Abstract
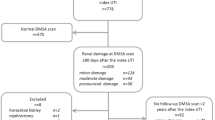
The finding of scintigraphic renal defects in children with febrile urinary tract infection (UTI) even in the absence of vesicoureteric reflux (VUR) has led to the conclusion that VUR is a weak predictor of renal defects in these patients. We used isotopic cystography (IC) for diagnosis of VUR in children with febrile UTI. Dimercaptosuccinic acid renal scintigraphy was performed 6 months after cure of the last UTI. Renal defects were defined by the finding of focal defects of radionuclide uptake and/or by a split renal function <43%. The study included 206 children with primary VUR and 77 without VUR. Among the subjects with and without VUR, respectively, renal defects were found in 40 and 6% (p=0.0001), focal uptake defects in 33 and 5% (p=0.0001) and split renal function <43% in 26 and 5% (p=0.0001). Permanent renal defects in children with febrile UTI are closely associated with VUR. The possibility that a child will have permanent renal defects can reasonably be ruled out on the basis of the absence of VUR by IC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin DS, Huang SH, Lin CC, Tung YC, Huang TT, Chiu NC, Koa HA, Hung HY, Hsu CH, Hsieh WS, Yang DI, Huang FY (2000) Urinary tract infection in febrile infants younger than eight weeks of age. Pediatrics 105:E20
Jacobson SH, Hansson S, Jakobsson B (1999) Vesicoureteric reflux: occurrence and long-term risks. Acta Paediatr Suppl 43:22–30
Patzer L, Seeman T, Luck C, Wuhl E, Janda J, Misselwitz J (2003) Day-and night-time blood pressure elevation in children with higher grades of renal scarring. J Pediatr 142:117–122
McGladdery SJ, Aparicio S, Verrier-Jones K, Roberts R, Sacks SH (1992) Outcome of pregnancy in an Oxford-Cardiff cohort of women with previous bacteriuria. Q J Med 83:533–539
Goldraich NP, Ramos AL, Goldraich IH (1989) Urography versus DMSA scan in children with vesicoureteric reflux. Pediatr Nephrol 3:1–5
Jakobsson B, Svensson L (1997) Transient pyelonephritic changes on 99mTechnetium-dimercaptosuccinic acid scan for at least 5 months after infection. Acta Paediatr 86:803–807
Gordon I, Barkovics M, Pindoria S, Cole TJ, Woolf AS (2003) Primary vesicoureteric reflux as a predictor of renal damage in children hospitalized with urinary tract infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:739–744
Paltiel HJ, Rupic RC, Kiruluta HG (1992) Enhanced detection of vesicoureteral reflux in infants and children with use of cyclic voiding cystourethrography. Radiology 184:753–755
Polito C, Moggio G, La Manna A, Cioce F, Cappabianca S, Di Toro R (2000) Cyclic voiding cystourethrography in the diagnosis of occult vesicoureteric reflux in infants and children. Pediatr Nephrol 14:39–41
Polito C, Rambaldi PF, La Manna A, Mansi PL, Di Toro R (2000) Enhanced detection of vesicoureteric reflux with isotopic cystography. Pediatr Nephrol 14:827–830
Nasrallah PF, Nara S, Crawford J (1982) Clinical applications of nuclear cystography. J Urol 128:550–553
Fretzaias A, Karpathios T, Dimitriou P, Nicolaidou P, Matsaniotis N (1984) Grading of vesicoureteral reflux by radionuclide cystography. Pediatr Radiol 14:148–150
Kogan SJ, Sigler L, Levitt SB, Reda EF, Weiss R, Greifer I (1986) Elusive vesicoureteral reflux in children with normal contrast cystograms. J Urol 136:325–328
Saraga M, Stanicic A, Markovic V (1996) The role of direct radionuclide cystography in evaluation of vesicoureteral reflux. Scand J Urol Nephrol 30:367–371
Poli-Merol ML, Francois S, Pfliger F, Lefebvre F, Roussel B, Liehn JC, Daoud S (1998) Interest of direct radionuclide cystography in repeated urinary tract infection exploration in childhood. Eur J Pediatr Surg 8:339–342
