Abstract
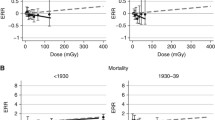
Controversy regarding potential health risks from increased use of medical diagnostic radiologic examinations has come to public attention. We evaluated whether chromosome damage, specifically translocations, which are a potentially intermediate biomarker for cancer risk, was increased after exposure to diagnostic X-rays, with particular interest in the ionizing radiation dose–response below the level of approximately 50 mGy. Chromosome translocation frequency data from three separately conducted occupational studies of ionizing radiation were pooled together. Studies 1 and 2 included 79 and 150 medical radiologic technologists, respectively, and study 3 included 83 airline pilots and 50 university faculty members (total = 155 women and 207 men; mean age = 62 years, range 34–90). Information on personal history of radiographic examinations was collected from a detailed questionnaire. We computed a cumulative red bone marrow (RBM) dose score based on the numbers and types of X-ray examinations reported with 1 unit approximating 1 mGy. Poisson regression analyses were adjusted for age and laboratory method. Mean RBM dose scores were 49, 42, and 11 for Studies 1–3, respectively (overall mean = 33.5, range 0–303). Translocation frequencies significantly increased with increasing dose score (P < 0.001). Restricting the analysis to the lowest dose scores of under 50 did not materially change these results. We conclude that chromosome damage is associated with low levels of radiation exposure from diagnostic X-ray examinations, including dose scores of approximately 50 and lower, suggesting the possibility of long-term adverse health effects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berrington de Gonzalez A, Darby S (2004) Risk of cancer from diagnostic X-rays: estimates for the UK and 14 other countries. Lancet 363(9406):345–351
Bhatti P, Preston DL, Doody MM, Hauptmann M, Kampa D, Alexander BH, Petibone D, Simon SL, Weinstock RM, Bouville A, Yong LC, Freedman DM, Mabuchi K, Linet MS, Edwards AA, Tucker JD, Sigurdson AJ (2007) Retrospective biodosimetry among United States radiologic technologists. Radiat Res 167(6):727–734
Bhatti P, Doody MM, Preston DL, Kampa D, Ron E, Weinstock RW, Simon S, Edwards AA, Sigurdson AJ (2008) Increased frequency of chromosome translocations associated with diagnostic x-ray examinations. Radiat Res 170(2):149–155
Boffetta P, van der Hel O, Norppa H, Fabianova E, Fucic A, Gundy S, Lazutka J, Cebulska-Wasilewska A, Puskailerova D, Znaor A, Kelecsenyi Z, Kurtinaitis J, Rachtan J, Forni A, Vermeulen R, Bonassi S (2007) Chromosomal aberrations and cancer risk: results of a cohort study from Central Europe. Am J Epidemiol 165(1):36–43
Bonassi S, Norppa H, Ceppi M, Stromberg U, Vermeulen R, Znaor A, Cebulska-Wasilewska A, Fabianova E, Fucic A, Gundy S, Hansteen IL, Knudsen LE, Lazutka J, Rossner P, Sram RJ, Boffetta P (2008) Chromosomal aberration frequency in lymphocytes predicts the risk of cancer: results from a pooled cohort study of 22 358 subjects in 11 countries. Carcinogenesis 29(6):1178–1183
Brenner DJ, Elliston CD (2004) Estimated radiation risks potentially associated with full-body CT screening. Radiology 232(3):735–738
Brenner DJ, Hall EJ (2007) Computed tomography—an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med 357(22):2277–2284
Burak LE, Kodama Y, Nakano M, Ohtaki K, Itoh M, Okladnikova ND, Vasilenko EK, Cologne JB, Nakamura N (2001) FISH examination of lymphocytes from Mayak workers for assessment of translocation induction rate under chronic radiation exposures. Int J Radiat Biol 77(8):901–908
Einstein AJ, Henzlova MJ, Rajagopalan S (2007) Estimating risk of cancer associated with radiation exposure from 64-slice computed tomography coronary angiography. JAMA 298(3):317–323
Fazel R, Krumholz HM, Wang Y, Ross JS, Chen J, Ting HH, Shah ND, Nasir K, Einstein AJ, Nallamothu BK (2009) Exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation from medical imaging procedures. N Engl J Med 361(9):849–857
Hampton T (2006) Researchers examine long-term risks of exposure to medical radiation. JAMA 296(6):638–640
Johnson KL, Brenner DJ, Nath J, Tucker JD, Geard CR (1999) Radiation-induced breakpoint misrejoining in human chromosomes: random or non-random? Int J Radiat Biol 75(2):131–141
Kodama Y, Pawel D, Nakamura N, Preston D, Honda T, Itoh M, Nakano M, Ohtaki K, Funamoto S, Awa AA (2001) Stable chromosome aberrations in atomic bomb survivors: results from 25 years of investigation. Radiat Res 156(4):337–346
Lee CI, Haims AH, Monico EP, Brink JA, Forman HP (2004) Diagnostic CT scans: assessment of patient, physician, and radiologist awareness of radiation dose and possible risks. Radiology 231(2):393–398
