Abstract
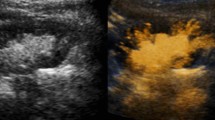
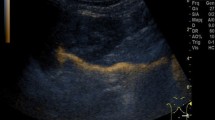
Three methods are currently used to identify vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) in children, namely X-ray voiding cystourethrography (VCUG), radionuclide voiding cystography (RVC), and, recently, echo-enhanced voiding urosonography (VUS). It is known that the sensitivity of VCUG and RVC for detecting VUR can be improved by using cyclic procedures, such as repeated bladder filling and voiding. The purpose of our prospective study was to evaluate whether the cyclic procedure is superior to the conventional (one cycle only) procedure in VUS also. VUS was performed in 49 patients, aged 1.4–15.8 years (mean 4.1 years). After the first micturition, the catheter was left in place and the whole procedure was repeated under the same conditions. The results of the first and second cycles and the combined procedure were compared. In the initial cycle, 7 of 35 (20%) refluxing renal units that were detected in the second cycle and 4 of 26 (15%) children with at least unilateral VUR were missed. Cyclic VUS detected 25% more VURs than the conventional (one cycle only) VUS (P=0.049) and revealed 50% more VUR III than the first cycle. Our results suggest that cyclic VUS is superior to conventional VUS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacobson SH, Eklof O, Eriksson CG, Lins LE, Tidgren B, Winberg J (1989) Development of hypertension and uremia after pyelonephritis in children: 27-year follow-up. BMJ 299:703–706
Martinell J, Claeson I, Lidin-Janson G, Jodal U (1995) Urinary infection, reflux and scarring in females continuously followed for 13–38 years. Pediatr Nephrol 9:131–136
Garin EH, Campos A, Homsy Y (1998) Primary vesicoureteral reflux: a review of current concepts. Pediatr Nephrol 12:249–256
Stefanidis CJ (2001) Reflux nephropathy in children. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16 [Suppl 6]:117–119
Elder JS, Snyder HM, Peters C, Arant B, Hawtrey CE, Hurwitz RS, Parrott TS, Weiss RA (1992) Variations in practice among urologists and nephrologists treating children with vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol 148:714–717
Kenda RB (2001) Imaging techniques for the detection of vesicoureteric reflux: what and when? Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:4–7
Bosio M (1998) Cystosonography with echocontrast: a new imaging modality to detect vesicoureteric reflux in children. Pediatr Radiol 28:250–255
Darge K, Troeger J, Duetting T, Zieger B, Rohrschneider W, Moehring K, Weber C, Toenshoff B (1999) Reflux in young patients: comparison of voiding US of the bladder and retrovesical space with echo enhancement versus voiding cystourethrography for diagnosis. Radiology 210:201–207
Kenda RB, Novljan G, Kenig A, Hojker S, Fettich JJ (2000) Echo-enhanced ultrasound voiding cystography in children: a new approach. Pediatr Nephrol 14:297–300
Mentzel HJ, Vogt S, John U, Kaiser WA (2002) Voiding urosonography with ultrasound contrast medium in children. Pediatr Nephrol 17:272–276
Berrocal T, Gaya F, Arjonilla A, Lonergan GJ (2001) Vesicoureteral reflux: diagnosis and grading with echo-enhanced cystography versus voiding cystourethrography. Radiology 221:359–365
Escape I, Martinez J, Bastart F, Solduga C, Sala P (2001) Usefulness of echocystography in the study of vesicoureteral reflux. J Ultrasound Med 20:145–149
Radmayr C, Klauser A, Pallwein L, Zurnedden D, Bartsch G, Frauscher F (2002) Contrast enhanced reflux sonography in children: a comparison to standard radiological imaging. J Urol 167:1428–1430
Piaggio G, Degl'Innocenti ML, Tomà P, Calevo MG, Perfumo F (2003) Cystography and voiding cystourethrography in the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux. Pediatr Nephrol 18:18–22
Kmetec A, Bren AF, Kandus A, Fettich J, Buturović-Ponikvar J (2001) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound voiding cystography as a screening examination for vesicoureteral reflux in the follow-up of renal transplant recipients: a new approach. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:120–123
