Abstract
Purpose
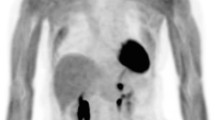
Variable uptake of 18FDG has been noticed in positron emission tomography (PET) studies of patients with oesophageal adenocarcinoma. The aim of the present study was to investigate biological parameters involved in 18FDG uptake in oesophageal adenocarcinoma for selection of patients with increased 18FDG uptake and prediction of prognostic value of 18FDG PET.
Patients and methods
Preoperative PET scans were performed in 26 patients with histologically proven oesophageal adenocarcinoma. 18FDG uptake was semiquantitatively measured by SUVBSAg. Tumour sections were stained by immunohistochemistry for angiogenic markers (VEGF, CD31), glucose transporter-1 (Glut-1), hexokinase (HK) isoforms, for proliferation marker (Ki67), for macrophage marker (CD68) and for apoptosis marker (cleaved caspase-3). Cell densities, differentiation grade, degree of necrosis and mucus, T-stage and tumour size were assessed. In addition follow-up was analysed.
Results
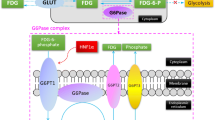
No association was found between 18FDG uptake and angiogenic markers. In contrast, a significant correlation was found between 18FDG uptake and Glut-1 expression. No correlations were found between 18FDG uptake and HK isoforms, Ki67 or cleaved caspase-3. Also, no correlations were found between 18FDG uptake and cell density, differentiation grade, CD68, mucus and necrosis. However, there was a significant correlation between 18FDG uptake and tumour size and between 18FDG uptake and tumour recurrence.
Conclusions
Glut-1 expression and tumour size seem parameters associated with 18FDG uptake in patients with biopsy proven oesophageal adenocarcinoma, and may be used to select oesophageal cancer patients in whom 18FDG-PET is of diagnostic value and may predict disease outcome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler LP, Blair HF, Makley JT, Williams RP, Joyce MJ, Leisure G, al-Kaisi N, Miraldi F (1991) Noninvasive grading of musculoskeletal tumors using PET. J Nucl Med 32:1508–1512
Ahuja V, Coleman RE, Herndon J, Patz EF Jr (1998) The prognostic significance of fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography imaging for patients with nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 83:918–924
Aloj L, Caraco C, Jagoda E, Eckelman WC, Neumann RD (1999) Glut-1 and hexokinase expression: relationship with 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake in A431 and T47D cells in culture. Cancer Res 59:4709–4714
Avril N (2004) GLUT1 expression in tissue and (18)F-FDG uptake. J Nucl Med 45(6):930–932
Avril N, Menzel M, Dose J, Schelling M, Weber W, Janicke F, Nathrath W, Schwaiger M (2001) Glucose metabolism of breast cancer assessed by 18F-FDG PET: histologic and immunohistochemical tissue analysis. J Nucl Med 42:9–16
Boellaard R, Krak NC, Hoekstra OS, Lammertsma AA (2004) Effects of noise, image resolution, and ROI definition on the accuracy of standard uptakevalues: a simulation study. J Nucl Med 45(9):1519–1527
Boellaard R, Hoetjes NJ, Lammertsma AA, Hoekstra OS (2007) Accuracy of partial volume correction: CT versus PET for tumor volume definition. J Nucl Med 48:412
Boon EM, Keller JJ, Wormhoudt TA, Giardiello FM, Offerhaus GJ, van der NR et al (2004) Sulindac targets nuclear beta-catenin accumulation and Wnt signalling in adenomas of patients with familial adenomatous polyposis and in human colorectal cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer 90(1):224–229
Bos R, van der Hoeven JJ, van der Wall E, van der Groep P, van Diest PJ, Comans EF, Joshi U, Semenza GL, Hoekstra OS, Lammertsma AA, Molthoff CF (2002) Biologic correlates of (18)fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in human breast cancer measured by positron emission tomography. J Clin Oncol 20:379–387
Brix G, Zaers J, Adam LE, Bellemann ME, Ostertag H, Trojan H, Haberkorn U, Doll J, Oberdorfer F, Lorenz WJ (1997) Performance evaluation of a whole-body PET scanner using the NEMA protocol. National Electrical Manufacturers Association. J Nucl Med 38:1614–1623