Lloyd DC, Edwards AA, Leonard A, Deknudt GL, Verschaeve L, Natarajan AT, Darroudi F, Obe G, Palitti F, Tanzarella C et al (1992) Chromosomal aberrations in human lymphocytes induced in vitro by very low doses of X-rays. Int J Radiat Biol 61(3):335–343
M’Kacher R, Violot D, Aubert B, Girinsky T, Dossou J, Beron-Gaillard N, Carde P, Parmentier C (2003) Premature chromosome condensation associated with fluorescence in situ hybridisation detects cytogenetic abnormalities after a CT scan: evaluation of the low-dose effect. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 103(1):35–40
Martin DR, Semelka RC (2006) Health effects of ionising radiation from diagnostic CT. Lancet 367(9524):1712–1714
Matsumoto K, Ramsey MJ, Nelson DO, Tucker JD (1998) Persistence of radiation-induced translocations in human peripheral blood determined by chromosome painting. Radiat Res 149(6):602–613
Mettler FA Jr, Thomadsen BR, Bhargavan M, Gilley DB, Gray JE, Lipoti JA, McCrohan J, Yoshizumi TT, Mahesh M (2008) Medical radiation exposure in the U.S. in 2006: preliminary results. Health Phys 95(5):502–507
Peloquin JM, Pardi DS, Sandborn WJ, Fletcher JG, McCollough CH, Schueler BA, Kofler JA, Enders FT, Achenbach SJ, Loftus EV Jr (2008) Diagnostic ionizing radiation exposure in a population-based cohort of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol 103(8):2015–2022
Preston-Martin S, Pogoda JM (2003) Estimation of radiographic doses in a case-control study of acute myelogenous leukemia. Health Phys 84(2):245–259
Ramsey MJ, Moore DH II, Briner JF, Lee DA, Olsen L, Senft JR, Tucker JD (1995) The effects of age and lifestyle factors on the accumulation of cytogenetic damage as measured by chromosome painting. Mutat Res 338(1–6):95–106
Ron E (2003) Cancer risks from medical radiation. Health Phys 85(1):47–59
Sigurdson AJ, Bhatti P, Preston DL, Doody MM, Kampa D, Alexander BH, Petibone D, Yong LC, Edwards AA, Ron E, Tucker JD (2008a) Routine diagnostic X-ray examinations and increased frequency of chromosome translocations among U.S. radiologic technologists. Cancer Res 68(21):8825–8831
Sigurdson AJ, Ha M, Hauptmann M, Bhatti P, Sram RJ, Beskid O, Tawn EJ, Whitehouse CA, Lindholm C, Nakano M, Kodama Y, Nakamura N, Vorobtsova I, Oestreicher U, Stephan G, Yong LC, Bauchinger M, Schmid E, Chung HW, Darroudi F, Roy L, Voisin P, Barquinero JF, Livingston G, Blakey D, Hayata I, Zhang W, Wang C, Bennett LM, Littlefield LG, Edwards AA, Kleinerman RA, Tucker JD (2008b) International study of factors affecting human chromosome translocations. Mutat Res 652(2):112–121
Simon SL, Weinstock RM, Doody MM, Neton J, Wenzl T, Stewart P, Mohan AK, Yoder RC, Hauptmann M, Freedman DM, Cardarelli J, Feng HA, Bouville A, Linet M (2006) Estimating historical radiation doses to a cohort of U.S. radiologic technologists. Radiat Res 166(1 Pt 2):174–192
Sodickson A, Baeyens PF, Andriole KP, Prevedello LM, Nawfel RD, Hanson R, Khorasani R (2009) Recurrent CT, cumulative radiation exposure, and associated radiation-induced cancer risks from CT of adults. Radiology 251(1):175–184
Tawn EJ, Whitehouse CA, Tarone RE (2004) FISH chromosome aberration analysis on retired radiation workers from the Sellafield nuclear facility. Radiat Res 162(3):249–256
Tucker JD, Breneman JW, Briner JF, Eveleth GG, Langlois RG, Moore DH II (1997) Persistence of radiation-induced translocations in rat peripheral blood determined by chromosome painting. Environ Mol Mutagen 30(3):264–272
Weber J, Scheid W, Traut H (1995) Biological dosimetry after extensive diagnostic x-ray exposure. Health Phys 68(2):266–269
Yong LC, Sigurdson AJ, Ward EM, Waters MA, Whelan EA, Petersen MR, Bhatti P, Ramsey MJ, Ron E, Tucker JD (2009) Increased frequency of chromosome translocations in airline pilots with long-term flying experience. Occup Environ Med 66:56–62
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, National Cancer Institute and in part by an interagency agreement between the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and the National Cancer Institute (contract Y1CP802904). Work was performed in part under the auspices of the US DOE by the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under contract no. W-7405-ENG-48. We thank the two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatti, P., Yong, L.C., Doody, M.M. et al. Diagnostic X-ray examinations and increased chromosome translocations: evidence from three studies. Radiat Environ Biophys 49, 685–692 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-010-0307-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-010-0307-z