaretti M, La Monica S, Bonomini S, Hojden M, Sammarelli G, Barillè S, Bataille R, Rizzoli V (2002) Human myeloma cells stimulate the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL) in T lymphocytes: a potential role in multiple myeloma bone disease. Blood 100:4615–4621
Heider U, Langelotz C, Jakob C, Zavrski I, Fleissner C, Eucker J, Possinger K, Hofbauer LC, Sezer O (2003) Expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand on bone marrow plasma cells correlates with osteolytic bone disease in patients with multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 9:1436–1440
Giuliani N, Colla S, Morandi F, Lazzaretti M, Sala R, Bonomini S, Grano M, Colucci S, Svaldi M, Rizzoli V (2005) Myeloma cells block RUNX2/CBFA1 activity in human bone marrow osteoblast progenitors and inhibit osteoblast formation and differentiation. Blood 106:2472–2483
Han X, Kawai T, Eastcott JW, Taubman MA (2006) Bacterial-responsive B lymphocytes induce periodontal bone resorption. J Immunol 176:625–631
Colucci S, Mori G, Brunetti G, Coricciati M, Pignataro P, Oranger A, Cirulli N, Mastrangelo F, Grassi FR, Grano M (2005) Interleukin-7 production by B lymphocytes affects the T cell-dependent osteoclast formation in an in vitro model derived from human periodontitis patients. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 18:13–19
McKenna HJ, Stocking KL, Miller RE, Brasel K, De Smedt T, Maraskovsky E, Maliszewski CR, Lynch DH, Smith J, Pulendran B, Roux ER, Teepe M, Lyman SD, Peschon JJ (2000) Mice lacking flt3 ligand have deficient hematopoiesis affecting hematopoietic progenitor cells, dendritic cells, and natural killer cells. Blood 95:3489–3497
Thomas R, MacDonald KP, Pettit AR, Cavanagh LL, Padmanabha J, Zehntner S (1999) Dendritic cells and the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. J Leukoc Biol 66:286–292
Highton J, Kean A, Hessian PA, Thomson J, Rietveld J, Hart DN (2000) Cells expressing dendritic cellmarkers are present in the rheumatoid nodule. J Rheumatol 27:339–346
Santiago-Schwarz F, Anand P, Liu S, Carsons SE (2001) Dendritic cells (DCs) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA): progenitor cells and soluble factors contained in RA synovial fluid yield a subset of myeloid DCs that preferentially activate Th1 inflammatory-type responses. J Immunol 167:1758–1768
Anderson DM, Maraskovsky E, Billingsley WL et al (1997) A homologue of the TNF receptor and its ligand enhance T-cell growth and dendritic-cell function. Nature 390:175–179
Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Suda T (1999) A new member of tumor necrosis factor ligand family, ODF/OPGL/TRANCE/RANKL, regulates osteoclast differentiation and function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 256:449–455
Rivollier A, Mazzorana M, Tebib J, Piperno M, Aitsiselmi T, Rabourdin-Combe C, Jurdic P, Servet-Delprat C (2004) Immature dendritic cell transdifferentiation into osteoclasts: a novel pathway sustained by the rheumatoid arthritis microenvironment. Blood 104:4029–4037
Pageau SC (2009) Denosumab. MAbs 1:210–215
Conflicts of Interest
The authors state they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maruotti, N., Grano, M., Colucci, S. et al. Osteoclastogenesis and arthritis. Clin Exp Med 11, 137–145 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-010-0117-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-010-0117-2