Brown RS, Leung JY, Fisher SJ, Frey KA, Ethier SP, Wahl RL (1996) Intratumoral distribution of tritiated-FDG in breast carcinoma: correlation between Glut-1 expression and FDG uptake. J Nucl Med 37:1042–1047
Buck AK, Schirrmeister H, Mattfeldt T, Reske SN (2004) Biological characterisation of breast cancer by means of PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31(Suppl 1):S80-S87
Cerfolio RJ, Bryant AS (2006) Maximum standardized uptake values on positron emission tomography of esophageal cancer predicts stage, tumor biology, survival. Ann Thorac Surg 82(2):391–394
Choi JY, Jang HJ, Shim YM, Kim K, Lee KS, Lee KH, Choi Y, Choe YS, Kim BT (2004) 18F-FDG PET in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma undergoing curative surgery: prognostic implications. J Nucl Med 5:1843–1850
Crippa F, Seregni E, Agresti R, Chiesa C, Pascali C, Bogni A, Decise D, De Sanctis V, Greco M, Daidone MG, Bombardieri E (1998) Association between [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose uptake and postoperative histopathology, hormone receptor status, thymidine labelling index and p53 in primary breast cancer: a preliminary observation. Eur J Nucl Med 25:1429–1434
Dhital K, Saunders CA, Seed PT, O’Doherty MJ, Dussek J (2000) [(18)F] Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and its prognostic value in lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 18:425–428
Di Chiro G, DeLaPaz RL, Brooks RA, Sokoloff L, Kornblith PL, Smith BH, Patronas NJ, Kufta CV, Kessler RM, Johnston GS, Manning RG, Wolf AP (1982) Glucose utilization of cerebral gliomas measured by [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose and positron emission tomography. Neurology 32:1323–1329
Flamen P, Lerut A, Van Cutsem E, De Wever W, Peeters M, Stroobants S, Dupont P, Bormans G, Hiele M, De Leyn P, Van Raemdonck D, Coosemans W, Ectors N, Haustermans K, Mortelmans L (2000) Utility of positron emission tomography for the staging of patients with potentially operable esophageal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 18:3202–3210
Haberkorn U, Altmann A, Kamencic H, Morr I, Traut U, Henze M, Jiang S, Metz J, Kinscherf R (2001) Glucose transport and apoptosis after gene therapy with HSV thymidine kinase. Eur J Nucl Med 28:1690–1696
Higashi K, Clavo AC, Wahl RL (1993) Does FDG uptake measure proliferative activity of human cancer cells? In vitro comparison with DNA flow cytometry and tritiated thymidine uptake. J Nucl Med 34:414–419
Higashi K, Ueda Y, Sakurai A, Wang XM, Xu L, Murakami M, Seki H, Oguchi M, Taki S, Nambu Y, Tonami H, Katsuda S, Yamamoto I (2000) Correlation of Glut-1 glucose transporter expression with 18FDG uptake in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Nucl Med 27:1778–1785
Higashi K, Ueda Y, Arisaka Y, Sakuma T, Nambu Y, Oguchi M, Seki H, Taki S, Tonami H, Yamamoto I (2002a) 18F-FDG uptake as a biologic prognostic factor for recurrence in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer. J Nucl Med 43:39–45
Higashi T, Saga T, Nakamoto Y, Ishimori T, Mamede MH, Wada M, Doi R, Hosotani R, Imamura M, Konishi J (2002b) Relationship between retention index in dual-phase (18)F-FDG PET, and hexokinase-II and glucose transporter-1 expression in pancreatic cancer. J Nucl Med 43:173–180
Hooft L, van der Veldt AA, van Diest PJ, Hoekstra OS, Berkhof J, Teule GJ, Molthoff CF (2005) [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in recurrent thyroid cancer is related to hexokinase I expression in the primary tumor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:328–334
Huang SC, Phelps ME, Hoffman EJ, Sideris K, Selin CJ, Kuhl DE (1980) Noninvasive determination of local cerebral metabolic rate of glucose in man. Am J Physiol 238(1):E69–E82
Imdahl A, Hentschel M, Kleimaier M, Hopt UT, Brink I (2004) Impact of FDG-PET for staging of oesophageal cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg 389:283–288
