Abstract
Purpose
Normalization of the tumor vasculature and microenvironment by several angiogenesis inhibitors has been reported. Given that recombinant human endostatin (rh-endostatin) is also an endogenous angiogenesis inhibitor, a comprehensive evaluation of the effects of rh-endostatin on tumor vasculature and microenvironment and chemotherapy sensitivity would be favorable.
Methods
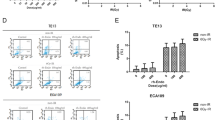
Multiple treatment schedules of the combination of rh-endostatin and paclitaxel were tested in Lewis lung carcinoma. Further, we monitored microvascular density, tumor hypoxic fraction, and collagen covered tumor vessels at three different time points following the treatment of rh-endostatin, as well as the transcription of angiogenesis related factors (vascular endothelial growth factor-A and thrombospondin-1) and vasculature markers (regulator of G-protein signaling 5 and platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1).
Results
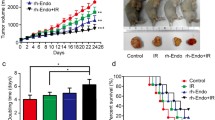
The anti-tumor efficacy of paclitaxel was significantly improved 7 days after the treatment of rh-endostatin. Tumor microvascular density was decreased by rh-endostatin, although it became even higher 7 days after termination of rh-endostatin. Non-necrotic hypoxic fraction was significantly reduced 7 days after treatment of rh-endostatin, accompanied with increased collagen covered tumor vessels and coverage of pericytes around endothelial cells. Rh-endostatin could transiently upregulate the transcription of thrombospondin-1 and modulate the imbalance between vascular endothelial growth factor-A and thrombospondin-1.
Conclusion
Rh-endostatin could normalize the tumor vasculature and microenvironment in Lewis lung carcinoma probably via modulation of the balance between vascular endothelial growth factor-A and thrombospondin-1. During the time of vascular normalization, paclitaxel treatment was found to have maximal effect on tumor growth delay.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Rh-endostatin:
-
Recombinant human endostatin
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- VEGF-A:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor-A
- TSP-1:
-
Thrombospondin-1
- MVD:
-
Microvascular density
- RT–PCR:
-
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- Rgs5:
-
Regulator of G-protein signaling 5
- PECAM-1:
-
Platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1
References
Benjaminsen IC, Graff BA, Brurberg KG, Rofstad EK (2004) Assessment of tumor blood perfusion by high-resolution dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI: a preclinical study of human melanoma xenografts. Magn Reson Med 52:269–276
Bergers G, Hanahan D (2008) Modes of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 8(8):592–603
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 407:249–257
Cerniglia GJ, Pore N, Tsai JH et al (2009) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition modulates the microenvironment by vascular normalization to improve chemotherapy and radiotherapy efficacy. PLoS One 4(8):e6539
Cho H, Kozasa T, Bondjers C et al (2003) Pericyte-specific expression of Rgs5: implications for PDGF and EDG receptor signaling during vascular maturation. FASEB J 17(3):440–442
di Tomaso E, London N, Fuja D, Logie J, Tyrrell JA, Kamoun W, Munn LL, Jain RK (2009) PDGF-C induces maturation of blood vessels in a model of glioblastoma and attenuates the response to anti-VEGF treatment. PLoS One 4(4):e5123
Dickson PV, Hamner JB, Sims TL et al (2007) Bevacizumab-induced transient remodeling of the vasculature in neuroblastoma xenografts results in improved delivery and efficacy of systemically administered chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 13:3942–3950
Dings RP, Loren M, Heun H, McNiel E, Griffioen AW, Mayo KH, Griffin RJ (2007) Scheduling of radiation with angiogenesis inhibitors anginex and Avastin improves therapeutic outcome via vessel normalization. Clin Cancer Res 13:3395–3402
Ebos JM, Lee CR, Cruz-Munoz W et al (2009) Accelerated metastasis after short-term treatment with a potent inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 15(3):232–239
Folkman J (2006) Antiangiogenesis in cancer therapy-endostatin and its mechanisms of action. Exp Cell Res 312:594–607
Folkman J (2007) Angiogenesis: an organizing principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:273–286
Fox SB, Leek RD, Weekes MP, Whitehouse RM, Gatter KC, Harris AL (1995) Quantitation and prognostic value of breast cancer angiogenesis: comparison of microvessel density, Chalkley count, and computer image analysis. J Pathol 177:275–283
Fukumura D, Jain RK (2007) Tumor microvasculature and microenvironment: targets for anti-angiogenesis and normalization. Microvasc Res 74:72–84
Herbst RS, Hess KR, Tran HT et al (2002) Phase I study of recombinant human endostatin in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 20:3792–3803