Darge K, Ghods S, Zieger B, Rohrschneider W, Troeger J (2001) Reduction in voiding cystourethrographies after the introduction of contrast enhanced sonographic reflux diagnosis. Pediatr Radiol 31:790–795
Paltiel HJ, Rupich RC, Kiruluta HG (1992) Enhanced detection of vesicoureteral reflux in infants and children with use of cyclic voiding cystourethrography. Radiology 184:753–755
Polito C, Moggio G, La Manna A, Cioce F, Cappabianca S, Di Toro R (2000) Cyclic voiding cystography in the diagnosis of occult vesicoureteric reflux. Pediatr Nephrol 14:39–41
Fettich JJ, Kenda RB (1992) Cyclic direct radionuclide voiding cystography: increasing reliability in detecting vesicoureteral reflux in children. Pediatr Radiol 22:337–338
Koff SA (1983) Estimating bladder capacity in children. Urology 21:248
Fettich JJ, Colarinha P, Fischer S, Frökier J, Gordon I, Hahn K, Kabasakal L, Mann M, Mitjavila M, Olivier P, Piepsz A, Porn U, Roca I, Sixt R, Van Velzen J on behalf of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine. 20 February 2003. Guidelines for direct radionuclide cystography in children. www.eanm.org
Darge K (2002) Diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux with ultrasonography. Pediatr Nephrol 17:52–60
Valentini AL, Salvaggio E, Manzoni C, Rendeli C, Destitio C, Summaria V, Campioni P, Marano P (2001) Contrast-enhanced gray-scale and color Doppler voiding urosonography versus voiding cystourethrography in the diagnosis and grading of vesicoureteral reflux. J Clin Ultrasound 29:65–71
Farina R, Arena C, Pennisi F, Di Benedetto V, Politi G, Benedetto A (2000) Vesico-ureteral reflux: diagnosing and staging with voiding color Doppler US: preliminary experience. Eur J Radiol 35:49–53
Ascenti G, Chimenz R, Zimbaro G, Mazziotti S, Scribano E, Fede C, Ricca M (2000) Potential role of colour-Doppler cystosonography with echocontrast in the screening and follow-up of vesicoureteral reflux. Acta Paediatr 89:1336–1339
Darge K, Zieger B, Rohrschneider W, Ghods S, Wunsch R, Troeger J (2001) Contrast-enhanced harmonic imaging for the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux in pediatric patients. Am J Roentgenol 177:1411–1415
Papadopoulou F, Efremidis SC, Oiconomou A, Badouraki M, Panteleli M, Papachristou F, Soteriou I, Economou A (2002) Cyclic voiding cystourethrography: is vesicoureteral reflux missed with standard voiding cystourethrography? Eur Radiol 12:666–670
Hellström M, Jacobsson B (1999) Diagnosis of vesico-ureteric reflux. Acta Paediatr [Suppl] 431:3–12
Hanna MK (1997) Occult vesicoureteral reflux. Dialogues Pediatr Urol 20:3–4
Jequier S, Jequier JC (1989) Reliability of voiding cystourethrography to detect reflux. AJR 153:807–810
Valentini AL, De Gaetano AM, Destito C, Marino V, Minordi LM, Marano P (2002) The accuracy of voiding urosonography in detecting vesico-ureteral reflux: a summary of existing data. Eur J Pediatr 161:380–384
Cleveland RH, Constantinou C, Blickman JG, Jaramillo D, Webster E (1992) Voiding cystourethrography in children: value of digital fluoroscopy in reducing radiation dose. Am J Roentgenol 158:137–142
Lederman HM, Khademian ZP, Felice M, Hurh PJ (2002) Dose reduction fluoroscopy in pediatrics. Pediatr Radiol 32:844–848
Stabin MG, Gelfand MJ (1998) Dosimetry of pediatric nuclear medicine procedures. Q J Nucl Med 42:93–112
Silverman FN, Kuhn JP (1993) Caffey's pediatric X-ray diagnosis: an integrated approach, 9th edn. Mosby, St. Louis, pp 1189–1191
Kenda RB, Kenig A, Novljan G, Ponikvar R, Buturović Ponikvar J (2001) Cyclic voiding urosonography for detecting vesicoureteric reflux in renal transplant recipients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:2229–2231
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Janez Stare, DSc, for help with statistical analysis. This study was partly supported by the Slovene Ministry of Education, Science and Sport (grant no. J3-3281).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novljan, G., Kenig, A., Rus, R. et al. Cyclic voiding urosonography in detecting vesicoureteral reflux in children. Pediatr Nephrol 18, 992–995 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-003-1228-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-003-1228-8