Jager PL, Que TH, Vaalburg W, Pruim J, Elsinga P, Plukker JT (2001) Carbon-11 choline or FDG-PET for staging of oesophageal cancer? Eur J Nucl Med 28:1845–1849
Kato H, Takita J, Miyazaki T, Nakajima M, Fukai Y, Masuda N, Fukuchi M, Manda R, Ojima H, Tsukada K, Kuwano H, Oriuchi N, Endo K (2003) Correlation of 18-F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) accumulation with glucose transporter (Glut-1) expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 23:3263–3272
Keyes JW Jr (1995) SUV: standard uptake or silly useless value? J Nucl Med 36(10):1836–1839
Kleespies A, Guba M, Jauch KW, Bruns CJ (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor in esophageal cancer. J Surg Oncol 87:95–104
Krak NC, Boellaard R, Hoekstra OS, Twisk JW, Hoekstra CJ, Lammertsma AA (2005) Effects of ROI definition and reconstruction method on quantitative outcome and applicability in a response monitoring trial. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32(3):294–301
Lee FY, Yu J, Chang SS, Fawwaz R, Parisien MV (2004) Diagnostic value and limitations of fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for cartilaginous tumors of bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86–A:2677–2685
Luketich JD, Friedman DM, Weigel TL, Meehan MA, Keenan RJ, Townsend DW, Meltzer CC (1999) Evaluation of distant metastases in esophageal cancer: 100 consecutive positron emission tomography scans. Ann Thorac Surg 68:1133–1136
Macheda ML, Rogers S, Best JD (2005) Molecular and cellular regulation of glucose transporter (GLUT) proteins in cancer. J Cell Physiol 202:654–662
Mathupala SP, Heese C, Pedersen PL (1997) Glucose catabolism in cancer cells. The type II hexokinase promoter contains functionally active response elements for the tumor suppressor p53. J Biol Chem 272:22776–22780
Medina RA, Owen GI (2002) Glucose transporters: expression, regulation and cancer. Biol Res 35:9–26
Meltzer CC, Luketich JD, Friedman D, Charron M, Strollo D, Meehan M, Urso GK, Dachille MA, Townsend DW (2000) Whole-body FDG positron emission tomographic imaging for staging esophageal cancer comparison with computed tomography. Clin Nucl Med 25:882–887
Menzel C, Dobert N, Rieker O, Kneist W, Mose S, Teising A et al (2003) [18F]-Deoxyglucose PET for the staging of oesophageal cancer: influence of histopathological subtype and tumour grading. Nuklearmedizin 42(3):90–93
Minn H, Joensuu H, Ahonen A, Klemi P (1988) Fluorodeoxyglucose imaging: a method to assess the proliferative activity of human cancer in vivo. Comparison with DNA flow cytometry in head and neck tumors. Cancer 61:1776–1781
Oshida M, Uno K, Suzuki M, Nagashima T, Hashimoto H, Yagata H (1998) Predicting the prognoses of breast carcinoma patients with positron emission tomography using 2-deoxy-2-fluoro[18F]-D-glucose. Cancer 82:2227–2234
Ott K, Weber WA, Lordick F, Becker K, Busch R, Herrmann K, Wieder H, Fink U, Schwaiger M, Siewert JR (2006) Metabolic imaging predicts response, survival, and recurrence in adenocarcinomas of the esophagogastric junction. J Clin Oncol 24(29):4692–4698
Pera M, Pera M (2001) Recent changes in the epidemiology of esophageal cancer. Surg Oncol 10:81–90
Rankin SC, Taylor H, Cook GJ, Mason R (1998) Computed tomography and positron emission tomography in the pre-operative staging of oesophageal carcinoma. Clin Radiol 53:659–665
Rizk N, Downey RJ, Akhurst T, Gonen M, Bains MS, Larson S et al (2006) Preoperative 18[F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography standardized uptake values predict survival after esophageal adenocarcinoma resection. Ann Thorac Surg 81(3):1076–1081
Schulte M, Brecht-Krauss D, Heymer B, Guhlmann A, Hartwig E, Sarkar MR, Diederichs CG, Schultheiss M, Kotzerke J, Reske SN (1999) Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography of soft tissue tumours: is a non-invasive determination of biological activity possible? Eur J Nucl Med 26:599–605
Schwartz DL, Rajendran J, Yueh B, Coltrera MD, Leblanc M, Eary J, Krohn K (2004) FDG-PET prediction of head and neck squamous cell cancer outcomes. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:1361–1367