Schwartz GJ, Brion LP, Spitzer A (1987) The use of plasma creatinine concentration for estimating glomerular filtration rate in infants, children and adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am 34:571–590
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on Hypertension Control in Children and Adolescents (1996) Update on the 1987 Task Force Report on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents: a working group report from the National High Blood Pressure Education Program. Pediatrics 98:649–658
Brendstrup L, Carlsen N, Nielsen SL, Dyrbye M, Eiken M, Krasilnikoff PA, Gertz TC (1983) Micturition cystourethrography using X-ray or scintigraphy in children with reflux. Acta Paediatr Scand 72:559–562
Dikshit MP, Acharya VN, Shikare S, Merchant S, Pardanani DS (1993) Comparison of direct radionuclide cystography with micturating cystourethrography for the diagnosis of vesicoureteric reflux and its correlation with cystoscopic appearances of the ureteric orifices. Nephrol Dial Transplant 8:600–602
Zechmann W, Raushmeier H, Dumfahrt H, Fill H, Joost J, Riccabona G (1983) Value and indication for isotope reflux cystography in children. Acta Medica Austriaca 10:57–60
Zhang G, Day DL, Loken M, Gonzalez R (1987) Grading of reflux by radionuclide cystography. Clin Nucl Med 12:106–109
Tamminen-Mobius T, Brunier E, Ebel KD, Lebowitz R, Olbing H, Seppanen U, Sixt R (1992) Cessation of vesicoureteral reflux for 5 years in infants and children allocated to medical treatment. The International Reflux Study in Children. J Urol 148:1662–1666
Anderson NG, Abbott GD, Mogridge N, Allen RB, Maling TM, Wells JE (1997) Vesicoureteric reflux in the newborn: relationship to fetal pelvic diameter. Pediatr Nephrol 11:610–616
Phan V, Traubici J, Hershenfield B, Stephens D, Rosenblum ND, Geary DF (2004) Vesicoureteral reflux in infants with isolated antenatal hydronephrosis. Pediatr Nephrol 19:819–820
Hoberman A, Charron M, Hickey RW, Baskin M, Kearney DH, Wald ER (2003) Imaging studies after a first febrile urinary tract infection in young children. N Engl J Med 348:195–202
Goldman M, Bistritzer T, Horne T, Zoareft I, Aladjem M (2000) The etiology of renal scars in infants with pyelonephritis and vesicoureteral reflux. Pediatr Nephrol 14:385–388
Olbing H, Smellie JM, Jodal U, Lax H (2003) New renal scars in children with severe VUR: a 10-year study of randomised treatment. Pediatr Nephrol 18:1128–1131
Wennerstrom M, Hansson S, Jodal U, Stokland E (2000) Primary and acquired renal scarring in boys and girls with urinary tract infection. J Pediatr 136:30–34
Ardissino G, Dacco V, Testa S, Bonaudo R, Claris-Appiani A, Taioli E, Marra G, Edefonti A, Sereni F, ItalKid Project (2003) Epidemiology of chronic renal failure in children: data from the ItalKid project. Pediatrics 111:e382–e387
Smellie JM, Barratt TM, Chantler C, Gordon I, Prescod NP, Ransley PG, Woolf AS (2001) Medical versus surgical treatment in children with severe bilateral vesicoureteric reflux and bilateral nephropathy: a randomized trial. Lancet 357:1329–1333
Mingin GC, Nguien HT, Baskin LS (2004) Abnormal dimercapto-succinic acid scans predict an increased risk of breakthrough infection in children with vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol 172:1075–1077
Rubenstein JN, Maizels M, Kim S, Houston JTB (2003) The PIC cystogram: a novel approach to identify “occult” vesicoureteric reflux in children with febrile urinary tract infections. J Urol 169:2339–2343
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polito, C., Rambaldi, P.F., Signoriello, G. et al. Permanent renal parenchymal defects after febrile UTI are closely associated with vesicoureteric reflux. Pediatr Nephrol 21, 521–526 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-006-0036-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-006-0036-3