Hillman GG, Singh-Gupta V, Zhang H et al (2009) Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of vascular changes induced by sunitinib in papillary renal cell carcinoma xenograft tumors. Neoplasia 11(9):910–920
Huang G, Chen L (2008) Tumor vasculature and microenvironment normalization: a possible mechanism of antiangiogenesis therapy. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 23:661–668
Huang G, Chen L (2009) Discrepancies between antiangiogenic and antitumor effects of recombinant human endostatin. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 24(5):589–596
Jain RK (2005) Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 307:58–62
Jain RK, Duda DG, Clark JW, Loeffler JS (2006) Lessons from phase III clinical trials on anti-VEGF therapy for cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 3:24–40
Jain RK, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Batchelor TT (2007) Angiogenesis in brain tumors. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:610–622
Kashiwagi S, Tsukada K, Xu L et al (2008) Perivascular nitric oxide gradients normalize tumor vasculature. Nat Med 14(3):255–257
Ling Y, Yang Y, Lu N, You QD, Wang S, Gao Y, Chen Y, Guo QL (2007) Endostar, a novel recombinant human endostatin, exerts antiangiogenic effect via blocking VEGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of KDR/Flk-1 of endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 361:79–84
Loges S, Mazzone M, Hohensinner P, Carmeliet P (2009) Silencing or fueling metastasis with VEGF inhibitors: antiangiogenesis revisited. Cancer Cell 15(3):167–170
Mitchell TS, Bradley J, Robinson GS, Shima DT, Ng YS (2008) RGS5 expression is a quantitative measure of pericyte coverage of blood vessels. Angiogenesis 11:141–151
Palmowski M, Peschke P, Huppert J et al (2009) Molecular ultrasound imaging of early vascular response in prostate tumors irradiated with carbon ions. Neoplasia 11(9):856–863
Preda A, Novikov V, Möglich M, Turetschek K, Shames DM, Brasch RC, Cavagna FM, Roberts TP (2004) MRI monitoring of Avastin antiangiogenesis therapy using B22956–1, a new blood pool contrast agent, in an experimental model of human cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging 20:865–873
Shojaei F, Ferrara N (2008) Role of the microenvironment in tumor growth and in refractoriness/resistance to anti-angiogenic therapies. Drug Resist Updat 11(6):219–230
Sorensen AG, Batchelor TT, Zhang WT, Chen PJ, Yeo P, Wang M, Jennings D, Wen PY, Lahdenranta J, Ancukiewicz M, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Jain RK (2009) A “vascular normalization index” as potential mechanistic biomarker to predict survival after a single dose of cediranib in recurrent glioblastoma patients. Cancer Res 69(13):5296–5300
Sun Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Song X, Zhang Y, Li K, Zhu Y, Zhou Q, You L, Yao C (2005) Results of phase III trial of rh-endostatin (YH-16) in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. J Clin Oncol 23:7138
te Velde EA, Vogten JM, Gebbink MF, van Gorp JM, Voest EE, Borel Rinkes IH (2002) Enhanced antitumor efficacy by combining conventional chemotherapy with angiostatin or endostatin in a liver metastasis model. Br J Surg 89:1302–1309
Tong RT, Boucher Y, Kozin SV, Winkler F, Hicklin DJ, Jain RK (2004) Vascular normalization by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 blockade induces a pressure gradient across the vasculature and improves drug penetration in tumors. Cancer Res 64:3731–3736
Vermeulen PB, Gasparini G, Fox SB et al (2002) Second international consensus on the methodology and criteria of evaluation of angiogenesis quantification in solid human tumors. Eur J Cancer 38:1564–1579
Winkler F, Kozin SV, Tong RT, Chae SS, Booth MF, Garkavtsev I, Xu L, Hicklin DJ, Fukumura D, di Tomaso E, Munn LL, Jain RK (2004) Kinetics of vascular normalization by VEGFR2 blockade governs brain tumor response to radiation: role of oxygenation, angiopoietin-1, and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Cell 6:553–563
Zhao J, Salmon H, Sarntinoranont M (2007) Effect of heterogenous vasculature on interstitial transport within a solid tumor. Microvasc Res 73:224–236
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30872979). We are grateful to the technique support of immunohistochemistry of Pathology Department of Jinling Hospital.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2010_770_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Masson’s trichrome staining of subcutaneous interstitial space. Collagen and red blood cells were indicated by white and black arrows, respectively. Scale bar, 50 µm
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, G., Chen, L. Recombinant human endostatin improves anti-tumor efficacy of paclitaxel by normalizing tumor vasculature in Lewis lung carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136, 1201–1211 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0770-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0770-6