Schwarzbach MH, Hinz U, Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss A, Willeke F, Cardona S, Mechtersheimer G, Lehnert T, Strauss LG, Herfarth C, Buchler MW (2005) Prognostic significance of preoperative [18-F] fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in patients with resectable soft tissue sarcomas. Ann Surg 241:286–294
Smith TA (2000) Mammalian hexokinases and their abnormal expression in cancer. Br J Biomed Sci 57:170–178
Tohma T, Okazumi S, Makino H, Cho A, Mochiduki R, Shuto K, Kudo H, Matsubara K, Gunji H, Ochiai T (2005) Relationship between glucose transporter, hexokinase and FDG-PET in esophageal cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 52:486–490
Vansteenkiste JF, Stroobants SG, Dupont PJ, De Leyn PR, Verbeken EK, Deneffe GJ, Mortelmans LA, Demedts MG (1999) Prognostic importance of the standardized uptake value on (18)F-fluoro-2-deoxy-glucose-positron emission tomography scan in non-small-cell lung cancer: an analysis of 125 cases. Leuven Lung Cancer Group. J Clin Oncol 17:3201–3206
Veronesi G, Landoni C, Pelosi G, Picchio M, Sonzogni A, Leon ME, Solli PG, Leo F, Spaggiari L, Bellomi M, Fazio F, Pastorino U (2002) Fluoro-deoxi-glucose uptake and angiogenesis are independent biological features in lung metastases. Br J Cancer 86:1391–1395
Vesselle H, Grierson J, Muzi M, Pugsley JM, Schmidt RA, Rabinowitz P, Peterson LM, Vallieres E, Wood DE (2002) In vivo validation of 3′deoxy-3′-[(18)F]fluorothymidine ([(18)F]FLT) as a proliferation imaging tracer in humans: correlation of [(18)F]FLT uptake by positron emission tomography with Ki-67 immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry in human lung tumors. Clin Cancer Res 8:3315–3323
Westerterp M, Pruim J, Oyen W, Hoekstra O, Paans A, Visser E et al (2006) Quantification of FDG PET studies using standardised uptake values in multi-centre trials: effects of image reconstruction, resolution and ROI definition parameters. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging
van Westreenen HL, Westerterp M, Bossuyt PM, Pruim J, Sloof GW, Van Lanschot JJ, Groen H, Plukker JT (2004) Systematic review of the staging performance of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol 22:3805–3812
van Westreenen HL, Plukker JT, Cobben DCP, Verhoogt CJM, Groen H, Jager PL (2005a) Clinical relevance of the standardized uptake value (SUV) in staging esophageal cancer with FDG-PET. Am J Roentgenol 185:436–40
van Westreenen HL, Heeren PA, van Dullemen HM, van der Jagt EJ, Jager PL, Groen H, Plukker JT (2005b) Positron emission tomography with F-18-fluorodeoxyglucose in a combined staging strategy of esophageal cancer prevents unnecessary surgical explorations. J Gastrointest Surg 9:54–61
Yamamoto T, Seino Y, Fukumoto H, Koh G, Yano H, Inagaki N, Yamada Y, Inoue K, Manabe T, Imura H (1990) Over-expression of facilitative glucose transporter genes in human cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 170:223–230
Yen TC, See LC, Chang TC, Huang KG, Ng KK, Tang SG, Chang YC, Hsueh S, Tsai CS, Hong JH, Lin CT, Chao A, Ma SY, Lin WJ, Fu YK, Fan CC, Lai CH (2004) Defining the priority of using 18F-FDG PET for recurrent cervical cancer. J Nucl Med 45:1632–1639
Yoon YC, Lee KS, Shim YM, Kim BT, Kim K, Kim TS (2003) Metastasis to regional lymph nodes in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: CT versus FDG PET for presurgical detection prospective study. Radiology 227:764–770
Acknowledgments
We thank the expert technical support of Marcelle van Gelder, Jurriaan Tuynman, and Jitske Weegenaar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westerterp, M., Sloof, G.W., Hoekstra, O.S. et al. 18FDG uptake in oesophageal adenocarcinoma: linking biology and outcome. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 134, 227–236 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-007-0275-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-007-0275-0